A Survey on Consumer IoT Traffic: Security and Privacy

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper provides a comprehensive survey of consumer Internet of Things (IoT) traffic, focusing on security and privacy concerns.
- It examines various aspects of consumer IoT traffic, including traffic analysis techniques, security vulnerabilities, and privacy implications.
- The survey covers a range of consumer IoT devices, such as smart home devices, wearables, and connected vehicles.
Plain English Explanation
The paper explores the security and privacy challenges associated with the growing number of connected consumer devices, commonly referred to as the Internet of Things (IoT). These devices, such as smart home appliances, fitness trackers, and in-car infotainment systems, are becoming increasingly prevalent in our daily lives.
The researchers analyze the traffic generated by these IoT devices, which can reveal sensitive information about users' activities, behaviors, and preferences. For example, monitoring the energy consumption of a smart home device can provide insights into the occupancy and usage patterns of the household. This information could be exploited by malicious actors to compromise user privacy or enable targeted cyberattacks.
The paper delves into various traffic analysis techniques that can be used to extract such sensitive information, as well as the security vulnerabilities that can lead to data breaches and unauthorized access to IoT devices. The researchers also discuss the privacy implications of this data collection and the potential for misuse.
Technical Explanation
The paper begins by providing an overview of the consumer IoT landscape, highlighting the rapid growth and widespread adoption of connected devices in various domains, such as smart homes, wearables, and connected vehicles.
The researchers then explore the different types of traffic analysis techniques that can be applied to consumer IoT data. These techniques include packet sniffing, flow-based analysis, and protocol-level analysis. The paper examines how these techniques can be used to extract sensitive information, such as user behavior patterns, device identities, and communication patterns.
The survey also covers the security vulnerabilities inherent in consumer IoT devices, including weak authentication mechanisms, outdated firmware, and insecure communication protocols. These vulnerabilities can lead to unauthorized access, data breaches, and even physical device control.
Finally, the paper discusses the privacy implications of consumer IoT traffic, highlighting how the collected data can be used to infer sensitive information about users, such as their daily routines, health conditions, and personal preferences.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive overview of the security and privacy challenges associated with consumer IoT traffic, but it also acknowledges the limitations of the current research. For instance, the authors note that the majority of the existing studies have focused on specific device categories or communication protocols, and there is a need for more holistic, cross-domain analyses.
Additionally, the paper suggests that the rapidly evolving nature of the consumer IoT landscape means that the identified vulnerabilities and privacy concerns may quickly become outdated. Ongoing research and regular updates are necessary to stay ahead of the curve and address the ever-changing security and privacy risks.
The authors also highlight the need for improved regulation and industry-wide standards to ensure the security and privacy of consumer IoT devices. Without such measures, the potential for misuse and abuse of consumer IoT data will continue to grow.
Conclusion
This comprehensive survey paper sheds light on the pressing security and privacy issues surrounding consumer IoT traffic. As the number of connected devices in our homes, on our bodies, and in our vehicles continues to rise, the need to address these concerns becomes increasingly urgent.
The findings of this paper underscore the importance of developing robust security measures, implementing strong privacy safeguards, and fostering greater transparency in the consumer IoT ecosystem. By addressing these challenges, we can unlock the full potential of the Internet of Things while ensuring the protection of user privacy and the security of our connected devices.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
A Survey on Consumer IoT Traffic: Security and Privacy
Yan Jia, Yuxin Song, Zihou Liu, Qingyin Tan, Yang Song, Yu Zhang, Zheli Liu
Although CIoT has improved the convenience of daily activities, it also introduces new security and privacy concerns. Network traffic analysis, a common technique employed by the security community, has been extensively utilized to investigate security and privacy concerns, and it has also been applied to CIoT. However, compared to network traffic analysis in other fields such as mobile apps and websites, CIoT presents special new characteristics, which may introduce new challenges and research opportunities. In this study, we reviewed 310 publications on traffic analysis within the CIoT security and privacy domain, covering the period from January 2018 to December 2023. Initially, we summarized the CIoT traffic analysis process, highlighting the newly identified characteristics of CIoT. Subsequently, we classified existing research according to its application objectives: device fingerprinting, user activity inference, malicious traffic detection, and measurement. Lastly, we explore emerging challenges and potential future research avenues.
Read more7/16/2024


0
A Survey on Intelligent Internet of Things: Applications, Security, Privacy, and Future Directions
Ons Aouedi, Thai-Hoc Vu, Alessio Sacco, Dinh C. Nguyen, Kandaraj Piamrat, Guido Marchetto, Quoc-Viet Pham
The rapid advances in the Internet of Things (IoT) have promoted a revolution in communication technology and offered various customer services. Artificial intelligence (AI) techniques have been exploited to facilitate IoT operations and maximize their potential in modern application scenarios. In particular, the convergence of IoT and AI has led to a new networking paradigm called Intelligent IoT (IIoT), which has the potential to significantly transform businesses and industrial domains. This paper presents a comprehensive survey of IIoT by investigating its significant applications in mobile networks, as well as its associated security and privacy issues. Specifically, we explore and discuss the roles of IIoT in a wide range of key application domains, from smart healthcare and smart cities to smart transportation and smart industries. Through such extensive discussions, we investigate important security issues in IIoT networks, where network attacks, confidentiality, integrity, and intrusion are analyzed, along with a discussion of potential countermeasures. Privacy issues in IIoT networks were also surveyed and discussed, including data, location, and model privacy leakage. Finally, we outline several key challenges and highlight potential research directions in this important area.
Read more6/24/2024
📊

0
Cyberattack Data Analysis in IoT Environments using Big Data
Neelam Patidar, Sally Zreiqat, Sirisha Mahesh, Jongwook Woo
In the landscape of the Internet of Things (IoT), transforming various industries, our research addresses the growing connectivity and security challenges, including interoperability and standardized protocols. Despite the anticipated exponential growth in IoT connections, network security remains a major concern due to inadequate datasets that fail to fully encompass potential cyberattacks in realistic IoT environments. Using Apache Hadoop and Hive, our in-depth analysis of security vulnerabilities identified intricate patterns and threats, such as attack behavior, network traffic anomalies, TCP flag usage, and targeted attacks, underscoring the critical need for robust data platforms to enhance IoT security.
Read more6/18/2024

0
AI-Driven Fast and Early Detection of IoT Botnet Threats: A Comprehensive Network Traffic Analysis Approach
Abdelaziz Amara korba, Aleddine Diaf, Yacine Ghamri-Doudane
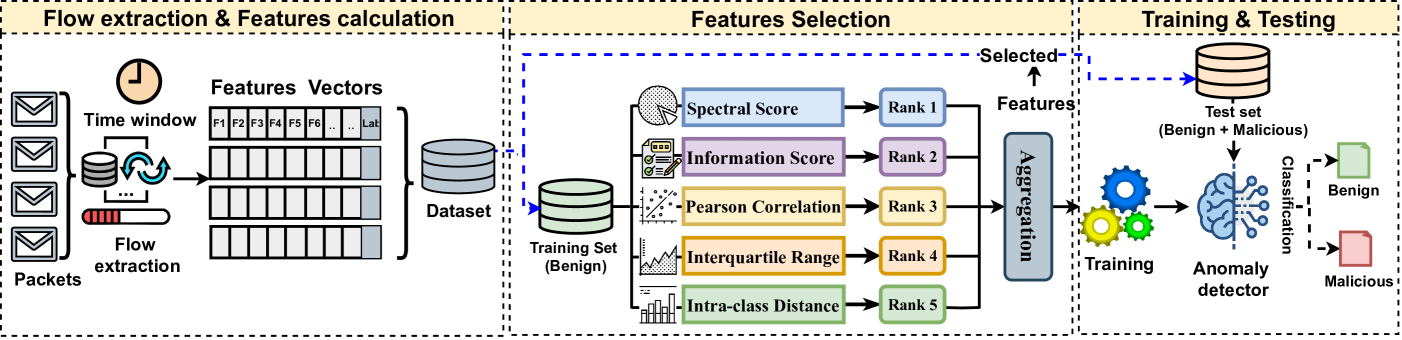
In the rapidly evolving landscape of cyber threats targeting the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem, and in light of the surge in botnet-driven Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) and brute force attacks, this study focuses on the early detection of IoT bots. It specifically addresses the detection of stealth bot communication that precedes and orchestrates attacks. This study proposes a comprehensive methodology for analyzing IoT network traffic, including considerations for both unidirectional and bidirectional flow, as well as packet formats. It explores a wide spectrum of network features critical for representing network traffic and characterizing benign IoT traffic patterns effectively. Moreover, it delves into the modeling of traffic using various semi-supervised learning techniques. Through extensive experimentation with the IoT-23 dataset - a comprehensive collection featuring diverse botnet types and traffic scenarios - we have demonstrated the feasibility of detecting botnet traffic corresponding to different operations and types of bots, specifically focusing on stealth command and control (C2) communications. The results obtained have demonstrated the feasibility of identifying C2 communication with a 100% success rate through packet-based methods and 94% via flow based approaches, with a false positive rate of 1.53%.
Read more7/23/2024