Toward 6G Optical Fronthaul: A Survey on Enabling Technologies and Research Perspectives

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores the enabling technologies and research perspectives for 6G optical fronthaul networks.
- It covers key technologies like point-to-point (P2P) links, passive optical networks (PON), free space optics (FSO), and their potential applications in future 6G radio access networks (RAN).
- The paper also discusses optical computing-enabled networks as a promising approach for 6G fronthaul.
- Additionally, it explores how 6G AI-enabled networks can enhance the performance and optimization of 6G optical fronthaul systems.
Plain English Explanation
This paper looks at the different technologies that could be used to build the "fronthaul" networks for 6G wireless networks. The fronthaul is the part of the network that connects the cell towers to the main network.
The paper discusses several optical technologies that could be used, like point-to-point links, passive optical networks, and free space optics. These technologies could provide high-speed, low-latency connections for the 6G fronthaul, which will be important as 6G networks are expected to handle much more data than today's 4G and 5G networks.
The paper also talks about how using optical computing, where information is processed using light instead of electricity, could be a good approach for 6G fronthaul networks. Additionally, it explores how artificial intelligence could be used to optimize the performance of these 6G optical fronthaul systems.
Overall, the paper provides an overview of the key technologies and research directions that could shape the fronthaul networks of future 6G wireless systems.
Technical Explanation
The paper begins by highlighting the need for high-performance fronthaul networks to support the anticipated demands of 6G wireless systems. It then delves into several enabling optical communication technologies that could be leveraged for 6G optical fronthaul:
Point-to-point (P2P) links offer direct, dedicated connections between cell sites and the core network, providing low latency and high bandwidth. The paper discusses how advanced modulation formats and wavelength division multiplexing can enhance the capacity of P2P fronthaul links.
Passive optical networks (PON) are another promising approach, as they can efficiently share optical fiber infrastructure among multiple cell sites. The paper examines how time- and wavelength-division multiple access schemes in PONs can enable 6G fronthaul connectivity.
Free space optics (FSO) are also explored as a potential solution for 6G fronthaul, particularly in scenarios where fiber deployment is challenging. The paper discusses how FSO can provide high-bandwidth, license-free wireless links for fronthaul connectivity.
Additionally, the paper investigates optical computing-enabled networks as a novel approach for 6G fronthaul. By leveraging the high speed and parallelism of optical processing, these networks could offer significant performance improvements over traditional electronic-based fronthaul solutions.
Finally, the paper explores how 6G AI-enabled networks can be utilized to enhance the optimization and performance of 6G optical fronthaul systems. Machine learning techniques could be applied to tasks like resource allocation, link adaptation, and fault detection to improve the overall efficiency and reliability of the fronthaul network.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive overview of the key enabling technologies for 6G optical fronthaul, highlighting their potential benefits and challenges. However, it does not delve into the specific trade-offs and limitations of each approach in depth.
For example, while the paper discusses the advantages of PONs, it does not address the potential bottlenecks that could arise from the shared nature of the optical infrastructure or the complexity of managing multiple access schemes. Similarly, the discussion on FSO could have explored the sensitivity of these links to environmental conditions, such as atmospheric turbulence and weather effects, which can degrade their performance.
Additionally, the paper's treatment of optical computing-enabled networks and the application of AI in 6G fronthaul optimization is relatively high-level, lacking a more detailed technical analysis of the underlying algorithms and architectural considerations.
Further research and experimentation will be needed to fully evaluate the feasibility and practical implementation challenges of these enabling technologies in the context of 6G optical fronthaul networks. Addressing these gaps could strengthen the paper's contribution and provide a more well-rounded understanding of the research landscape.
Conclusion
This paper presents a comprehensive survey of the enabling technologies and research perspectives for 6G optical fronthaul networks. It highlights the potential of various optical communication solutions, including point-to-point links, passive optical networks, and free space optics, to meet the high-bandwidth and low-latency requirements of future 6G radio access networks.
The paper also explores the promising role of optical computing-enabled networks and the application of 6G AI-enabled networks in enhancing the performance and optimization of 6G optical fronthaul systems.
As 6G wireless technologies continue to evolve, the insights and research directions outlined in this paper will be crucial in guiding the development of the next-generation optical fronthaul infrastructure to support the ambitious goals of 6G networks.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Toward 6G Optical Fronthaul: A Survey on Enabling Technologies and Research Perspectives
Abdulhalim Fayad, Tibor Cinkler, Jacek Rak
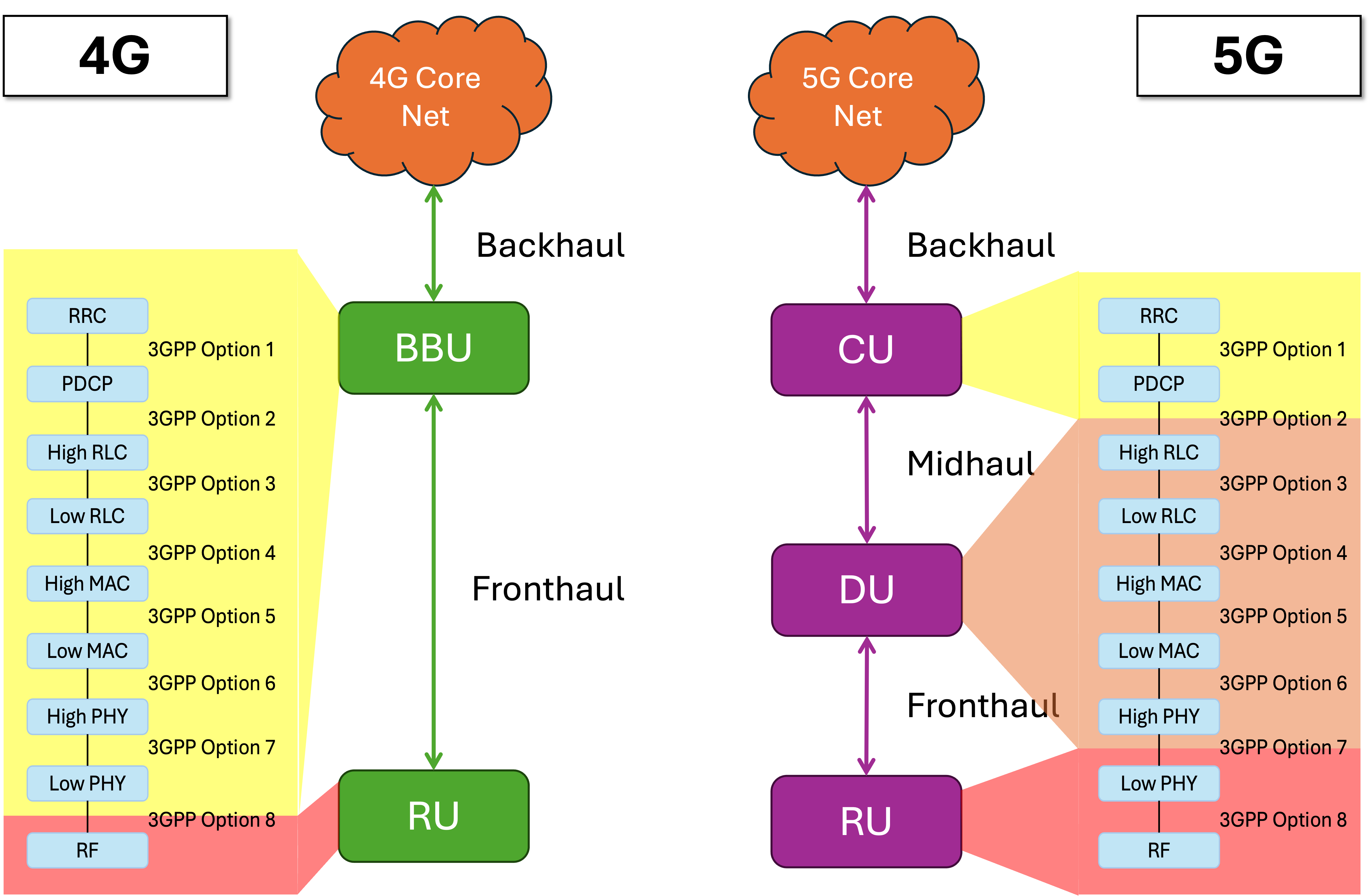
The anticipated launch of the Sixth Generation (6G) of mobile technology by 2030 will mark a significant milestone in the evolution of wireless communication, ushering in a new era with advancements in technology and applications. 6G is expected to deliver ultra-high data rates and almost instantaneous communications, with three-dimensional coverage for everything, everywhere, and at any time. In the 6G Radio Access Networks (RANs) architecture, the Fronthaul connects geographically distributed Remote Units (RUs) to Distributed/Digital Units (DUs)pool. Among all possible solutions for implementing 6G fronthaul, optical technologies will remain crucial in supporting the 6G fronthaul, as they offer high-speed, low-latency, and reliable transmission capabilities to meet the 6G strict requirements. This survey provides an explanation of the 5G and future 6G optical fronthaul concept and presents a comprehensive overview of the current state of the art and future research directions in 6G optical fronthaul, highlighting the key technologies and research perspectives fundamental in designing fronthaul networks for 5G and future 6G. Additionally, it examines the benefits and drawbacks of each optical technology and its potential applications in 6G fronthaul networks. This paper aims to serve as a comprehensive resource for researchers and industry professionals about the current state and future prospects of 6G optical fronthaul technologies, facilitating the development of robust and efficient wireless networks of the future.
Read more6/4/2024


0
Exploring the 6G Potentials: Immersive, Hyper Reliable, and Low-Latency Communication
Afsoon Alidadi Shamsabadi, Animesh Yadav, Yasser Gadallah, Halim Yanikomeroglu
The transition towards the sixth-generation (6G) wireless telecommunications networks introduces significant challenges for researchers and industry stakeholders. The 6G technology aims to enhance existing usage scenarios, particularly supporting innovative applications requiring stringent performance metrics. Among the key performance indicators (KPIs) for 6G, immersive throughput, hyper-reliability, and hyper-low latency must be achieved simultaneously in some critical applications to achieve the application requirements. However, this is challenging due to the conflicting nature of these KPIs. This article proposes a new service class of 6G as immersive, hyper reliable, and low-latency communication (IHRLLC), and introduces a potential network architecture to achieve the associated KPIs. Specifically, technologies such as ultra-massive multiple-input multiple-output (umMIMO)-aided terahertz (THz) communications, and reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS) are viewed as the key enablers for achieving immersive data rate and hyper reliability. Given the computational complexity involved in employing these technologies, and the challenges encountered in designing real-time algorithms for efficient resource allocation and management strategies as well as dynamic beamforming and tracking techniques, we also propose the involvement of other potential enabling technologies such as non-terrestrial networks (NTN), learn-to-optimize (L2O) and generative-AI (GenAI) technologies, quantum computing, and network digital twin (NDT) for limiting the latency.
Read more7/17/2024


0
6G at $frac{1}{6}g$: The Future of Cislunar Communications
Sahan Liyanaarachchi, Stavros Mitrolaris, Purbesh Mitra, Sennur Ulukus
What will the future of cislunar communications be? The ever-expanding horizons of the space exploration missions, and the need for establishing sustainable space communication and navigation infrastructure necessitate to think this question thoroughly. In this article, we examine how some of the concepts of 6G technologies developed for terrestrial networks can be relevant in the context of cislunar networks. We discuss how 6G concepts, such as reconfigurable intelligent surfaces, quantum-resistant physical layer security, private information read/write/cache networks, semantic and goal-oriented communications, information freshness based quality of communication metrics, multi-relay and cooperative networks, hold the potential to shape the future of cislunar communications.
Read more7/24/2024

0
Shaping Radio Access to Match Variable Wireless Fronthaul Quality in Next-Generation Networks
Marcello Morini, Eugenio Moro, Ilario Filippini, Danilo De Donno, Antonio Capone
The emergence of Centralized-RAN (C-RAN) has revolutionized mobile network infrastructure, offering streamlined cell-site engineering and enhanced network management capabilities. As C-RAN gains momentum, the focus shifts to optimizing fronthaul links. While fiber fronthaul guarantees performance, wireless alternatives provide cost efficiency and scalability, making them preferable in densely urbanized areas. However, wireless fronthaul often requires expensive over-dimensioning to overcome the challenging atmospheric attenuation typical of high frequencies. We propose a framework designed to continuously align radio access capacity with fronthaul link quality to overcome this rigidity. By gradually adapting radio access capacity to available fronthaul capacity, the framework ensures smooth degradation rather than complete service loss. Various strategies are proposed, considering factors like functional split and beamforming technology and exploring the tradeoff between adaptation strategy complexity and end-to-end system performance. Numerical evaluations using experimental rain attenuation data illustrate the framework's effectiveness in optimizing radio access capacity under realistically variable fronthaul link quality, ultimately proving the importance of adaptive capacity management in maximizing C-RAN efficiency.
Read more6/26/2024