TV White Space and LTE Network Optimization towards Energy Efficiency in Suburban and Rural Scenarios
2405.02693

0
0
🌐
Abstract
The radio spectrum is a limited resource. Demand for wireless communication services is increasing exponentially, stressing the availability of radio spectrum to accommodate new services. TV White Space (TVWS) technologies allow a dynamic usage of the spectrum. These technologies provide wireless connectivity, in the channels of the Very High Frequency (VHF) and Ultra High Frequency (UHF) television broadcasting bands. In this paper, we investigate and compare the coverage range, network capacity, and network energy efficiency for TVWS technologies and LTE. We consider Ghent, Belgium and Boyeros, Havana, Cuba to evaluate a realistic outdoor suburban and rural area, respectively. The comparison shows that TVWS networks have an energy efficiency 9-12 times higher than LTE networks.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- The radio spectrum is a limited resource, but demand for wireless services is increasing exponentially.
- TV White Space (TVWS) technologies allow dynamic usage of the spectrum in the Very High Frequency (VHF) and Ultra High Frequency (UHF) bands used for TV broadcasting.
- This paper investigates and compares the coverage range, network capacity, and energy efficiency of TVWS technologies and LTE in suburban and rural areas.
Plain English Explanation
The radio waves that wireless devices use to communicate are a finite resource. As more people and devices rely on wireless services like internet and mobile communication, the demand for this radio spectrum is growing rapidly. TVWS technologies offer a way to use the spectrum more efficiently by taking advantage of unused TV broadcast channels.
This study looked at how well TVWS networks performed compared to traditional cellular LTE networks in terms of how far the signals could reach, how much data they could handle, and how much energy they used. The researchers tested these factors in a suburban area of Belgium and a rural area of Cuba to see how the technologies compared in different environments.
The results showed that TVWS networks were significantly more energy-efficient than LTE, using 9 to 12 times less power. This could make TVWS an attractive option for providing wireless connectivity, especially in areas where power supply is limited. The paper provides insights into the tradeoffs and benefits of using TVWS as an alternative to traditional cellular networks.
Technical Explanation
The researchers evaluated the performance of TVWS technologies and LTE networks in two real-world environments - the suburban area of Ghent, Belgium and the rural area of Boyeros, Havana, Cuba. They measured the coverage range, network capacity, and energy efficiency of each technology.
For the coverage analysis, the team deployed TVWS and LTE base stations and measured the signal strength at various distances. The results showed that TVWS had a longer range than LTE in both the suburban and rural settings.
To assess network capacity, the researchers simulated data traffic and measured the maximum number of users the networks could support. They found that TVWS could serve more concurrent users than LTE in the rural scenario, but LTE had higher capacity in the suburban area.
Finally, the team evaluated the energy efficiency of the two technologies by measuring the power consumption of the base stations. The results indicate that TVWS networks consumed 9-12 times less power than comparable LTE networks, demonstrating significantly higher energy efficiency.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a thorough, data-driven comparison of TVWS and LTE technologies in realistic outdoor environments. The inclusion of both suburban and rural test sites gives a more comprehensive view of how the technologies perform in different settings.
However, the paper does not delve into the potential limitations or challenges of TVWS adoption. For example, it does not address issues around spectrum coordination, device availability, or regulatory barriers that could hinder the real-world deployment of TVWS networks. Wireless resource optimization and cognitive radio techniques may be needed to fully unlock the potential of TVWS.
Additionally, the energy efficiency advantages of TVWS could be further explored in the context of sustainable networking paradigms and their implications for broadband access in rural or underserved areas. The paper stops short of speculating on the broader societal and environmental impacts of the technology.
Conclusion
This paper provides a valuable comparison of TVWS and LTE technologies, highlighting the strengths of TVWS in terms of coverage range and energy efficiency. The results suggest that TVWS could be a promising alternative to traditional cellular networks, particularly in rural or resource-constrained environments where power efficiency and extended range are crucial.
The insights from this research can inform the evolution of military broadband wireless communication systems and guide future developments in dynamic spectrum access and sustainable wireless networking solutions.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Slice-aware Resource Allocation and Admission Control for Smart Factory Wireless Networks
Regina Ochonu, Josep Vidal

0
0
The 5th generation (5G) and beyond network offers substantial promise as the ideal wireless technology to replace the existing inflexible wired connections in traditional factories of today. 5G network slicing allows for tailored allocation of resources to different network services, each with unique Quality of Service (QoS) requirements. This paper presents a novel solution for slice-aware radio resource allocation based on a convex optimisation control framework for applications in smart factory wireless networks. The proposed framework dynamically allocates minimum power and sub-channels to downlink mixed service type industrial users categorised into three slices: Capacity Limited (CL), Ultra Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC), and Time Sensitive (TS) slices. Given that the base station (BS) has limited transmission power, we enforce admission control by effectively relaxing the target rate constraints for current connections in the CL slice. This rate readjustment occurs whenever power consumption exceeds manageable levels. Simulation results show that our approach minimises power, allocates sub-channels to users, maintains slice isolation, and delivers QoS-specific communications to users in all the slices despite time-varying number of users and changing network conditions.
5/17/2024
🏋️
Evolving Military Broadband Wireless Communication Systems: WiMAX, LTE and WLAN
P. Fraga-Lamas, L. Castedo-Ribas, A. Morales-M'endez, J. M. Camas-Albar

0
0
Emerging technologies for mobile broadband wireless are being considered as a Commercial Off-The-Shelf solution to cover the operational requirements of the future warfare. The capabilities of these technologies are being enhanced to meet the growing market demands on performance. In this context, several standards such as WiMAX, LTE or WLAN are introducing themselves as strong candidates to fulfill these requirements. This paper presents an innovative scenario-based approach to develop a Military Broadband Wireless Communication System (MBWCS). Its main objective is to analyze how similar a military MBWCS can be to the identified civil standards, taking operational and high level technical requirements into account. This specification will be used for analyzing the applicability and the modifications of each of the standards layers individually. Proving the feasibility and aptitude of each standard provides strong foundations to address a MBWCS in the most efficient way.
4/12/2024
🐍
Exploring Wireless Channels in Rural Areas: A Comprehensive Measurement Study
Tianyi Zhang, Guoying Zu, Taimoor Ul Islam, Evan Gossling, Sarath Babu, Daji Qiao, Hongwei Zhang

0
0
The study of wireless channel behavior has been an active research topic for many years. However, there exists a noticeable scarcity of studies focusing on wireless channel characteristics in rural areas. With the advancement of smart agriculture practices in rural regions, there has been an increasing demand for affordable, high-capacity, and low-latency wireless networks to support various precision agriculture applications such as plant phenotyping, livestock health monitoring, and agriculture automation. To address this research gap, we conducted a channel measurement study on multiple wireless frequency bands at various crop and livestock farms near Ames, Iowa, based on Iowa State University~(ISU)'s ARA Wireless Living lab - one of the NSF PAWR platforms. We specifically investigate the impact of weather conditions, humidity, temperature, and farm buildings on wireless channel behavior. The resulting measurement dataset, which will soon be made publicly accessible, represents a valuable resource for researchers interested in wireless channel prediction and optimization.
4/29/2024
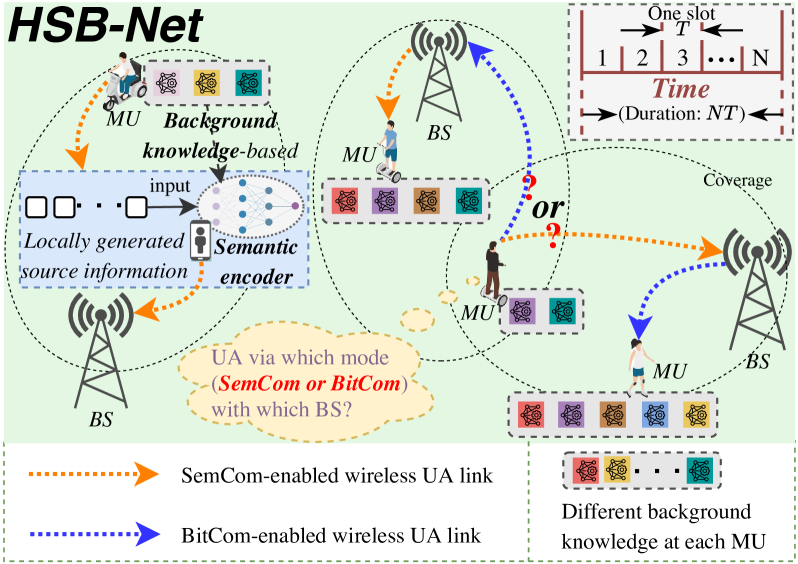
Wireless Resource Optimization in Hybrid Semantic/Bit Communication Networks
Le Xia, Yao Sun, Dusit Niyato, Lan Zhang, Muhammad Ali Imran

0
0
Recently, semantic communication (SemCom) has shown great potential in significant resource savings and efficient information exchanges, thus naturally introducing a novel and practical cellular network paradigm where two modes of SemCom and conventional bit communication (BitCom) coexist. Nevertheless, the involved wireless resource management becomes rather complicated and challenging, given the unique background knowledge matching and time-consuming semantic coding requirements in SemCom. To this end, this paper jointly investigates user association (UA), mode selection (MS), and bandwidth allocation (BA) problems in a hybrid semantic/bit communication network (HSB-Net). Concretely, we first identify a unified performance metric of message throughput for both SemCom and BitCom links. Next, we specially develop a knowledge matching-aware two-stage tandem packet queuing model and theoretically derive the average packet loss ratio and queuing latency. Combined with practical constraints, we then formulate a joint optimization problem for UA, MS, and BA to maximize the overall message throughput of HSB-Net. Afterward, we propose an optimal resource management strategy by utilizing a Lagrange primal-dual transformation method and a preference list-based heuristic algorithm with polynomial-time complexity. Numerical results not only demonstrate the accuracy of our analytical queuing model, but also validate the performance superiority of our proposed strategy compared with different benchmarks.
4/16/2024