Wireless Resource Optimization in Hybrid Semantic/Bit Communication Networks
2404.04162

0
0
Abstract
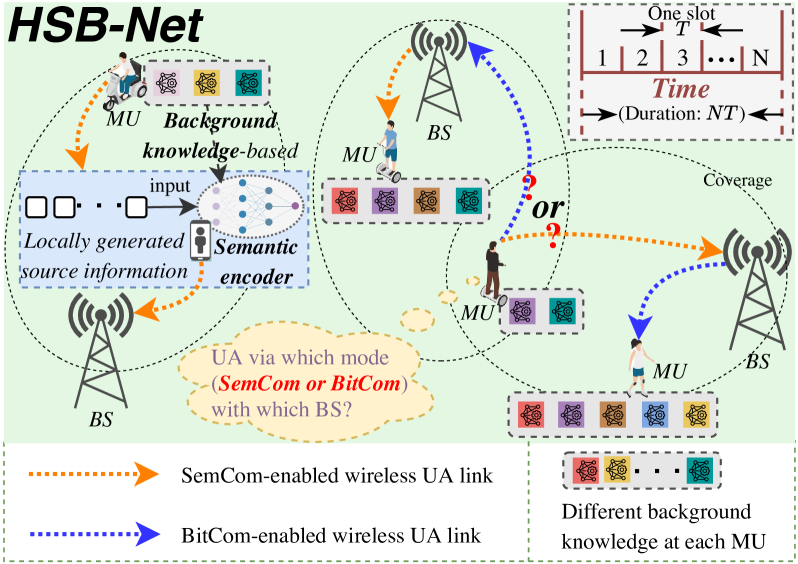
Recently, semantic communication (SemCom) has shown great potential in significant resource savings and efficient information exchanges, thus naturally introducing a novel and practical cellular network paradigm where two modes of SemCom and conventional bit communication (BitCom) coexist. Nevertheless, the involved wireless resource management becomes rather complicated and challenging, given the unique background knowledge matching and time-consuming semantic coding requirements in SemCom. To this end, this paper jointly investigates user association (UA), mode selection (MS), and bandwidth allocation (BA) problems in a hybrid semantic/bit communication network (HSB-Net). Concretely, we first identify a unified performance metric of message throughput for both SemCom and BitCom links. Next, we specially develop a knowledge matching-aware two-stage tandem packet queuing model and theoretically derive the average packet loss ratio and queuing latency. Combined with practical constraints, we then formulate a joint optimization problem for UA, MS, and BA to maximize the overall message throughput of HSB-Net. Afterward, we propose an optimal resource management strategy by utilizing a Lagrange primal-dual transformation method and a preference list-based heuristic algorithm with polynomial-time complexity. Numerical results not only demonstrate the accuracy of our analytical queuing model, but also validate the performance superiority of our proposed strategy compared with different benchmarks.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Explores the optimization of wireless resources in hybrid semantic/bit communication networks
- Focuses on mode selection, user association, and bandwidth allocation to maximize network performance
- Analyzes the queuing dynamics of semantic data packets to optimize network utilization
Plain English Explanation
In modern communication networks, there are two main ways to transmit data: using traditional binary encoding (bits) or using semantic encoding that conveys meaning directly. This paper looks at how to best manage the wireless resources in a network that uses both of these communication modes.
The key challenges involve deciding when to use bit-based vs. semantic-based transmission, how to assign users to different access points, and how to allocate the available wireless bandwidth. The researchers develop optimization techniques to address these challenges and improve the overall performance of the hybrid network.
A key part of their approach is analyzing how semantic data packets get queued and processed in the network. This queuing analysis helps them understand network bottlenecks and find ways to more efficiently utilize the available resources.
By carefully managing the mode selection, user associations, and bandwidth allocation, the techniques proposed in this paper can significantly boost the performance and efficiency of these hybrid communication networks. This is an important advance as networks increasingly need to support a mix of traditional and more advanced semantic-based data transmissions.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes a framework for optimizing wireless resource allocation in a hybrid semantic/bit communication network. The system model consists of multiple access points (APs) serving a set of users, where users can transmit both semantic and bit-based data.
The key optimization problems addressed are:
- Mode selection - Determining when a user should transmit semantic or bit-based data
- User association - Assigning users to the most appropriate AP
- Bandwidth allocation - Partitioning the available wireless bandwidth across users and data types
To capture the queuing dynamics of semantic data, the authors develop a queueing-theoretic analysis that models the arrival and service processes. This provides insights into potential bottlenecks and informs the optimization decisions.
The paper formulates a joint optimization problem that aims to maximize a weighted sum of the users' bit-based and semantic data rates, subject to constraints on transmit power, bandwidth, and queue stability. It proposes an alternating optimization algorithm to efficiently solve this problem.
Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed approach can significantly improve network performance compared to baseline schemes that do not jointly optimize mode selection, user association, and bandwidth allocation.
Critical Analysis
The key strength of this paper is its comprehensive treatment of the resource optimization problem in hybrid semantic/bit communication networks. By jointly considering mode selection, user association, and bandwidth allocation, the authors are able to unlock substantial performance gains compared to siloed approaches.
That said, the analysis and optimization framework rely on several simplifying assumptions, such as perfect channel state information, Poisson arrival processes, and stationary queues. In practice, relaxing these assumptions could introduce additional complexities that are not addressed.
Additionally, the paper does not provide much insight into the practical implementation challenges of deploying such a system. Issues around signaling overhead, network coordination, and compatibility with existing standards are not deeply explored.
Further research could also investigate the robustness of the proposed techniques to factors like user mobility, imperfect channel information, and dynamic traffic patterns. Exploring the fairness and equity implications of the resource allocation policies would also be valuable.
Overall, this paper makes an important contribution by laying the groundwork for optimizing wireless resources in these emerging hybrid communication networks. But there remains significant room for further refinement and real-world validation of the concepts presented.
Conclusion
This paper tackles the critical challenge of optimizing wireless resource allocation in hybrid semantic/bit communication networks. By jointly considering mode selection, user association, and bandwidth partitioning, the proposed techniques can significantly improve network performance compared to siloed approaches.
The key innovations include a queueing-theoretic analysis of semantic data packet flows and an alternating optimization algorithm to solve the complex resource allocation problem. While relying on some simplifying assumptions, this work represents an important step forward in enabling efficient utilization of wireless resources in next-generation communication systems that blend traditional bit-based and more advanced semantic-based transmissions.
As networks continue to evolve to support diverse data types and application requirements, optimizing wireless resource usage in these hybrid environments will only grow in importance. The concepts and methods outlined in this paper provide a strong foundation for further research and development in this critical area.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
Semantic-Aware Resource Allocation Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning for 5G-V2X HetNets
Zhiyu Shao, Qiong Wu, Pingyi Fan, Nan Cheng, Qiang Fan, Jiangzhou Wang

0
0
This letter proposes a semantic-aware resource allocation (SARA) framework with flexible duty cycle (DC) coexistence mechanism (SARADC) for 5G-V2X Heterogeneous Network (HetNets) based on deep reinforcement learning (DRL) proximal policy optimization (PPO). Specifically, we investigate V2X networks within a two-tiered HetNets structure. In response to the needs of high-speed vehicular networking in urban environments, we design a semantic communication system and introduce two resource allocation metrics: high-speed semantic transmission rate (HSR) and semantic spectrum efficiency (HSSE). Our main goal is to maximize HSSE. Additionally, we address the coexistence of vehicular users and WiFi users in 5G New Radio Unlicensed (NR-U) networks. To tackle this complex challenge, we propose a novel approach that jointly optimizes flexible DC coexistence mechanism and the allocation of resources and base stations (BSs). Unlike traditional bit transmission methods, our approach integrates the semantic communication paradigm into the communication system. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed solution outperforms traditional bit transmission methods with traditional DC coexistence mechanism in terms of HSSE and semantic throughput (ST) for both vehicular and WiFi users.
6/13/2024

On the Computing and Communication Tradeoff in Reasoning-Based Multi-User Semantic Communications
Nitisha Singh, Christo Kurisummoottil Thomas, Walid Saad, Emilio Calvanese Strinati

0
0
Semantic communication (SC) is recognized as a promising approach for enabling reliable communication with minimal data transfer while maintaining seamless connectivity for a group of wireless users. Unlocking the advantages of SC for multi-user cases requires revisiting how communication and computing resources are allocated. This reassessment should consider the reasoning abilities of end-users, enabling receiving nodes to fill in missing information or anticipate future events more effectively. Yet, state-of-the-art SC systems primarily focus on resource allocation through compression based on semantic relevance, while overlooking the underlying data generation mechanisms and the tradeoff between communications and computing. Thus, they cannot help prevent a disruption in connectivity. In contrast, in this paper, a novel framework for computing and communication resource allocation is proposed that seeks to demonstrate how SC systems with reasoning capabilities at the end nodes can improve reliability in an end-to-end multi-user wireless system with intermittent communication links. Towards this end, a novel reasoning-aware SC system is proposed for enabling users to utilize their local computing resources to reason the representations when the communication links are unavailable. To optimize communication and computing resource allocation in this system, a noncooperative game is formulated among multiple users whose objective is to maximize the effective semantic information (computed as a product of reliability and semantic information) while controlling the number of semantically relevant links that are disrupted. Simulation results show that the proposed reasoning-aware SC system results in at least a $16.6%$ enhancement in throughput and a significant improvement in reliability compared to classical communications systems that do not incorporate reasoning.
6/24/2024

Uplink resource allocation optimization for user-centric cell-free MIMO networks
Zehua Li, Raviraj Adve

0
0
We examine the problem of optimizing resource allocation in the uplink for a user-centric, cell-free, multi-input multi-output network. We start by modeling and developing resource allocation algorithms for two standard network operation modes. The centralized mode provides high data rates but suffers multiple issues, including scalability. On the other hand, the distributed mode has the opposite problem: relatively low rates, but is scalable. To address these challenges, we combine the strength of the two standard modes, creating a new semi-distributed operation mode. To avoid the need for information exchange between access points, we introduce a new quality of service metric to decentralize the resource allocation algorithms. Our results show that we can eliminate the need for information exchange with a relatively small penalty on data rates.
6/11/2024
✨
Joint Spectrum Partitioning and Power Allocation for Energy Efficient Semi-Integrated Sensing and Communications
Ammar Mohamed Abouelmaati, Sylvester Aboagye, Hina Tabassum

0
0
With spectrum resources becoming congested and the emergence of sensing-enabled wireless applications, conventional resource allocation methods need a revamp to support communications-only, sensing-only, and integrated sensing and communication (ISaC) services together. In this letter, we propose two joint spectrum partitioning (SP) and power allocation (PA) schemes to maximize the aggregate sensing and communication performance as well as corresponding energy efficiency (EE) of a semi-ISaC system that supports all three services in a unified manner. The proposed framework captures the priority of the distinct services, impact of target clutters, power budget and bandwidth constraints, and sensing and communication quality-of-service (QoS) requirements. We reveal that the former problem is jointly convex and the latter is a non-convex problem that can be solved optimally by exploiting fractional and parametric programming techniques. Numerical results verify the effectiveness of proposed schemes and extract novel insights related to the impact of the priority and QoS requirements of distinct services on the performance of semi-ISaC networks.
4/30/2024