Vector Signal Reconstruction Sparse and Parametric Approach of direction of arrival Using Single Vector Hydrophone
2404.15160

0
0
❗
Abstract
This article discusses the application of single vector hydrophones in the field of underwater acoustic signal processing for Direction Of Arrival (DOA) estimation. Addressing the limitations of traditional DOA estimation methods in multi-source environments and under noise interference, this study introduces a Vector Signal Reconstruction Sparse and Parametric Approach (VSRSPA). This method involves reconstructing the signal model of a single vector hydrophone, converting its covariance matrix into a Toeplitz structure suitable for the Sparse and Parametric Approach (SPA) algorithm. The process then optimizes it using the SPA algorithm to achieve more accurate DOA estimation. Through detailed simulation analysis, this research has confirmed the performance of the proposed algorithm in single and dual-target DOA estimation scenarios, especially under various signal-to-noise ratio(SNR) conditions. The simulation results show that, compared to traditional DOA estimation methods, this algorithm has significant advantages in estimation accuracy and resolution, particularly in multi-source signals and low SNR environments. The contribution of this study lies in providing an effective new method for DOA estimation with single vector hydrophones in complex environments, introducing new research directions and solutions in the field of vector hydrophone signal processing.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper introduces a new method for estimating the direction of arrival (DOA) of underwater acoustic signals using a single vector hydrophone.
- The proposed approach, called the Vector Signal Reconstruction Sparse and Parametric Approach (VSRSPA), aims to address the limitations of traditional DOA estimation methods in complex environments with multiple signal sources and noise interference.
- The method involves reconstructing the signal model of the vector hydrophone and converting its covariance matrix to a Toeplitz structure, which is then optimized using the Sparse and Parametric Approach (SPA) algorithm to improve DOA estimation accuracy.
Plain English Explanation
The paper discusses a new way of figuring out the direction that underwater sounds are coming from using a single specialized microphone called a vector hydrophone. Traditional methods for determining the direction of sound sources can struggle when there are multiple sound sources or a lot of background noise.
The researchers' approach, called VSRSPA, tries to overcome these challenges. It involves reconstructing the mathematical model of the signal received by the vector hydrophone and then converting it to a specific form that can be optimized using a special algorithm called SPA. This allows for more accurate estimation of the direction the sound is coming from, even when there are multiple sound sources or low signal strength.
The paper presents detailed computer simulations showing that VSRSPA outperforms traditional DOA estimation methods, particularly in scenarios with multiple sound sources and low signal-to-noise ratios. This suggests it could be a useful tool for underwater navigation and acoustic target tracking applications.
Technical Explanation
The paper introduces the Vector Signal Reconstruction Sparse and Parametric Approach (VSRSPA) for Direction Of Arrival (DOA) estimation using a single vector hydrophone. Traditional DOA estimation methods can struggle in complex environments with multiple signal sources and noise interference.
The VSRSPA approach involves first reconstructing the signal model of the vector hydrophone. It then converts the covariance matrix of the signal into a Toeplitz structure, which is suitable for processing using the Sparse and Parametric Approach (SPA) algorithm. The SPA algorithm is then used to optimize the Toeplitz covariance matrix and achieve more accurate DOA estimation.
Through detailed simulation analysis, the researchers demonstrate the performance of the VSRSPA algorithm in single and dual-target DOA estimation scenarios under various signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) conditions. The results show that the proposed method outperforms traditional DOA estimation techniques, particularly in terms of estimation accuracy and resolution in multi-source signals and low SNR environments.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a thorough evaluation of the VSRSPA method through simulation experiments, demonstrating its advantages over existing DOA estimation approaches. However, the research is limited to simulation-based analysis, and the authors acknowledge the need for further validation through real-world experiments and field trials.
Additionally, the paper does not delve into the computational complexity and implementation challenges of the VSRSPA method, which could be important considerations for real-world applications, especially in resource-constrained underwater acoustic systems.
While the VSRSPA algorithm shows promising results, there may be opportunities to further improve its performance, such as exploring alternative signal reconstruction and optimization techniques or investigating the integration of the method with other advanced signal processing approaches for underwater acoustic applications.
Conclusion
This paper presents a novel Vector Signal Reconstruction Sparse and Parametric Approach (VSRSPA) for Direction Of Arrival (DOA) estimation using a single vector hydrophone. The method aims to address the limitations of traditional DOA estimation techniques in complex underwater environments with multiple signal sources and noise interference.
The simulation results demonstrate the superior performance of VSRSPA compared to existing methods, particularly in terms of estimation accuracy and resolution in multi-source scenarios and low signal-to-noise ratio conditions. This suggests that the proposed approach could be a valuable tool for underwater acoustic applications, such as navigation, target tracking, and environmental monitoring.
Further research and validation through real-world experiments will be necessary to assess the practical feasibility and potential impact of the VSRSPA method in the field of underwater acoustic signal processing.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
👨🏫
Sparse Direction of Arrival Estimation Method Based on Vector Signal Reconstruction with a Single Vector Sensor
Jiabin Guo

0
0
This study investigates the application of single vector hydrophones in underwater acoustic signal processing for Direction of Arrival (DOA) estimation. Addressing the limitations of traditional DOA estimation methods in multi-source environments and under noise interference, this research proposes a Vector Signal Reconstruction (VSR) technique. This technique transforms the covariance matrix of single vector hydrophone signals into a Toeplitz structure suitable for gridless sparse methods through complex calculations and vector signal reconstruction. Furthermore, two sparse DOA estimation algorithms based on vector signal reconstruction are introduced. Theoretical analysis and simulation experiments demonstrate that the proposed algorithms significantly improve the accuracy and resolution of DOA estimation in multi-source signals and low Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) environments compared to traditional algorithms. The contribution of this study lies in providing an effective new method for DOA estimation with single vector hydrophones in complex environments, introducing new research directions and solutions in the field of vector hydrophone signal processing.
4/23/2024
Study of Robust Direction Finding Based on Joint Sparse Representation
Y. Li, W. Xiao, L. Zhao, Z. Huang, Q. Li, L. Li, R. C. de Lamare

0
0
Standard Direction of Arrival (DOA) estimation methods are typically derived based on the Gaussian noise assumption, making them highly sensitive to outliers. Therefore, in the presence of impulsive noise, the performance of these methods may significantly deteriorate. In this paper, we model impulsive noise as Gaussian noise mixed with sparse outliers. By exploiting their statistical differences, we propose a novel DOA estimation method based on sparse signal recovery (SSR). Furthermore, to address the issue of grid mismatch, we utilize an alternating optimization approach that relies on the estimated outlier matrix and the on-grid DOA estimates to obtain the off-grid DOA estimates. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method exhibits robustness against large outliers.
5/28/2024

Multiple Mobile Target Detection and Tracking in Active Sonar Array Using a Track-Before-Detect Approach
Avi Abu, Nikola Miskovic, Oleg Chebotar, Neven Cukrov, Roee Diamant

0
0
We present an algorithm for detecting and tracking underwater mobile objects using active acoustic transmission of broadband chirp signals whose reflections are received by a hydrophone array. The method overcomes the problem of high false alarm rate by applying a track-before-detect ap- proach to the sequence of received reflections. A 2D time- space matrix is created for the reverberations received from each transmitted probe signal by performing delay and sum beamforming and pulse compression. The result is filtered by a 2D constant false alarm rate (CFAR) detector to identify reflection patterns corresponding to potential targets. Closely spaced signals for multiple probe transmissions are combined into blobs to avoid multiple detections of a single object. A track- before-detect method using a Nearly Constant Velocity (NCV) model is employed to track multiple objects. The position and velocity is estimated by the debiased converted measurement Kalman filter. Results are analyzed for simulated scenarios and for experiments at sea, where GPS tagged gilt-head seabream fish were tracked. Compared to two benchmark schemes, the results show a favorable track continuity and accuracy that is robust to the choice of detection threshold.
4/17/2024
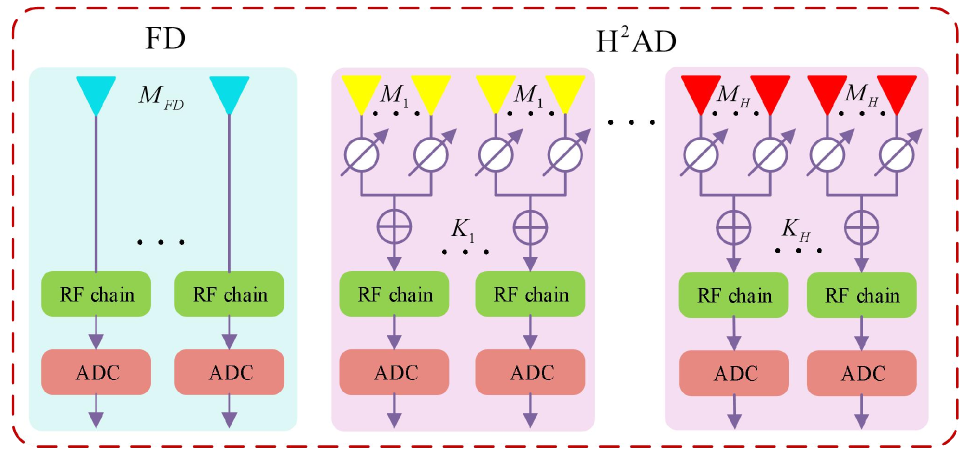
Co-learning-aided Multi-modal-deep-learning Framework of Passive DOA Estimators for a Heterogeneous Hybrid Massive MIMO Receiver
Jiatong Bai, Feng Shu, Qinghe Zheng, Bo Xu, Baihua Shi, Yiwen Chen, Weibin Zhang, Xianpeng Wang

0
0
Due to its excellent performance in rate and resolution, fully-digital (FD) massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) antenna arrays has been widely applied in data transmission and direction of arrival (DOA) measurements, etc. But it confronts with two main challenges: high computational complexity and circuit cost. The two problems may be addressed well by hybrid analog-digital (HAD) structure. But there exists the problem of phase ambiguity for HAD, which leads to its low-efficiency or high-latency. Does exist there such a MIMO structure of owning low-cost, low-complexity and high time efficiency at the same time. To satisfy the three properties, a novel heterogeneous hybrid MIMO receiver structure of integrating FD and heterogeneous HAD ($rm{H}^2$AD-FD) is proposed and corresponding multi-modal (MD)-learning framework is developed. The framework includes three major stages: 1) generate the candidate sets via root multiple signal classification (Root-MUSIC) or deep learning (DL); 2) infer the class of true solutions from candidate sets using machine learning (ML) methods; 3) fuse the two-part true solutions to achieve a better DOA estimation. The above process form two methods named MD-Root-MUSIC and MDDL. To improve DOA estimation accuracy and reduce the clustering complexity, a co-learning-aided MD framework is proposed to form two enhanced methods named CoMDDL and CoMD-RootMUSIC. Moreover, the Cramer-Rao lower bound (CRLB) for the proposed $rm{H}^2$AD-FD structure is also derived. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed four methods could approach the CRLB for signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) > 0 dB and the proposed CoMDDL and MDDL perform better than CoMD-RootMUSIC and MD-RootMUSIC, particularly in the extremely low SNR region.
6/13/2024