Virtual avatar generation models as world navigators
2406.01056

2
0

Abstract
We introduce SABR-CLIMB, a novel video model simulating human movement in rock climbing environments using a virtual avatar. Our diffusion transformer predicts the sample instead of noise in each diffusion step and ingests entire videos to output complete motion sequences. By leveraging a large proprietary dataset, NAV-22M, and substantial computational resources, we showcase a proof of concept for a system to train general-purpose virtual avatars for complex tasks in robotics, sports, and healthcare.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores the use of virtual avatar generation models as "world navigators" - systems that can generate virtual avatars that can explore and interact with 3D virtual environments.
- The researchers investigate the potential of these models to serve as efficient and flexible tools for various applications, such as embodied agents for efficient exploration and smart scene description, stratified avatar generation from sparse observations, and hierarchical world models as visual whole-body.
- The paper also discusses the challenges and limitations of current virtual avatar generation models and explores potential avenues for future research and development in this area.
Plain English Explanation
Virtual avatar generation models are computer systems that can create lifelike digital representations of people, animals, or other entities. These models are becoming increasingly sophisticated, allowing them to generate avatars that can navigate and interact with 3D virtual environments.
The researchers in this paper are exploring the potential of these avatar generation models to serve as "world navigators" - tools that can explore and interact with virtual worlds in useful ways. For example, they could be used to efficiently explore and describe virtual environments, generate detailed avatars from limited information, or create comprehensive visual models of the world.
The paper discusses the current state of this technology and the challenges that researchers are working to overcome, such as improving the realism and flexibility of the generated avatars. The researchers also explore potential future applications and directions for further development in this exciting field.
Technical Explanation
The paper begins by providing an overview of recent advancements in virtual avatar generation, highlighting the potential of these models to serve as "world navigators" - systems that can generate virtual avatars capable of exploring and interacting with 3D virtual environments.
The researchers discuss several relevant areas of related work, including embodied agents for efficient exploration and smart scene description, stratified avatar generation from sparse observations, and hierarchical world models as visual whole-body. These studies demonstrate the growing capabilities of avatar generation models and their potential applications in areas such as virtual reality, robotics, and simulation.
The paper then delves into the core technical aspects of the researchers' work, describing their approach to leveraging avatar generation models as world navigators. This includes details on the model architectures, training procedures, and evaluation methodologies used to assess the performance of these systems in various virtual environment tasks.
The key insights from the study include the ability of these models to efficiently explore and describe virtual spaces, generate high-fidelity avatars from limited input data, and construct comprehensive hierarchical world models. The researchers also discuss the limitations of the current approaches and identify areas for future research, such as improving the robustness and generalization capabilities of the models.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a compelling vision for the use of virtual avatar generation models as "world navigators" - systems that can leverage these advanced AI models to explore, interact with, and even construct representations of 3D virtual environments. The researchers demonstrate the potential of these models to address a range of practical challenges, from efficient exploration and scene description to generating detailed avatars from limited data and building comprehensive world models.
However, the paper also acknowledges several limitations and areas for further research. For example, the authors note that the current models may struggle with robustness and generalization, particularly when faced with unfamiliar or complex virtual environments. Additionally, the paper does not address potential ethical and social implications of these technologies, such as the risks of misuse or the impact on individual privacy and identity.
As the field of virtual avatar generation continues to evolve, it will be important for researchers to carefully consider these types of issues and work to develop the technology in a responsible and inclusive manner. Future studies could explore ways to improve the reliability and fairness of these models, as well as investigate the broader societal implications of their widespread adoption.
Conclusion
This paper presents a compelling vision for the use of virtual avatar generation models as "world navigators" - flexible and efficient tools for exploring, interacting with, and constructing representations of 3D virtual environments. The researchers demonstrate the potential of these models to address a range of practical challenges, from embodied exploration and avatar generation from sparse data to building comprehensive world models.
While the current state of the technology shows promise, the paper also highlights several limitations and areas for further research, such as improving the robustness and generalization capabilities of the models. As this field continues to evolve, it will be important for researchers to consider the broader ethical and social implications of these technologies, ensuring that they are developed and deployed in a responsible and inclusive manner.
Overall, the work presented in this paper demonstrates the exciting potential of virtual avatar generation models as powerful "world navigators," with applications across a wide range of domains. As the technology continues to advance, it will be fascinating to see how these models are leveraged to enhance our understanding and exploration of virtual environments.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Real-Time Simulated Avatar from Head-Mounted Sensors
Zhengyi Luo, Jinkun Cao, Rawal Khirodkar, Alexander Winkler, Jing Huang, Kris Kitani, Weipeng Xu

0
0
We present SimXR, a method for controlling a simulated avatar from information (headset pose and cameras) obtained from AR / VR headsets. Due to the challenging viewpoint of head-mounted cameras, the human body is often clipped out of view, making traditional image-based egocentric pose estimation challenging. On the other hand, headset poses provide valuable information about overall body motion, but lack fine-grained details about the hands and feet. To synergize headset poses with cameras, we control a humanoid to track headset movement while analyzing input images to decide body movement. When body parts are seen, the movements of hands and feet will be guided by the images; when unseen, the laws of physics guide the controller to generate plausible motion. We design an end-to-end method that does not rely on any intermediate representations and learns to directly map from images and headset poses to humanoid control signals. To train our method, we also propose a large-scale synthetic dataset created using camera configurations compatible with a commercially available VR headset (Quest 2) and show promising results on real-world captures. To demonstrate the applicability of our framework, we also test it on an AR headset with a forward-facing camera.
4/26/2024
🔄
Embodied Agents for Efficient Exploration and Smart Scene Description
Roberto Bigazzi, Marcella Cornia, Silvia Cascianelli, Lorenzo Baraldi, Rita Cucchiara

0
0
The development of embodied agents that can communicate with humans in natural language has gained increasing interest over the last years, as it facilitates the diffusion of robotic platforms in human-populated environments. As a step towards this objective, in this work, we tackle a setting for visual navigation in which an autonomous agent needs to explore and map an unseen indoor environment while portraying interesting scenes with natural language descriptions. To this end, we propose and evaluate an approach that combines recent advances in visual robotic exploration and image captioning on images generated through agent-environment interaction. Our approach can generate smart scene descriptions that maximize semantic knowledge of the environment and avoid repetitions. Further, such descriptions offer user-understandable insights into the robot's representation of the environment by highlighting the prominent objects and the correlation between them as encountered during the exploration. To quantitatively assess the performance of the proposed approach, we also devise a specific score that takes into account both exploration and description skills. The experiments carried out on both photorealistic simulated environments and real-world ones demonstrate that our approach can effectively describe the robot's point of view during exploration, improving the human-friendly interpretability of its observations.
4/16/2024

Hierarchical World Models as Visual Whole-Body Humanoid Controllers
Nicklas Hansen, Jyothir S V, Vlad Sobal, Yann LeCun, Xiaolong Wang, Hao Su

0
0
Whole-body control for humanoids is challenging due to the high-dimensional nature of the problem, coupled with the inherent instability of a bipedal morphology. Learning from visual observations further exacerbates this difficulty. In this work, we explore highly data-driven approaches to visual whole-body humanoid control based on reinforcement learning, without any simplifying assumptions, reward design, or skill primitives. Specifically, we propose a hierarchical world model in which a high-level agent generates commands based on visual observations for a low-level agent to execute, both of which are trained with rewards. Our approach produces highly performant control policies in 8 tasks with a simulated 56-DoF humanoid, while synthesizing motions that are broadly preferred by humans. Code and videos: https://nicklashansen.com/rlpuppeteer
6/3/2024
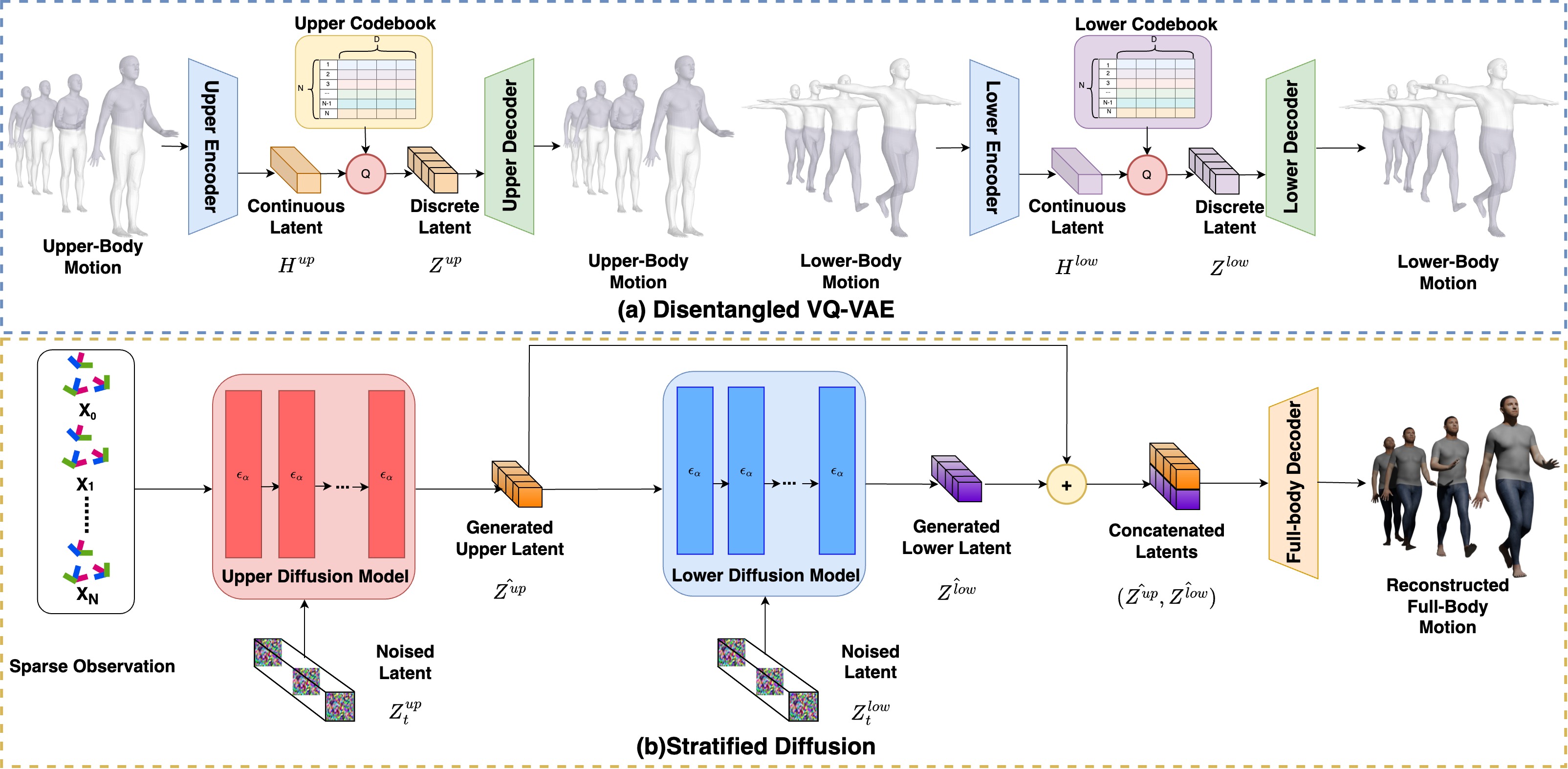
Stratified Avatar Generation from Sparse Observations
Han Feng, Wenchao Ma, Quankai Gao, Xianwei Zheng, Nan Xue, Huijuan Xu

0
0
Estimating 3D full-body avatars from AR/VR devices is essential for creating immersive experiences in AR/VR applications. This task is challenging due to the limited input from Head Mounted Devices, which capture only sparse observations from the head and hands. Predicting the full-body avatars, particularly the lower body, from these sparse observations presents significant difficulties. In this paper, we are inspired by the inherent property of the kinematic tree defined in the Skinned Multi-Person Linear (SMPL) model, where the upper body and lower body share only one common ancestor node, bringing the potential of decoupled reconstruction. We propose a stratified approach to decouple the conventional full-body avatar reconstruction pipeline into two stages, with the reconstruction of the upper body first and a subsequent reconstruction of the lower body conditioned on the previous stage. To implement this straightforward idea, we leverage the latent diffusion model as a powerful probabilistic generator, and train it to follow the latent distribution of decoupled motions explored by a VQ-VAE encoder-decoder model. Extensive experiments on AMASS mocap dataset demonstrate our state-of-the-art performance in the reconstruction of full-body motions.
6/4/2024