Stratified Avatar Generation from Sparse Observations
2405.20786

0
0
Abstract
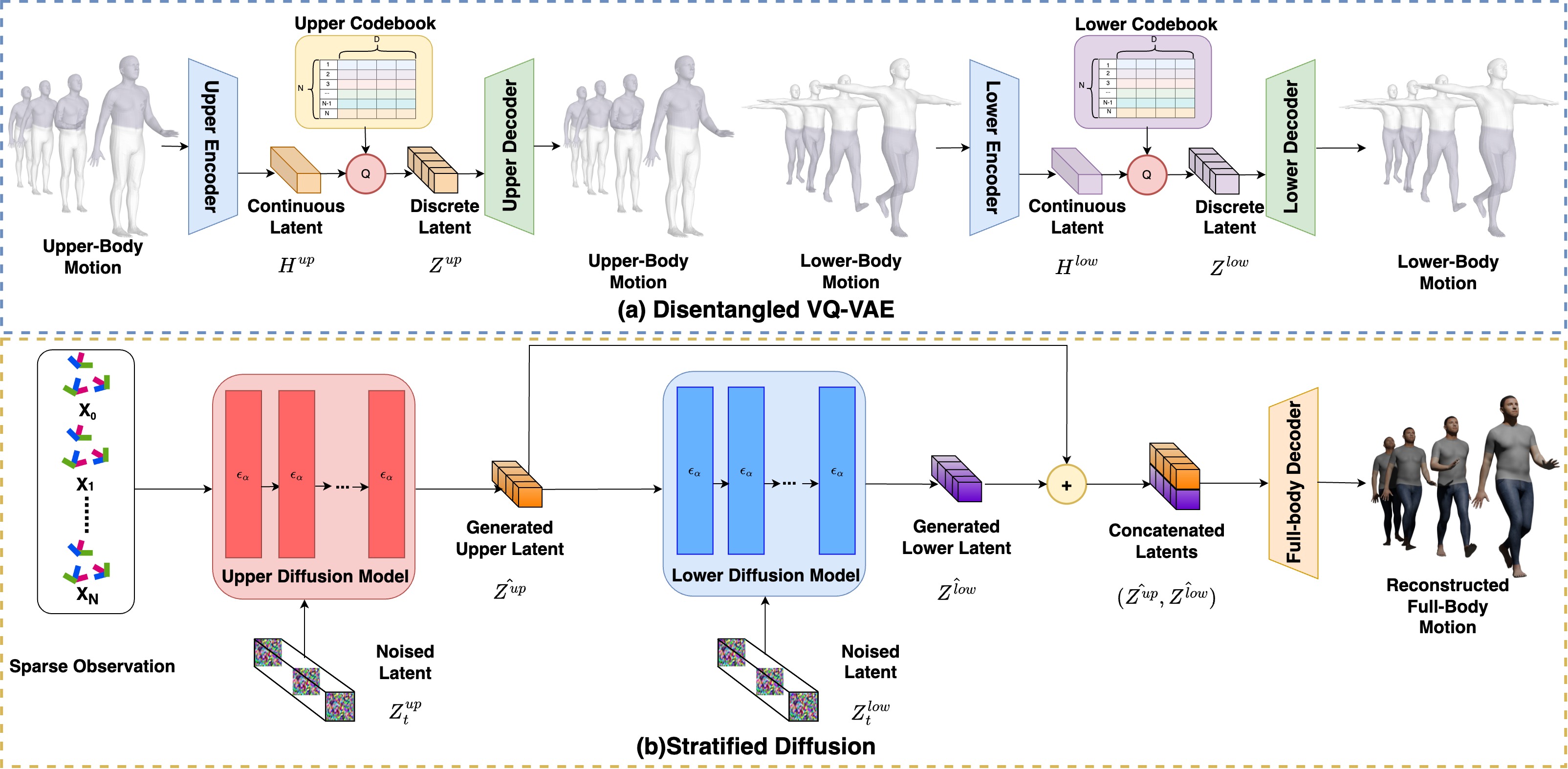
Estimating 3D full-body avatars from AR/VR devices is essential for creating immersive experiences in AR/VR applications. This task is challenging due to the limited input from Head Mounted Devices, which capture only sparse observations from the head and hands. Predicting the full-body avatars, particularly the lower body, from these sparse observations presents significant difficulties. In this paper, we are inspired by the inherent property of the kinematic tree defined in the Skinned Multi-Person Linear (SMPL) model, where the upper body and lower body share only one common ancestor node, bringing the potential of decoupled reconstruction. We propose a stratified approach to decouple the conventional full-body avatar reconstruction pipeline into two stages, with the reconstruction of the upper body first and a subsequent reconstruction of the lower body conditioned on the previous stage. To implement this straightforward idea, we leverage the latent diffusion model as a powerful probabilistic generator, and train it to follow the latent distribution of decoupled motions explored by a VQ-VAE encoder-decoder model. Extensive experiments on AMASS mocap dataset demonstrate our state-of-the-art performance in the reconstruction of full-body motions.
Create account to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

A Simple Strategy for Body Estimation from Partial-View Images
Yafei Mao, Xuelu Li, Brandon Smith, Jinjin Li, Raja Bala

0
0
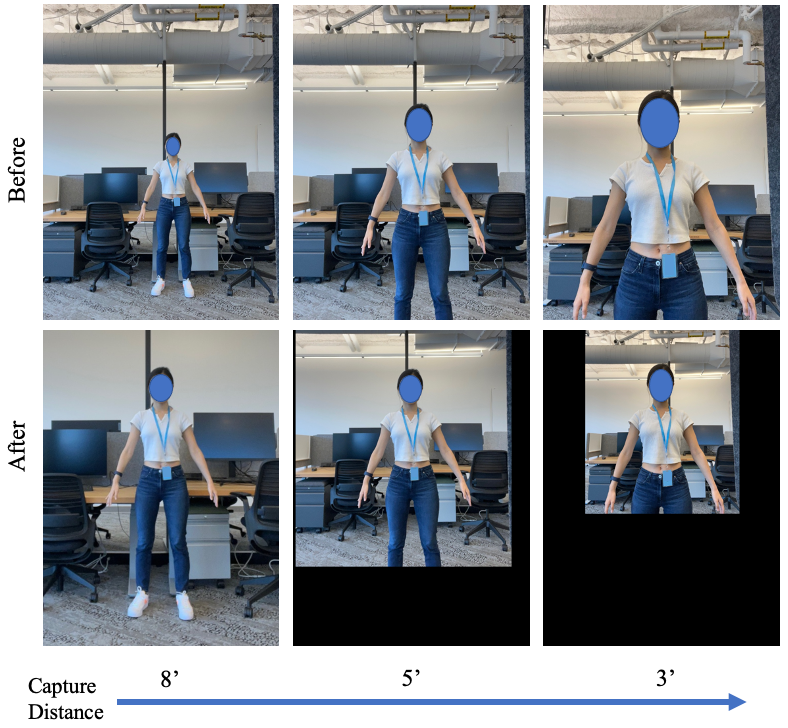
Virtual try-on and product personalization have become increasingly important in modern online shopping, highlighting the need for accurate body measurement estimation. Although previous research has advanced in estimating 3D body shapes from RGB images, the task is inherently ambiguous as the observed scale of human subjects in the images depends on two unknown factors: capture distance and body dimensions. This ambiguity is particularly pronounced in partial-view scenarios. To address this challenge, we propose a modular and simple height normalization solution. This solution relocates the subject skeleton to the desired position, thereby normalizing the scale and disentangling the relationship between the two variables. Our experimental results demonstrate that integrating this technique into state-of-the-art human mesh reconstruction models significantly enhances partial body measurement estimation. Additionally, we illustrate the applicability of this approach to multi-view settings, showcasing its versatility.
4/17/2024

SMPLX-Lite: A Realistic and Drivable Avatar Benchmark with Rich Geometry and Texture Annotations
Yujiao Jiang, Qingmin Liao, Zhaolong Wang, Xiangru Lin, Zongqing Lu, Yuxi Zhao, Hanqing Wei, Jingrui Ye, Yu Zhang, Zhijing Shao

0
0
Recovering photorealistic and drivable full-body avatars is crucial for numerous applications, including virtual reality, 3D games, and tele-presence. Most methods, whether reconstruction or generation, require large numbers of human motion sequences and corresponding textured meshes. To easily learn a drivable avatar, a reasonable parametric body model with unified topology is paramount. However, existing human body datasets either have images or textured models and lack parametric models which fit clothes well. We propose a new parametric model SMPLX-Lite-D, which can fit detailed geometry of the scanned mesh while maintaining stable geometry in the face, hand and foot regions. We present SMPLX-Lite dataset, the most comprehensive clothing avatar dataset with multi-view RGB sequences, keypoints annotations, textured scanned meshes, and textured SMPLX-Lite-D models. With the SMPLX-Lite dataset, we train a conditional variational autoencoder model that takes human pose and facial keypoints as input, and generates a photorealistic drivable human avatar.
5/31/2024
Gaussian Head & Shoulders: High Fidelity Neural Upper Body Avatars with Anchor Gaussian Guided Texture Warping
Tianhao Wu, Jing Yang, Zhilin Guo, Jingyi Wan, Fangcheng Zhong, Cengiz Oztireli

0
0
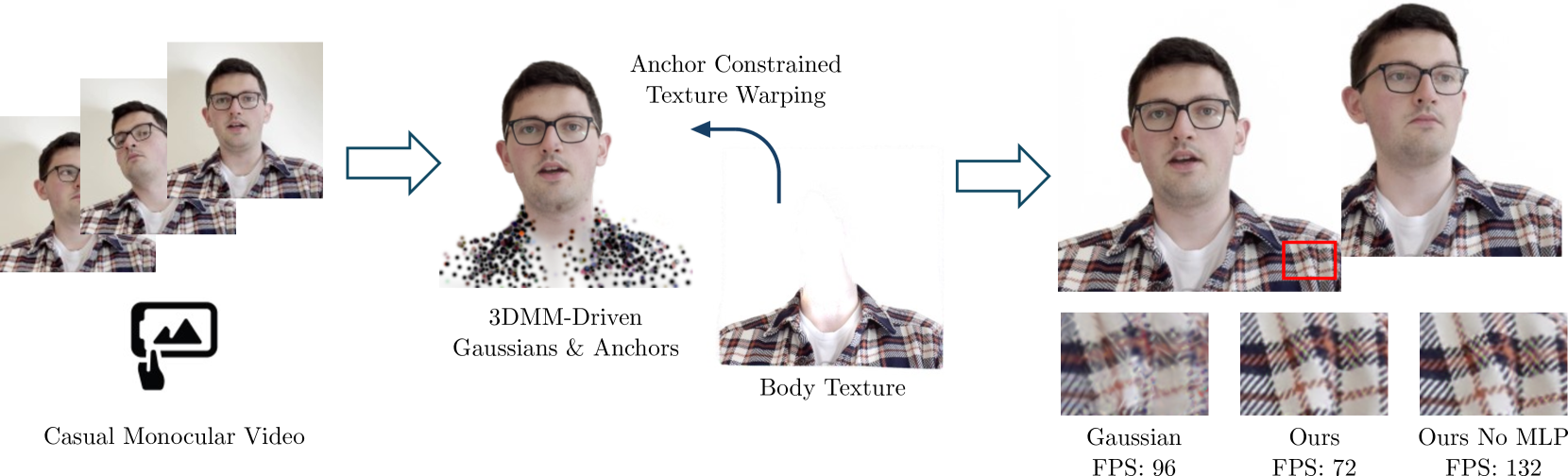
By equipping the most recent 3D Gaussian Splatting representation with head 3D morphable models (3DMM), existing methods manage to create head avatars with high fidelity. However, most existing methods only reconstruct a head without the body, substantially limiting their application scenarios. We found that naively applying Gaussians to model the clothed chest and shoulders tends to result in blurry reconstruction and noisy floaters under novel poses. This is because of the fundamental limitation of Gaussians and point clouds -- each Gaussian or point can only have a single directional radiance without spatial variance, therefore an unnecessarily large number of them is required to represent complicated spatially varying texture, even for simple geometry. In contrast, we propose to model the body part with a neural texture that consists of coarse and pose-dependent fine colors. To properly render the body texture for each view and pose without accurate geometry nor UV mapping, we optimize another sparse set of Gaussians as anchors that constrain the neural warping field that maps image plane coordinates to the texture space. We demonstrate that Gaussian Head & Shoulders can fit the high-frequency details on the clothed upper body with high fidelity and potentially improve the accuracy and fidelity of the head region. We evaluate our method with casual phone-captured and internet videos and show our method archives superior reconstruction quality and robustness in both self and cross reenactment tasks. To fully utilize the efficient rendering speed of Gaussian splatting, we additionally propose an accelerated inference method of our trained model without Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) queries and reach a stable rendering speed of around 130 FPS for any subjects.
5/22/2024
Self-Avatar Animation in Virtual Reality: Impact of Motion Signals Artifacts on the Full-Body Pose Reconstruction
Antoine Maiorca, Seyed Abolfazl Ghasemzadeh, Thierry Ravet, Franc{c}ois Cresson, Thierry Dutoit, Christophe De Vleeschouwer

0
0
Virtual Reality (VR) applications have revolutionized user experiences by immersing individuals in interactive 3D environments. These environments find applications in numerous fields, including healthcare, education, or architecture. A significant aspect of VR is the inclusion of self-avatars, representing users within the virtual world, which enhances interaction and embodiment. However, generating lifelike full-body self-avatar animations remains challenging, particularly in consumer-grade VR systems, where lower-body tracking is often absent. One method to tackle this problem is by providing an external source of motion information that includes lower body information such as full Cartesian positions estimated from RGB(D) cameras. Nevertheless, the limitations of these systems are multiples: the desynchronization between the two motion sources and occlusions are examples of significant issues that hinder the implementations of such systems. In this paper, we aim to measure the impact on the reconstruction of the articulated self-avatar's full-body pose of (1) the latency between the VR motion features and estimated positions, (2) the data acquisition rate, (3) occlusions, and (4) the inaccuracy of the position estimation algorithm. In addition, we analyze the motion reconstruction errors using ground truth and 3D Cartesian coordinates estimated from textit{YOLOv8} pose estimation. These analyzes show that the studied methods are significantly sensitive to any degradation tested, especially regarding the velocity reconstruction error.
4/30/2024