Vision-based FDM Printing for Fabricating Airtight Soft Actuators
2312.01135

0
0

Abstract
Pneumatic soft robots are typically fabricated by molding, a manual fabrication process that requires skilled labor. Additive manufacturing has the potential to break this limitation and speed up the fabrication process but struggles with consistently producing high-quality prints. We propose a low-cost approach to improve the print quality of desktop fused deposition modeling by adding a webcam to the printer to monitor the printing process and detect and correct defects such as holes or gaps. We demonstrate that our approach improves the air-tightness of printed pneumatic actuators without fine-tuning printing parameters. Our approach presents a new option for robustly fabricating airtight, soft robotic actuators.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents a novel vision-based approach for 3D printing airtight soft actuators using Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) technology.
- The proposed system combines real-time visual feedback and closed-loop control to fabricate customized soft actuators with precise control over their shape and internal air-tight structures.
- The research aims to address the challenges of achieving airtight seals and complex internal geometries when using traditional 3D printing methods for soft robotics.
Plain English Explanation
The researchers have developed a new way to 3D print soft robotic parts that can hold air inside without leaking. Traditional 3D printing methods often struggle to create airtight structures or complex internal designs needed for soft robots.
To solve this, the researchers used a camera to watch the 3D printing process in real-time and automatically adjust the printer to create the desired airtight shape. This vision-based feedback system allows for precise control over the final part, ensuring it can properly inflate and actuate without air leaks.
By combining this advanced printing technique with the flexibility of soft materials, the researchers were able to fabricate customized soft robotic actuators with intricate internal air pathways. This breakthrough could lead to the development of more capable and adaptable soft robots for a variety of applications, such as [link to https://aimodels.fyi/papers/arxiv/stretchable-pneumatic-sleeve-adaptable-low-displacement-anchoring]soft robotic grippers[/link] or [link to https://aimodels.fyi/papers/arxiv/novel-seamless-magnetic-based-actuating-mechanism-end]compliant robotic manipulators[/link].
Technical Explanation
The key innovation of this work is the use of real-time vision-based feedback and closed-loop control to enable Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D printing of airtight soft actuators.
The researchers first developed a print pre-processing step to generate custom toolpaths that can create the desired internal air chambers and seals. During printing, a camera monitors the extruded material and detects any air gaps or inconsistencies. A control system then dynamically adjusts the printer parameters, such as flow rate and speed, to ensure the printed structure remains airtight.
This closed-loop vision-based approach allows for precise control over the internal geometry, enabling the fabrication of soft actuators with intricate air pathways. The researchers demonstrated the capabilities of their system by printing a variety of soft robotic components, including [link to https://aimodels.fyi/papers/arxiv/femtosecond-laser-fabricated-nitinol-living-hinges-millimeter]compliant hinges[/link] and [link to https://aimodels.fyi/papers/arxiv/automated-machine-learning-approach-to-inkjet-printed]soft pneumatic chambers[/link].
Critical Analysis
The primary strength of this research is the ability to overcome the longstanding challenge of achieving airtight seals and complex internal structures when 3D printing soft robotic components. The vision-based closed-loop control system represents a significant advancement in the field of additive manufacturing for soft robotics.
However, the paper does not provide a comprehensive analysis of the limitations or potential issues with this approach. For example, the impact of printing speed, material properties, and part geometry on the reliability and repeatability of the airtight structures is not thoroughly explored. Additionally, the researchers do not address the scalability of their system or the feasibility of integrating it with existing 3D printing workflows.
Further research is needed to fully understand the capabilities and constraints of this vision-based FDM printing technique. Potential areas for improvement include [link to https://aimodels.fyi/papers/arxiv/differentiable-rendering-as-way-to-program-cable]incorporating more advanced computer vision algorithms[/link] to enhance the detection and correction of printing defects, as well as exploring the use of alternative soft material formulations to expand the range of printable soft robotic components.
Conclusion
The vision-based FDM printing approach presented in this paper represents a significant advancement in the field of additive manufacturing for soft robotics. By enabling the fabrication of airtight soft actuators with complex internal geometries, this research could pave the way for the development of more capable and adaptable soft robotic systems.
The demonstrated ability to precisely control the internal structure of printed soft components opens up new possibilities for designing and fabricating soft robotic devices with enhanced functionality and versatility. As the field of soft robotics continues to evolve, innovations like this vision-based printing technique will be crucial for unlocking the full potential of these compliant and adaptable systems.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🤖
Creation of Novel Soft Robot Designs using Generative AI
Wee Kiat Chan, PengWei Wang, Raye Chen-Hua Yeow

0
0
Soft robotics has emerged as a promising field with the potential to revolutionize industries such as healthcare and manufacturing. However, designing effective soft robots presents challenges, particularly in managing the complex interplay of material properties, structural design, and control strategies. Traditional design methods are often time-consuming and may not yield optimal designs. In this paper, we explore the use of generative AI to create 3D models of soft actuators. We create a dataset of over 70 text-shape pairings of soft pneumatic robot actuator designs, and adapt a latent diffusion model (SDFusion) to learn the data distribution and generate novel designs from it. By employing transfer learning and data augmentation techniques, we significantly improve the performance of the diffusion model. These findings highlight the potential of generative AI in designing complex soft robotic systems, paving the way for future advancements in the field.
5/6/2024

A Mobile Additive Manufacturing Robot Framework for Smart Manufacturing Systems
Yifei Li, Jeongwon Park, Guha Manogharan, Feng Ju, Ilya Kovalenko

0
0
Recent technological innovations in the areas of additive manufacturing and collaborative robotics have paved the way toward realizing the concept of on-demand, personalized production on the shop floor. Additive manufacturing process can provide the capability of printing highly customized parts based on various customer requirements. Autonomous, mobile systems provide the flexibility to move custom parts around the shop floor to various manufacturing operations, as needed by product requirements. In this work, we proposed a mobile additive manufacturing robot framework for merging an additive manufacturing process system with an autonomous mobile base. Two case studies showcase the potential benefits of the proposed mobile additive manufacturing framework. The first case study overviews the effect that a mobile system can have on a fused deposition modeling process. The second case study showcases how integrating a mobile additive manufacturing machine can improve the throughput of the manufacturing system. The major findings of this study are that the proposed mobile robotic AM has increased throughput by taking advantage of the travel time between operations/processing sites. It is particularly suited to perform intermittent operations (e.g., preparing feedstock) during the travel time of the robotic AM. One major implication of this study is its application in manufacturing structural components (e.g., concrete construction, and feedstock preparation during reconnaissance missions) in remote or extreme terrains with on-site or on-demand feedstocks.
4/22/2024

SPONGE: Open-Source Designs of Modular Articulated Soft Robots
Tim-Lukas Habich, Jonas Haack, Mehdi Belhadj, Dustin Lehmann, Thomas Seel, Moritz Schappler

0
0
Soft-robot designs are manifold, but only a few are publicly available. Often, these are only briefly described in their publications. This complicates reproduction, and hinders the reproducibility and comparability of research results. If the designs were uniform and open source, validating researched methods on real benchmark systems would be possible. To address this, we present two variants of a soft pneumatic robot with antagonistic bellows as open source. Starting from a semi-modular design with multiple cables and tubes routed through the robot body, the transition to a fully modular robot with integrated microvalves and serial communication is highlighted. Modularity in terms of stackability, actuation, and communication is achieved, which is the crucial requirement for building soft robots with many degrees of freedom and high dexterity for real-world tasks. Both systems are compared regarding their respective advantages and disadvantages. The robots' functionality is demonstrated in experiments on airtightness, gravitational influence, position control with mean tracking errors of <3 deg, and long-term operation of cast and printed bellows. All soft- and hardware files required for reproduction are provided.
4/17/2024
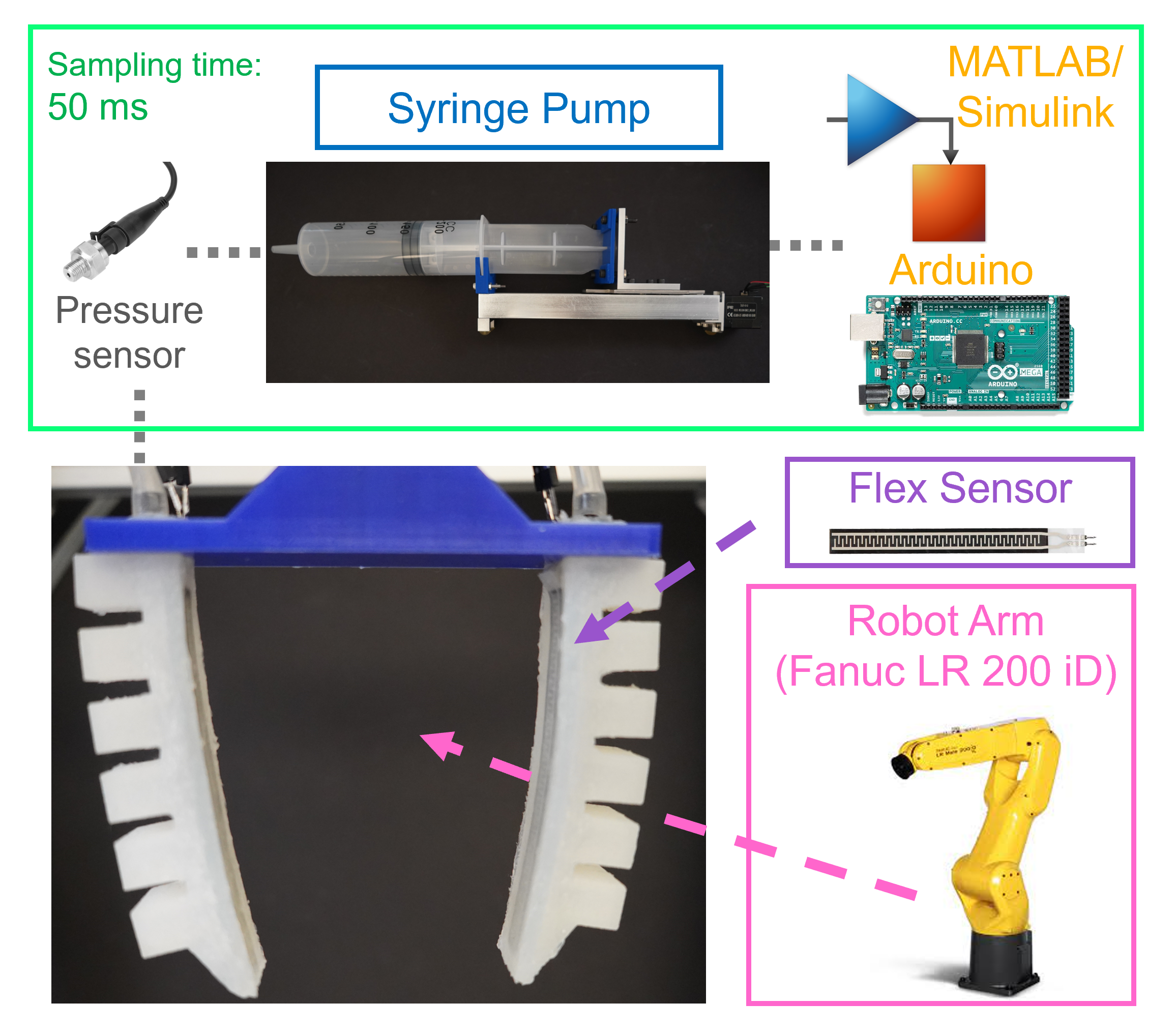
Underactuated Control of Multiple Soft Pneumatic Actuators via Stable Inversion
Wu-Te Yang, Burak Kurkcu, Masayoshi Tomizuka

0
0
Soft grippers, with their inherent compliance and adaptability, show advantages for delicate and versatile manipulation tasks in robotics. This paper presents a novel approach to underactuated control of multiple soft actuators, specifically focusing on the synchronization of soft fingers within a soft gripper. Utilizing a single syringe pump as the actuation mechanism, we address the challenge of coordinating multiple degrees of freedom of a compliant system. The theoretical framework applies concepts from stable inversion theory, adapting them to the unique dynamics of the underactuated soft gripper. Through meticulous mechatronic system design and controller synthesis, we demonstrate both in simulation and experimentation the efficacy and applicability of our approach in achieving precise and synchronized manipulation tasks. Our findings not only contribute to the advancement of soft robot control but also offer practical insights into the design and control of underactuated systems for real-world applications.
6/10/2024