Vulnerable Road User Detection and Safety Enhancement: A Comprehensive Survey
2405.19202

0
0
🔎
Abstract
Traffic incidents involving vulnerable road users (VRUs) constitute a significant proportion of global road accidents. Advances in traffic communication ecosystems, coupled with sophisticated signal processing and machine learning techniques, have facilitated the utilization of data from diverse sensors. Despite these advancements and the availability of extensive datasets, substantial progress is required to mitigate traffic casualties. This paper provides a comprehensive survey of state-of-the-art technologies and methodologies to enhance the safety of VRUs. The study delves into the communication networks between vehicles and VRUs, emphasizing the integration of advanced sensors and the availability of relevant datasets. It explores preprocessing techniques and data fusion methods to enhance sensor data quality. Furthermore, our study assesses critical simulation environments essential for developing and testing VRU safety systems. Our research also highlights recent advances in VRU detection and classification algorithms, addressing challenges such as variable environmental conditions. Additionally, we cover cutting-edge research in predicting VRU intentions and behaviors, which is crucial for proactive collision avoidance strategies. Through this survey, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current landscape of VRU safety technologies, identifying areas of progress and areas needing further research and development.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper provides a comprehensive survey of state-of-the-art technologies and methodologies to enhance the safety of vulnerable road users (VRUs).
- It explores the communication networks between vehicles and VRUs, the integration of advanced sensors, and the availability of relevant datasets.
- The study also covers preprocessing techniques, data fusion methods, simulation environments, VRU detection and classification algorithms, and research on predicting VRU intentions and behaviors.
Plain English Explanation
The paper focuses on improving the safety of vulnerable road users, such as pedestrians, cyclists, and motorcyclists, who are at a higher risk of being involved in traffic accidents. Advances in technology, including communication systems between vehicles and VRUs, as well as sophisticated signal processing and machine learning techniques, have opened up new possibilities for enhancing VRU safety.
The researchers reviewed the latest developments in this field, including how data from various sensors can be used to better detect and understand the movements and intentions of VRUs. This information is crucial for developing proactive collision avoidance strategies and improving overall road safety. The paper also discusses the importance of simulation environments for testing and refining VRU safety systems before deploying them in the real world.
By providing a comprehensive overview of the current state of VRU safety technologies, the researchers aim to identify areas of progress and highlight the need for further research and development to mitigate traffic casualties involving vulnerable road users.
Technical Explanation
The paper examines the use of communication networks between vehicles and VRUs, as well as the integration of advanced sensors, to gather data that can be used to enhance VRU safety. The researchers discuss preprocessing techniques and data fusion methods to improve the quality of sensor data.
The study also evaluates critical simulation environments that are essential for developing and testing VRU safety systems. The researchers then explore recent advancements in VRU detection and classification algorithms, which aim to address challenges such as variable environmental conditions.
Additionally, the paper covers cutting-edge research on predicting VRU intentions and behaviors, which is crucial for implementing proactive collision avoidance strategies.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive overview of the current landscape of VRU safety technologies, highlighting areas of progress and identifying gaps that require further research and development. While the researchers have covered a wide range of topics, they acknowledge the need for continued improvement in areas such as sensor reliability, data fusion algorithms, and the accuracy of VRU intention prediction models.
One potential limitation of the study is the reliance on simulation environments, as real-world conditions may present additional challenges that are not fully captured in the simulations. Researchers may need to explore more extensive field testing and data collection to validate the effectiveness of the proposed solutions in real-world scenarios.
Additionally, the paper does not delve deeply into the ethical implications of some of the technologies discussed, such as the potential privacy concerns associated with the collection and use of VRU data. Future research may need to address these societal considerations more explicitly.
Conclusion
This comprehensive survey provides a valuable overview of the current state of VRU safety technologies and the ongoing efforts to mitigate traffic casualties involving vulnerable road users. By highlighting the advancements in communication networks, sensor integration, data processing, and predictive algorithms, the researchers have identified promising directions for future research and development.
The insights gained from this study can inform the design of more effective VRU safety systems, ultimately contributing to the broader goal of improving overall road safety and reducing the number of traffic-related injuries and fatalities. As technology continues to evolve, the researchers emphasize the importance of maintaining a holistic approach that considers the human factors, ethical implications, and real-world challenges in the deployment of these safety-enhancing solutions.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
⛏️
A Data-Driven Analysis of Vulnerable Road User Safety in Interaction with Connected Automated Vehicles
Edmir Xhoxhi, Vincent Albert Wolff

0
0
According to the World Health Organization, the involvement of Vulnerable Road Users (VRUs) in traffic accidents remains a significant concern, with VRUs accounting for over half of traffic fatalities. The increase of automation and connectivity levels of vehicles has still an uncertain impact on VRU safety. By deploying the Collective Perception Service (CPS), vehicles can include information about VRUs in Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) messages, thus raising the general perception of the environment. Although an increased awareness is considered positive, one could argue that the awareness ratio, the metric used to measure perception, is only implicitly connected to the VRUs' safety. This paper introduces a tailored metric, the Risk Factor (RF), to measure the risk level for the interactions between Connected Automated Vehicles (CAVs) and VRUs. By evaluating the RF, we assess the impact of V2X communication on VRU risk mitigation. Our results show that high V2X penetration rates can reduce mean risk, quantified by our proposed metric, by up to 44%. Although the median risk value shows a significant decrease, suggesting a reduction in overall risk, the distribution of risk values reveals that CPS's mitigation effectiveness is overestimated, which is indicated by the divergence between RF and awareness ratio. Additionally, by analyzing a real-world traffic dataset, we pinpoint high-risk locations within a scenario, identifying areas near intersections and behind parked cars as especially dangerous. Our methodology can be ported and applied to other scenarios in order to identify high-risk areas. We value the proposed RF as an insightful metric for quantifying VRU safety in a highly automated and connected environment.
4/24/2024
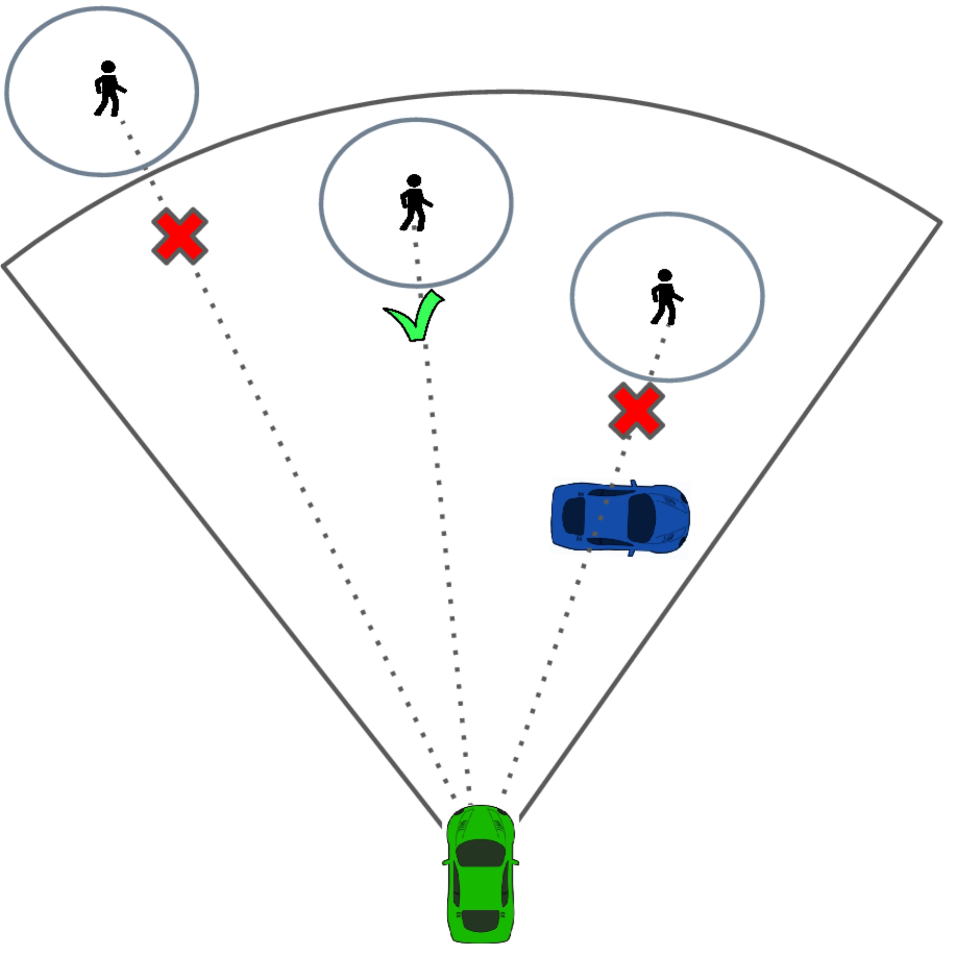
Mitigating Vulnerable Road Users Occlusion Risk Via Collective Perception: An Empirical Analysis
Vincent Albert Wolff, Edmir Xhoxhi

0
0
Recent reports from the World Health Organization highlight that Vulnerable Road Users (VRUs) have been involved in over half of the road fatalities in recent years, with occlusion risk - a scenario where VRUs are hidden from drivers' view by obstacles like parked vehicles - being a critical contributing factor. To address this, we present a novel algorithm that quantifies occlusion risk based on the dynamics of both vehicles and VRUs. This algorithm has undergone testing and evaluation using a real-world dataset from German intersections. Additionally, we introduce the concept of Maximum Tracking Loss (MTL), which measures the longest consecutive duration a VRU remains untracked by any vehicle in a given scenario. Our study extends to examining the role of the Collective Perception Service (CPS) in VRU safety. CPS enhances safety by enabling vehicles to share sensor information, thereby potentially reducing occlusion risks. Our analysis reveals that a 25% market penetration of CPS-equipped vehicles can substantially diminish occlusion risks and significantly curtail MTL. These findings demonstrate how various scenarios pose different levels of risk to VRUs and how the deployment of Collective Perception can markedly improve their safety. Furthermore, they underline the efficacy of our proposed metrics to capture occlusion risk as a safety factor.
4/12/2024
🧠
Cognitive Internet of Vulnerable Road Users in Traffic: Predictive Neural Modulations of Road Crossing Intention
Xiaoshan Zhou, Carol C. Menassa, Vineet R. Kamat

0
0
Vulnerable Road Users (VRUs) present a significant challenge for road safety due to the frequent unpredictability of their behaviors. In typical Intelligent Transportation Systems, vision-based approaches supported by networked cameras are often used to anticipate VRUs motion intentions and trajectories. However, several limitations posed by occlusions and distractions set a boundary for the efficacy of such methods. To address these challenges, this study introduces a framework that leverages data collected using wearable neurophysiological sensors on VRUs to integrate them seamlessly into the Vehicle-to-Everything communication framework. This integration empowers VRUs to autonomously broadcast their intended movements to other road agents, especially autonomous vehicles, thereby bridging a critical gap in current vehicular communication systems. To validate this concept, we conducted an experiment involving 12 participants, from whom EEG signals were collected as they engaged in road-crossing decisions within simulated environments. Employing Hidden Markov Models, we identified four cognitive stages intrinsic to a pedestrian's decision-making process. Our statistical analysis further revealed significant variations in EEG activities across these stages, shedding light on the neural correlates and cognitive dynamics underpinning pedestrian road-crossing behavior. We then developed a predictive cognitive model using dynamic time warping and K-nearest neighbors algorithms, optimized through a data-driven sliding window approach. This model demonstrated high predictive accuracy, evidenced by an Area Under the Curve of 0.91, indicating its capability to anticipate pedestrian road-crossing actions approximately 1 second in advance of any pedestrian movement. This research paves the way for a novel VRU-Vehicle interaction paradigm and signifies a shift towards a forward-thinking ecosystem.
5/24/2024
🔗
Vulnerable Road User Clustering for Collective Perception Messages: Efficient Representation Through Geometric Shapes
Edmir Xhoxhi, Vincent Albert Wolff, Yao Li, Florian Alexander Schiegg

0
0
Ensuring the safety of Vulnerable Road Users (VRUs) is a critical concern in transportation, demanding significant attention from researchers and engineers. Recent advancements in Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) technology offer promising solutions to enhance VRU safety. Notably, VRUs often travel in groups, exhibiting similar movement patterns that facilitate the formation of clusters. The standardized Collective Perception Message (CPM) and VRU Awareness Message in ETSI's Release 2 consider this clustering behavior, allowing for the description of VRU clusters. Given the constraints of narrow channel bandwidth, the selection of an appropriate geometric shape for representing a VRU cluster becomes crucial for efficient data transmission. In our study we conduct a comprehensive evaluation of different geometric shapes used to describe VRU clusters. We introduce two metrics: Cluster Accuracy (CA) and Comprehensive Area Density Information (CADI), to assess the precision and efficiency of each shape. Beyond comparing predefined shapes, we propose an adaptive algorithm that selects the preferred shape for cluster description, prioritizing accuracy while maintaining a high level of efficiency. The study culminates by demonstrating the benefits of clustering on data transmission rates. We simulate VRU movement using real-world data and the transmission of CPMs by a roadside unit. The results reveal that broadcasting cluster information, as opposed to individual object data, can reduce the data transmission volume by two-thirds on average. This finding underscores the potential of clustering in V2X communications to enhance VRU safety while optimizing network resources.
4/24/2024