xApp Distillation: AI-based Conflict Mitigation in B5G O-RAN

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents an AI-based approach called "xApp Distillation" for mitigating conflicts between different applications (xApps) in a Beyond 5G (B5G) Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) environment.
- The authors propose a reinforcement learning-based framework that allows xApps to learn from each other, distilling knowledge to resolve potential conflicts and optimize network performance.
- The system model includes an xApp controller that coordinates the interactions between xApps and facilitates the knowledge distillation process.
Plain English Explanation
In a B5G O-RAN system, multiple software applications called "xApps" work together to manage the network. However, these xApps may sometimes have conflicting goals or decisions, which can negatively impact the network's performance.
The researchers developed a novel approach called "xApp Distillation" to address this challenge. The key idea is to enable the xApps to learn from each other using reinforcement learning. An "xApp Controller" coordinates the interactions between the xApps and facilitates the knowledge distillation process.
Through this process, the xApps can learn from each other's experiences and decisions, and gradually optimize their own actions to avoid conflicts and improve overall network performance. This is similar to how students in a classroom can learn from each other's mistakes and successes to improve their own understanding and performance.
By implementing this AI-based conflict mitigation system, the researchers aim to make B5G O-RAN networks more robust, efficient, and adaptive to changing conditions, without requiring manual intervention or complex configuration changes.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a reinforcement learning-based framework for conflict mitigation between xApps in a B5G O-RAN environment. The proposed "xApp Distillation" approach leverages the concept of knowledge distillation, where the xApps learn from each other's experiences and decisions to optimize their own actions.
The system model includes an "xApp Controller" that serves as the central coordinator, facilitating the interactions and knowledge exchange between the xApps. The xApps are modeled as autonomous agents that make decisions based on their local observations and the information they receive from the xApp Controller.
The knowledge distillation process involves the xApps sharing their learned policies, which are then used by the xApp Controller to derive a "distilled policy" that represents the collective knowledge of the xApp ensemble. The xApps then update their own policies based on this distilled knowledge, allowing them to learn from each other's experiences and mitigate potential conflicts.
The authors evaluate the performance of the xApp Distillation framework through simulations, comparing it to other conflict mitigation approaches in terms of various metrics, such as network throughput, latency, and resource utilization. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach in resolving conflicts and improving overall network performance.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a well-designed and innovative approach to addressing the challenge of conflict mitigation in B5G O-RAN systems. The authors have carefully considered the system model and the interactions between the xApps, as well as the role of the xApp Controller in facilitating the knowledge distillation process.
One potential limitation of the research is the reliance on simulations for evaluating the proposed framework. While simulations can provide valuable insights, it would be beneficial to also validate the approach through real-world deployments or experiments to better understand its practicality and robustness in an operational environment.
Additionally, the paper does not delve into the potential security implications of the AI-based conflict mitigation system, such as the risk of adversarial attacks targeting the knowledge distillation process or the xApp Controller. Exploring these aspects could further strengthen the practical applicability of the proposed solution.
Overall, the xApp Distillation approach presents a promising direction for enhancing the flexibility, adaptability, and resilience of B5G O-RAN networks through the use of advanced AI techniques. Further research and real-world validation could help solidify the practical impact of this work.
Conclusion
The paper introduces an innovative AI-based approach called "xApp Distillation" for mitigating conflicts between xApps in a B5G O-RAN environment. By leveraging reinforcement learning and knowledge distillation, the proposed framework enables xApps to learn from each other's experiences and optimize their decisions to avoid conflicts and improve overall network performance.
The xApp Distillation approach demonstrates the potential of AI and machine learning techniques to enhance the flexibility, adaptability, and resilience of next-generation wireless networks. As the complexity and heterogeneity of O-RAN systems continue to grow, solutions like this could play a crucial role in ensuring the reliable and efficient operation of these critical infrastructure components.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
xApp Distillation: AI-based Conflict Mitigation in B5G O-RAN
Hakan Erdol, Xiaoyang Wang, Robert Piechocki, George Oikonomou, Arjun Parekh
The advancements of machine learning-based (ML) decision-making algorithms created various research and industrial opportunities. One of these areas is ML-based near-real-time network management applications (xApps) in Open-Radio Access Network (O-RAN). Normally, xApps are designed solely for the desired objectives, and fine-tuned for deployment. However, telecommunication companies can employ multiple xApps and deploy them in overlapping areas. Consider the different design objectives of xApps, the deployment might cause conflicts. To prevent such conflicts, we proposed the xApp distillation method that distills knowledge from multiple xApps, then uses this knowledge to train a single model that has retained the capabilities of Previous xApps. Performance evaluations show that compared conflict mitigation schemes can cause up to six times more network outages than xApp distillation in some cases.
Read more7/4/2024
👀

0
QACM: QoS-Aware xApp Conflict Mitigation in Open RAN
Abdul Wadud, Fatemeh Golpayegani, Nima Afraz
The advent of Open Radio Access Network (RAN) has revolutionized the field of RAN by introducing elements of native support of intelligence and openness into the next generation of mobile network infrastructure. Open RAN paves the way for standardized interfaces and enables the integration of network applications from diverse vendors, thereby enhancing network management flexibility. However, control decision conflicts occur when components from different vendors are deployed together. This article provides an overview of various types of conflicts that may occur in Open RAN, with a particular focus on intra-component conflict mitigation among Extended Applications (xApps) in the Near Real Time RAN Intelligent Controller (Near-RT-RIC). A QoS-Aware Conflict Mitigation (QACM) method is proposed that finds the optimal configuration of conflicting parameters while maximizing the number of xApps that have their Quality of Service (QoS) requirements met. We compare the performance of the proposed QACM method with two benchmark methods for priority and non-priority cases. The results indicate that our proposed method is the most effective in maintaining QoS requirements for conflicting xApps.
Read more5/14/2024
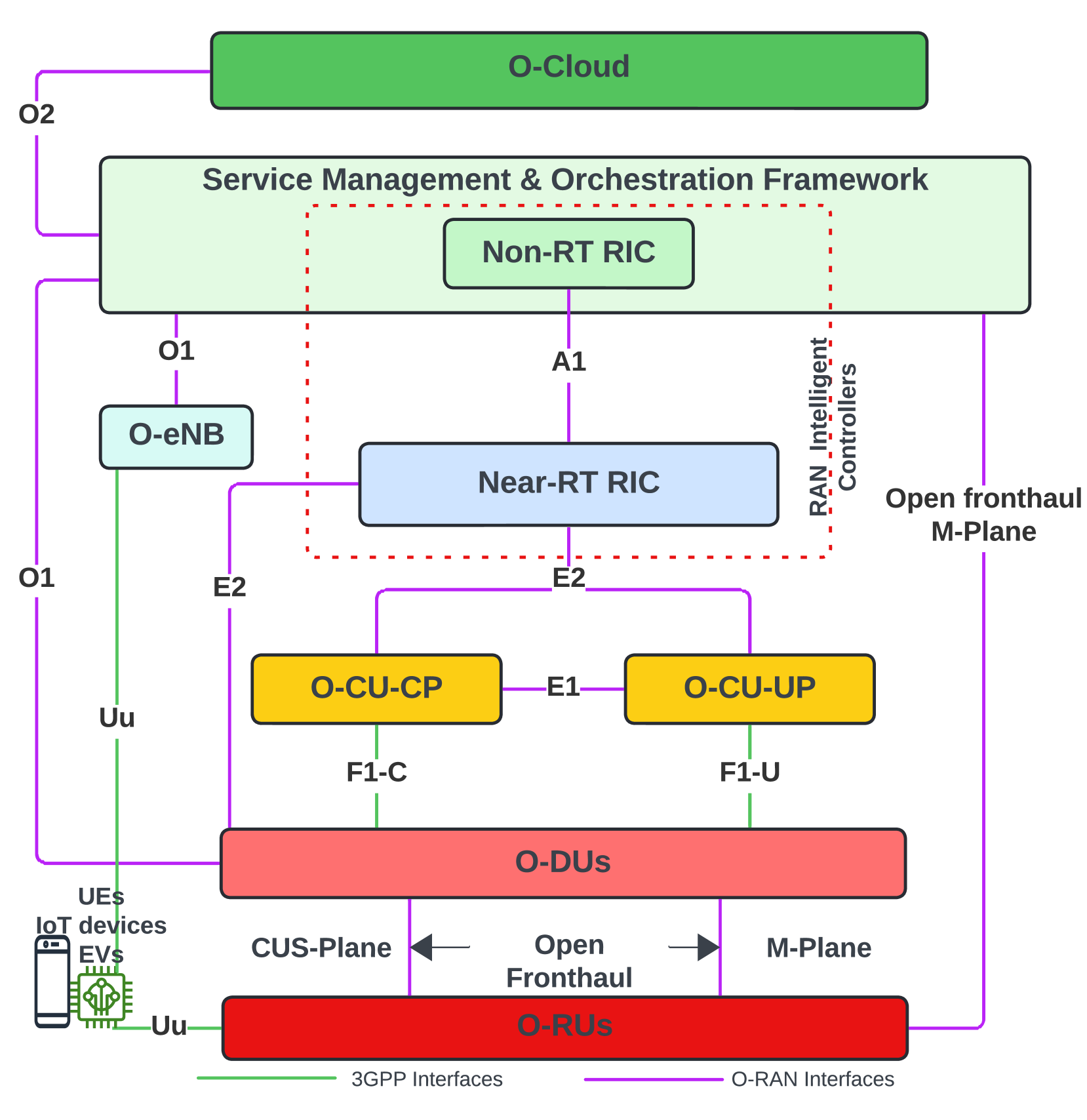

0
Exploiting and Securing ML Solutions in Near-RT RIC: A Perspective of an xApp
Thusitha Dayaratne, Viet Vo, Shangqi Lai, Sharif Abuadbba, Blake Haydon, Hajime Suzuki, Xingliang Yuan, Carsten Rudolph
Open Radio Access Networks (O-RAN) are emerging as a disruptive technology, revolutionising traditional mobile network architecture and deployments in the current 5G and the upcoming 6G era. Disaggregation of network architecture, inherent support for AI/ML workflows, cloud-native principles, scalability, and interoperability make O-RAN attractive to network providers for beyond-5G and 6G deployments. Notably, the ability to deploy custom applications, including Machine Learning (ML) solutions as xApps or rApps on the RAN Intelligent Controllers (RICs), has immense potential for network function and resource optimisation. However, the openness, nascent standards, and distributed architecture of O-RAN and RICs introduce numerous vulnerabilities exploitable through multiple attack vectors, which have not yet been fully explored. To address this gap and ensure robust systems before large-scale deployments, this work analyses the security of ML-based applications deployed on the RIC platform. We focus on potential attacks, defence mechanisms, and pave the way for future research towards a more robust RIC platform.
Read more6/19/2024
🏋️

0
PACIFISTA: Conflict Evaluation and Management in Open RAN
Pietro Brach del Prever, Salvatore D'Oro, Leonardo Bonati, Michele Polese, Maria Tsampazi, Heiko Lehmann, Tommaso Melodia
The O-RAN ALLIANCE is defining architectures, interfaces, operations, and security requirements for cellular networks based on Open Radio Access Network (RAN) principles. In this context, O-RAN introduced the RAN Intelligent Controllers (RICs) to enable dynamic control of cellular networks via data-driven applications referred to as rApps and xApps. RICs enable for the first time truly intelligent and self-organizing cellular networks. However, enabling the execution of many Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms taking autonomous control decisions to fulfill diverse (and possibly conflicting) goals poses unprecedented challenges. For instance, the execution of one xApp aiming at maximizing throughput and one aiming at minimizing energy consumption would inevitably result in diametrically opposed resource allocation strategies. Therefore, conflict management becomes a crucial component of any functional intelligent O-RAN system. This article studies the problem of conflict mitigation in O-RAN and proposes PACIFISTA, a framework to detect, characterize, and mitigate conflicts. PACIFISTA leverages a profiling pipeline to tests O-RAN applications in a sandbox environment, and combines hierarchical graphs with statistical models to detect the existence of conflicts and evaluate their severity. Experiments on Colosseum and OpenRAN Gym demonstrate PACIFISTA's ability to predict conflicts and provide valuable information before potentially conflicting xApps are deployed in production systems. We demonstrate that even O-RAN applications with similar goals can result in 16% throughput loss, and show how applications with conflicting goals might cause severe instability and result in up to 30% performance degradation. We also show that PACIFISTA can help operators to identify coexisting applications and maintain performance degradation below a tolerable threshold.
Read more5/8/2024