3D Guidance Law for Maximal Coverage and Target Enclosing with Inherent Safety
2404.16312

0
0
👨🏫
Abstract
In this paper, we address the problem of enclosing an arbitrarily moving target in three dimensions by a single pursuer, which is an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), for maximum coverage while also ensuring the pursuer's safety by preventing collisions with the target. The proposed guidance strategy steers the pursuer to a safe region of space surrounding the target, allowing it to maintain a certain distance from the latter while offering greater flexibility in positioning and converging to any orbit within this safe zone. Our approach is distinguished by the use of nonholonomic constraints to model vehicles with accelerations serving as control inputs and coupled engagement kinematics to craft the pursuer's guidance law meticulously. Furthermore, we leverage the concept of the Lyapunov Barrier Function as a powerful tool to constrain the distance between the pursuer and the target within asymmetric bounds, thereby ensuring the pursuer's safety within the predefined region. To validate the efficacy and robustness of our algorithm, we conduct experimental tests by implementing a high-fidelity quadrotor model within Software-in-the-loop (SITL) simulations, encompassing various challenging target maneuver scenarios. The results obtained showcase the resilience of the proposed guidance law, effectively handling arbitrarily maneuvering targets, vehicle/autopilot dynamics, and external disturbances. Our method consistently delivers stable global enclosing behaviors, even in response to aggressive target maneuvers, and requires only relative information for successful execution.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper addresses the problem of a single unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) pursuer enclosing an arbitrarily moving target in 3D space while ensuring the pursuer's safety and preventing collisions.
- The proposed guidance strategy steers the pursuer to a safe region surrounding the target, allowing it to maintain a certain distance while offering flexibility in positioning and converging to any orbit within this safe zone.
- The approach uses nonholonomic constraints to model vehicle dynamics and coupled engagement kinematics to craft the pursuer's guidance law.
- The Lyapunov Barrier Function is leveraged to constrain the distance between the pursuer and target within asymmetric bounds, ensuring the pursuer's safety.
- Experimental tests are conducted using a high-fidelity quadrotor model in Software-in-the-loop (SITL) simulations, validating the efficacy and robustness of the algorithm in various challenging target maneuver scenarios.
Plain English Explanation
The paper presents a method for a single unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) to track and enclose an arbitrarily moving target in 3D space. The key goal is to keep the UAV at a safe distance from the target while maintaining flexibility in positioning and allowing the UAV to orbit around the target.
The researchers use a special mathematical model to represent the vehicle's dynamic constraints, such as its acceleration and turning capabilities. They also carefully design the UAV's guidance algorithm to take into account the relative position and movement of the target.
Importantly, the researchers employ a powerful mathematical tool called the Lyapunov Barrier Function to ensure the UAV stays within a predefined safe distance from the target, preventing collisions. This allows the UAV to confidently and reliably track the target, even when it is making unpredictable or aggressive maneuvers.
To test the effectiveness of their approach, the researchers implement a high-fidelity simulation of a quadrotor UAV and conduct various experiments, including scenarios with external disturbances. The results show the resilience and stability of the proposed guidance method, which can successfully enclose the target using only information about its relative position and movement.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a guidance strategy for a single unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) to enclose an arbitrarily moving 3D target while ensuring the pursuer's safety and preventing collisions. The proposed approach leverages nonholonomic constraints to model the vehicle dynamics, with accelerations serving as control inputs, and coupled engagement kinematics to craft the pursuer's guidance law.
A key innovation is the use of the Lyapunov Barrier Function, a powerful mathematical tool, to constrain the distance between the pursuer and the target within asymmetric bounds. This ensures the pursuer's safety within a predefined region surrounding the target, allowing for greater flexibility in positioning and convergence to any orbit within this safe zone.
To validate the efficacy and robustness of the algorithm, the researchers conduct experimental tests by implementing a high-fidelity quadrotor model within Software-in-the-loop (SITL) simulations. These simulations encompass various challenging target maneuver scenarios, including aggressive movements and external disturbances. The results demonstrate the resilience and stability of the proposed guidance law, which can effectively handle arbitrarily maneuvering targets while consistently delivering stable global enclosing behaviors.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a comprehensive and well-designed approach to the problem of a single UAV enclosing an arbitrarily moving 3D target while ensuring the pursuer's safety. The use of nonholonomic constraints and coupled engagement kinematics to model the vehicle dynamics and craft the guidance law is a thoughtful and technically sound approach.
The incorporation of the Lyapunov Barrier Function to constrain the distance between the pursuer and target is a particularly innovative aspect of the research, as it provides a robust and reliable method for maintaining the UAV within a predefined safe zone. This addresses a crucial practical concern for real-world implementation, as it helps prevent collisions and ensures the pursuer's safety.
The extensive experimental testing using a high-fidelity quadrotor simulation lends strong credibility to the proposed approach, as it demonstrates the algorithm's ability to handle a variety of challenging target maneuver scenarios, including external disturbances.
However, the paper does not discuss any potential limitations or caveats of the proposed method. For example, it would be helpful to understand the computational complexity of the algorithm and its implications for real-time implementation on resource-constrained UAV platforms. Additionally, the paper does not explore the algorithm's performance in the presence of sensor noise or other practical considerations that may arise in real-world deployments.
Conclusion
This paper presents a robust and innovative guidance strategy for a single UAV to enclose an arbitrarily moving 3D target while ensuring the pursuer's safety and preventing collisions. The key contributions include the use of nonholonomic constraints and coupled engagement kinematics to model the vehicle dynamics, as well as the leveraging of the Lyapunov Barrier Function to constrain the distance between the pursuer and target.
The extensive experimental testing conducted using a high-fidelity quadrotor simulation demonstrates the resilience and stability of the proposed guidance law, which can effectively handle aggressive target maneuvers and external disturbances. This research represents a significant advancement in the field of autonomous UAV target enclosure and pursuit, with potential applications in areas such as search and rescue, surveillance, and environmental monitoring.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Self-organizing Multiagent Target Enclosing under Limited Information and Safety Guarantees
Praveen Kumar Ranjan, Abhinav Sinha, Yongcan Cao

0
0
This paper introduces an approach to address the target enclosing problem using non-holonomic multiagent systems, where agents autonomously self-organize themselves in the desired formation around a fixed target. Our approach combines global enclosing behavior and local collision avoidance mechanisms by devising a novel potential function and sliding manifold. In our approach, agents independently move toward the desired enclosing geometry when apart and activate the collision avoidance mechanism when a collision is imminent, thereby guaranteeing inter-agent safety. We rigorously show that an agent does not need to ensure safety with every other agent and put forth a concept of the nearest colliding agent (for any arbitrary agent) with whom ensuring safety is sufficient to avoid collisions in the entire swarm. The proposed control eliminates the need for a fixed or pre-established agent arrangement around the target and requires only relative information between an agent and the target. This makes our design particularly appealing for scenarios with limited global information, hence significantly reducing communication requirements. We finally present simulation results to vindicate the efficacy of the proposed method.
4/9/2024

Adaptive Line-Of-Sight guidance law based on vector fields path following for underactuated unmanned surface vehicle
Jie Qi, Ronghua Wanga, Nailong Wu

0
0
The focus of this paper is to develop a methodology that enables an unmanned surface vehicle (USV) to efficiently track a planned path. The introduction of a vector field-based adaptive line of-sight guidance law (VFALOS) for accurate trajectory tracking and minimizing the overshoot response time during USV tracking of curved paths improves the overall line-of-sight (LOS) guidance method. These improvements contribute to faster convergence to the desired path, reduce oscillations, and can mitigate the effects of persistent external disturbances. It is shown that the proposed guidance law exhibits k-exponential stability when converging to the desired path consisting of straight and curved lines. The results in the paper show that the proposed method effectively improves the accuracy of the USV tracking the desired path while ensuring the safety of the USV work.
4/8/2024
🖼️
Towards Safe Mid-Air Drone Interception: Strategies for Tracking & Capture
Michal Pliska, Matouv{s} Vrba, Tom'av{s} B'av{c}a, Martin Saska

0
0
A unique approach for the mid-air autonomous aerial interception of non-cooperating UAV by a flying robot equipped with a net is presented in this paper. A novel interception guidance method dubbed EPN is proposed, designed to catch agile maneuvering targets while relying on onboard state estimation and tracking. The proposed method is compared with state-of-the-art approaches in simulations using 100 different trajectories of the target with varying complexity comprising almost 14 hours of flight data, and EPN demonstrates the shortest response time and the highest number of interceptions, which are key parameters of agile interception. To enable robust transfer from theory and simulation to a real-world implementation, we aim to avoid overfitting to specific assumptions about the target, and to tackle interception of a target following an unknown general trajectory. Furthermore, we identify several often overlooked problems related to tracking and estimation of the target's state that can have a significant influence on the overall performance of the system. We propose the use of a novel state estimation filter based on the IMM filter and a new measurement model. Simulated experiments show that the proposed solution provides significant improvements in estimation accuracy over the commonly employed KF approaches when considering general trajectories. Based on these results, we employ the proposed filtering and guidance methods to implement a complete autonomous interception system, which is thoroughly evaluated in realistic simulations and tested in real-world experiments with a maneuvering target going far beyond the performance of any state-of-the-art solution.
5/24/2024
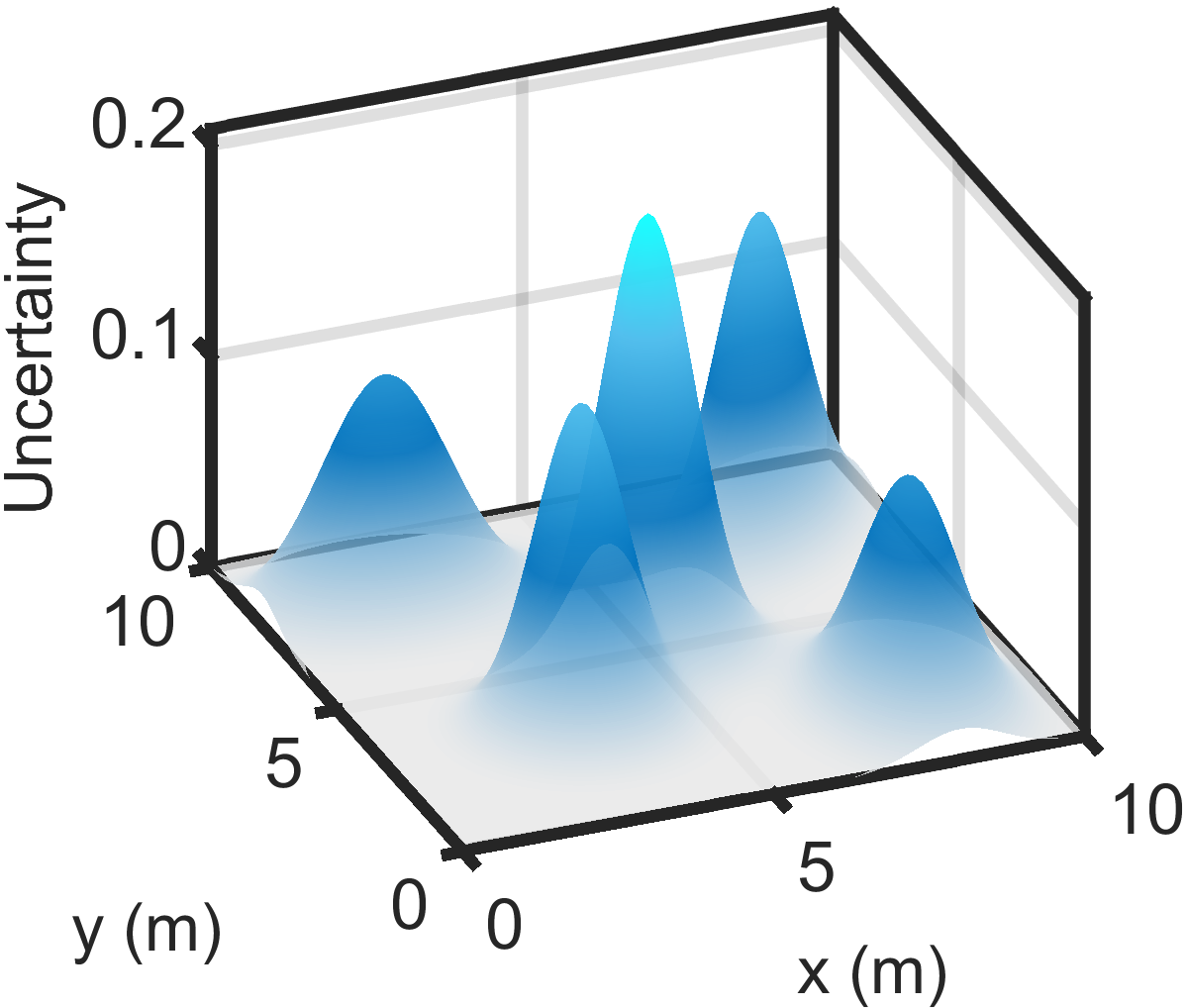
Model-Predictive Trajectory Generation for Autonomous Aerial Search and Coverage
Hugo Matias, Daniel Silvestre

0
0
This paper addresses the trajectory planning problem for search and coverage missions with an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV). The objective is to devise optimal coverage trajectories based on a utility map describing prior region information, assumed to be effectively approximated by a Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM). We introduce a Model Predictive Control (MPC) algorithm employing a relaxed formulation that promotes the exploration of the map by preventing the UAV from revisiting previously covered areas. This is achieved by penalizing intersections between the UAV's visibility regions along its trajectory. The algorithm is assessed in MATLAB and validated in Gazebo, as well as in outdoor experimental tests. The results show that the proposed strategy can generate efficient and smooth trajectories for search and coverage missions.
4/8/2024