6GSoft: Software for Edge-to-Cloud Continuum

0
📉
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper introduces 6GSoft, a software platform for the edge-to-cloud continuum in 6G networks.
- The platform aims to address key challenges in 6G, including sustainability, scalability, and energy efficiency.
- The paper describes the consortium behind 6GSoft and its approach to software engineering for collective cyber-physical ecosystems.
Plain English Explanation
6GSoft is a software platform designed to support the seamless integration of devices and services across the edge-to-cloud continuum in 6G networks. The platform is being developed by a consortium of researchers and industry partners who are working to address the key challenges facing 6G networks, such as sustainability, scalability, and energy efficiency.
The 6GSoft platform aims to provide a comprehensive software solution that can help organizations and developers build, deploy, and manage applications and services across the entire edge-to-cloud spectrum. By leveraging the latest advancements in integrated sensing, communication, and computation at the edge and AI-powered network security, the platform promises to enable more efficient, sustainable, and secure 6G networks.
Technical Explanation
The 6GSoft platform is being developed by a consortium of researchers and industry partners with expertise in areas such as software engineering, cyber-physical systems, and 6G network architecture. The platform is designed to address the challenges of building and deploying applications and services across the edge-to-cloud continuum, which is expected to be a key feature of 6G networks.
The platform incorporates several key components, including:
- Edge Computing Infrastructure: Provides the necessary hardware and software frameworks for deploying and managing edge computing resources, such as sensors, gateways, and micro-data centers.
- Cloud-to-Edge Orchestration: Facilitates the seamless integration and coordination of resources across the edge-to-cloud spectrum, enabling efficient task offloading and data processing.
- Distributed AI/ML Frameworks: Supports the deployment and management of AI and machine learning models at the edge, enhancing local decision-making and reducing the need for constant cloud connectivity.
- Sustainability and Energy Optimization: Implements strategies for reducing the energy footprint and environmental impact of the 6G network, including dynamic resource allocation and power management.
- Secure and Resilient Architecture: Incorporates advanced security measures, such as AI-powered network security, to protect the 6G ecosystem from cyber threats and ensure the reliability of critical applications and services.
The 6GSoft platform is being developed using a software engineering approach that emphasizes the creation of collective cyber-physical ecosystems, where hardware and software components seamlessly interact to deliver a cohesive and efficient 6G experience.
Critical Analysis
The 6GSoft platform addresses several key challenges facing 6G networks, including sustainability, scalability, and energy efficiency. By integrating edge computing, cloud-to-edge orchestration, and distributed AI/ML frameworks, the platform aims to enable more efficient and sustainable 6G deployments.
However, the paper does not provide a detailed evaluation of the platform's performance or a comprehensive assessment of its limitations. It would be helpful to see more information on the platform's scalability, the accuracy and reliability of its AI/ML models, and the effectiveness of its energy optimization strategies.
Additionally, the paper does not discuss the potential security and privacy implications of the 6GSoft platform, particularly in the context of the large-scale integration of edge devices and the distribution of AI/ML models across the network. Further research may be needed to address these concerns and ensure the overall trustworthiness of the 6GSoft ecosystem.
Conclusion
The 6GSoft platform represents a promising approach to addressing the challenges of building and deploying applications and services across the edge-to-cloud continuum in 6G networks. By incorporating advanced technologies such as edge computing, distributed AI/ML, and energy optimization, the platform aims to enable more sustainable, scalable, and efficient 6G deployments.
As 6G networks continue to evolve, the 6GSoft platform and similar software solutions will play a crucial role in shaping the future of the edge-to-cloud continuum, with potential implications for a wide range of industries and applications.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
📉

0
6GSoft: Software for Edge-to-Cloud Continuum
Muhammad Azeem Akbar, Matteo Esposito, Sami Hyrynsalmi, Karthikeyan Dinesh Kumar, Valentina Lenarduzzi, Xiaozhou Li, Ali Mehraj, Tommi Mikkonen, Sergio Moreschini, Niko Makitalo, Markku Oivo, Anna-Sofia Paavonen, Risha Parveen, Kari Smolander, Ruoyu Su, Kari Systa, Davide Taibi, Nan Yang, Zheying Zhang, Muhammad Zohaib
In the era of 6G, developing and managing software requires cutting-edge software engineering (SE) theories and practices tailored for such complexity across a vast number of connected edge devices. Our project aims to lead the development of sustainable methods and energy-efficient orchestration models specifically for edge environments, enhancing architectural support driven by AI for contemporary edge-to-cloud continuum computing. This initiative seeks to position Finland at the forefront of the 6G landscape, focusing on sophisticated edge orchestration and robust software architectures to optimize the performance and scalability of edge networks. Collaborating with leading Finnish universities and companies, the project emphasizes deep industry-academia collaboration and international expertise to address critical challenges in edge orchestration and software architecture, aiming to drive significant advancements in software productivity and market impact.
Read more7/10/2024


0
Discovery of 6G Services and Resources in Edge-Cloud-Continuum
Mohammad Farhoudi, Masoud Shokrnezhad, Tarik Taleb, Richard Li, JaeSeung Song
The advent of 6G networks will present a pivotal juncture in the evolution of telecommunications, marked by the proliferation of devices, dynamic service requests, and the integration of edge and cloud computing. In response to these transformative shifts, this paper proposes a service and resource discovery architecture as part of service provisioning for the future 6G edge-cloud-continuum. Through the architecture's orchestration and platform components, users will have access to services efficiently and on time. Blockchain underpins trust in this inherently trustless environment, while semantic networking dynamically extracts context from service requests, fostering efficient communication and service delivery. A key innovation lies in dynamic overlay zoning, which not only optimizes resource allocation but also endows our architecture with scalability, adaptability, and resilience. Notably, our architecture excels at predictive capabilities, harnessing learning algorithms to anticipate user and service instance behavior, thereby enhancing network responsiveness and preserving service continuity. This comprehensive architecture paves the way for unparalleled resource optimization, latency reduction, and seamless service delivery, positioning it as an instrumental pillar in the unfolding 6G landscape. Simulation results show that our architecture provides near-optimal timely responses that significantly improve the network's potential, offering scalable and efficient service and resource discovery.
Read more8/1/2024
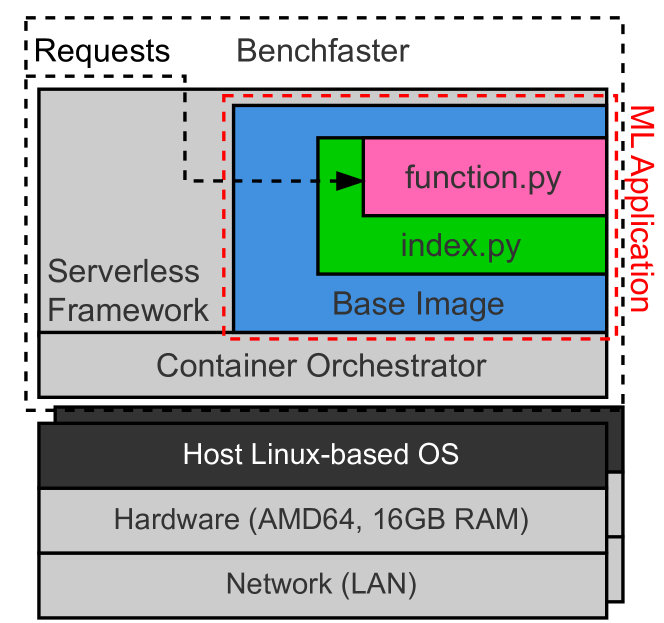

0
Deploying AI-Based Applications with Serverless Computing in 6G Networks: An Experimental Study
Marc Michalke, Chukwuemeka Muonagor, Admela Jukan
Future 6G networks are expected to heavily utilize machine learning capabilities in a wide variety of applications with features and benefits for both, the end user and the provider. While the options for utilizing these technologies are almost endless, from the perspective of network architecture and standardized service, the deployment decisions on where to execute the AI-tasks are critical, especially when considering the dynamic and heterogeneous nature of processing and connectivity capability of 6G networks. On the other hand, conceptual and standardization work is still in its infancy, as to how to categorizes ML applications in 6G landscapes; some of them are part of network management functions, some target the inference itself, while many others emphasize model training. It is likely that future mobile services may all be in the AI domain, or combined with AI. This work makes a case for the serverless computing paradigm to be used to this end. We first provide an overview of different machine learning applications that are expected to be relevant in 6G networks. We then create a set of general requirements for software engineering solutions executing these workloads from them and propose and implement a high-level edge-focused architecture to execute such tasks. We then map the ML-serverless paradigm to the case study of 6G architecture and test the resulting performance experimentally for a machine learning application against a setup created in a more traditional, cloud-based manner. Our results show that, while there is a trade-off in predictability of the response times and the accuracy, the achieved median accuracy in a 6G setup remains the same, while the median response time decreases by around 25% compared to the cloud setup.
Read more7/2/2024


0
Edge-Cloud Continuum Orchestration of Critical Services: A Smart-City Approach
Rodrigo Rosmaninho, Duarte Raposo, Pedro Rito, Susana Sargento
Smart-city services are typically developed as closed systems within each city's vertical, communicating and interacting with cloud services while remaining isolated within each provider's domain. With the emergence of 5G private domains and the introduction of new M2M services focusing on autonomous systems, there is a shift from the cloud-based approach to a distributed edge computing paradigm, in a textit{continuum} orchestration. However, an essential component is missing. Current orchestration tools, designed for cloud-based deployments, lack robust workload isolation, fail to meet timing constraints, and are not tailored to the resource-constrained nature of edge devices. Therefore, new orchestration methods are needed to support MEC environments. The work presented in this paper addresses this gap. Based on the real needs of a smart-city testbed - the Aveiro Living Lab-, we developed a set of orchestration components to facilitate the seamless orchestration of both cloud and edge-based services, encompassing both critical and non-critical services. This work extends the current Kubernetes orchestration platform to include a novel location-specific resource definition, a custom scheduler to accommodate real-time and legacy services, continuous service monitoring to detect sub-optimal states, and a refined load balancing mechanism that prioritizes the fastest response times.
Read more7/25/2024