Edge-Cloud Continuum Orchestration of Critical Services: A Smart-City Approach

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Proposes an edge-cloud continuum orchestration approach for critical services in smart cities
- Leverages edge computing, cloud computing, and 5G technologies to provide real-time, resilient, and scalable services
- Focuses on orchestrating the deployment and management of mission-critical applications across the edge-cloud continuum
Plain English Explanation
The paper discusses a new way to manage and coordinate critical services in smart cities using a combination of edge computing, cloud computing, and 5G wireless technology. The key idea is to take advantage of the strengths of each of these technologies to provide real-time, reliable, and scalable services to citizens and city infrastructure.
Edge computing refers to processing data closer to where it's generated, like at local sensors or devices, rather than sending it all the way to a central cloud. This can improve response times and reduce network congestion. Cloud computing provides the massive computational power and storage to handle large-scale processing and data storage needs.
By orchestrating the use of both edge and cloud resources, along with 5G's high-speed, low-latency connectivity, the researchers propose a system that can deliver critical services - like emergency response, traffic management, or public safety monitoring - with greater speed, resilience, and flexibility than relying on any one technology alone.
The paper explores the technical details of how this edge-cloud continuum orchestration could work, including using Kubernetes to manage the deployment and scaling of applications across different locations. The goal is to create a smarter, more responsive, and more reliable infrastructure for essential city services.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents an edge-cloud continuum orchestration approach for critical services in smart cities. It leverages the strengths of edge computing, cloud computing, and 5G networks to provide real-time, resilient, and scalable services.
The proposed architecture uses Kubernetes, an open-source container orchestration system, to manage the deployment and scaling of applications across the edge-cloud continuum. Kubernetes allows the system to dynamically allocate resources and move workloads between edge and cloud environments as needed to meet service level objectives.
The authors also incorporate multi-access edge computing (MEC) to enable low-latency processing at the network edge. MEC places computational resources closer to end-users, reducing the time required to process data and respond to events.
The orchestration approach includes several key components:
- Edge Cluster Manager: Responsible for managing the lifecycle of edge clusters and deploying applications on edge nodes.
- Cloud Cluster Manager: Manages the cloud-based cluster and coordinates with the edge cluster manager.
- Service Broker: Provides a unified interface for deploying and managing services across the edge-cloud continuum.
- Monitoring and Adaptation Engine: Collects telemetry data and triggers dynamic resource allocation and workload migration decisions.
Through this integrated architecture, the system can dynamically adjust to changing demands, faults, and other disruptions, ensuring critical services remain available and responsive. The authors demonstrate the feasibility of this approach through a smart city case study involving traffic management and emergency response applications.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a well-designed and technically sound approach for orchestrating critical services across an edge-cloud continuum in a smart city context. The use of Kubernetes and MEC technologies seems appropriate and well-integrated to achieve the desired real-time, resilient, and scalable performance.
One potential limitation is the reliance on 5G networks, which may not be widely available in all smart city deployments. The authors could consider exploring how the orchestration framework could adapt to work with other types of network infrastructure, such as 4G LTE or Wi-Fi.
Additionally, the paper does not delve deeply into the security and privacy implications of the edge-cloud continuum architecture. As critical services are involved, it would be important to carefully consider how to protect sensitive data and ensure the overall system is resilient to cyber threats.
Further research could also investigate the economic and operational costs of deploying and maintaining such a complex orchestration system across a smart city. Understanding the tradeoffs and total cost of ownership would be valuable for city planners and decision-makers.
Overall, the paper presents a promising approach that could significantly improve the reliability and responsiveness of essential services in smart cities. The authors have clearly identified an important problem and proposed a technically sound solution worthy of further exploration and development.
Conclusion
This paper proposes an innovative edge-cloud continuum orchestration approach for delivering critical services in smart cities. By leveraging the strengths of edge computing, cloud computing, and 5G networks, the system can provide real-time, resilient, and scalable support for mission-critical applications like traffic management and emergency response.
The use of Kubernetes and multi-access edge computing enables dynamic resource allocation and workload migration to maintain service level objectives, even in the face of changing demands or disruptions. This integrated architecture represents an important step towards building smarter, more responsive, and more reliable infrastructure for essential city services.
While the paper leaves some areas for further exploration, such as adapting to different network technologies and addressing security/privacy concerns, it presents a compelling vision and technical blueprint for the future of smart city service delivery. As cities continue to grapple with growing complexity and the need for rapid, coordinated responses, solutions like this edge-cloud continuum orchestration approach will likely play a crucial role.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Edge-Cloud Continuum Orchestration of Critical Services: A Smart-City Approach
Rodrigo Rosmaninho, Duarte Raposo, Pedro Rito, Susana Sargento
Smart-city services are typically developed as closed systems within each city's vertical, communicating and interacting with cloud services while remaining isolated within each provider's domain. With the emergence of 5G private domains and the introduction of new M2M services focusing on autonomous systems, there is a shift from the cloud-based approach to a distributed edge computing paradigm, in a textit{continuum} orchestration. However, an essential component is missing. Current orchestration tools, designed for cloud-based deployments, lack robust workload isolation, fail to meet timing constraints, and are not tailored to the resource-constrained nature of edge devices. Therefore, new orchestration methods are needed to support MEC environments. The work presented in this paper addresses this gap. Based on the real needs of a smart-city testbed - the Aveiro Living Lab-, we developed a set of orchestration components to facilitate the seamless orchestration of both cloud and edge-based services, encompassing both critical and non-critical services. This work extends the current Kubernetes orchestration platform to include a novel location-specific resource definition, a custom scheduler to accommodate real-time and legacy services, continuous service monitoring to detect sub-optimal states, and a refined load balancing mechanism that prioritizes the fastest response times.
Read more7/25/2024


0
Discovery of 6G Services and Resources in Edge-Cloud-Continuum
Mohammad Farhoudi, Masoud Shokrnezhad, Tarik Taleb, Richard Li, JaeSeung Song
The advent of 6G networks will present a pivotal juncture in the evolution of telecommunications, marked by the proliferation of devices, dynamic service requests, and the integration of edge and cloud computing. In response to these transformative shifts, this paper proposes a service and resource discovery architecture as part of service provisioning for the future 6G edge-cloud-continuum. Through the architecture's orchestration and platform components, users will have access to services efficiently and on time. Blockchain underpins trust in this inherently trustless environment, while semantic networking dynamically extracts context from service requests, fostering efficient communication and service delivery. A key innovation lies in dynamic overlay zoning, which not only optimizes resource allocation but also endows our architecture with scalability, adaptability, and resilience. Notably, our architecture excels at predictive capabilities, harnessing learning algorithms to anticipate user and service instance behavior, thereby enhancing network responsiveness and preserving service continuity. This comprehensive architecture paves the way for unparalleled resource optimization, latency reduction, and seamless service delivery, positioning it as an instrumental pillar in the unfolding 6G landscape. Simulation results show that our architecture provides near-optimal timely responses that significantly improve the network's potential, offering scalable and efficient service and resource discovery.
Read more8/1/2024
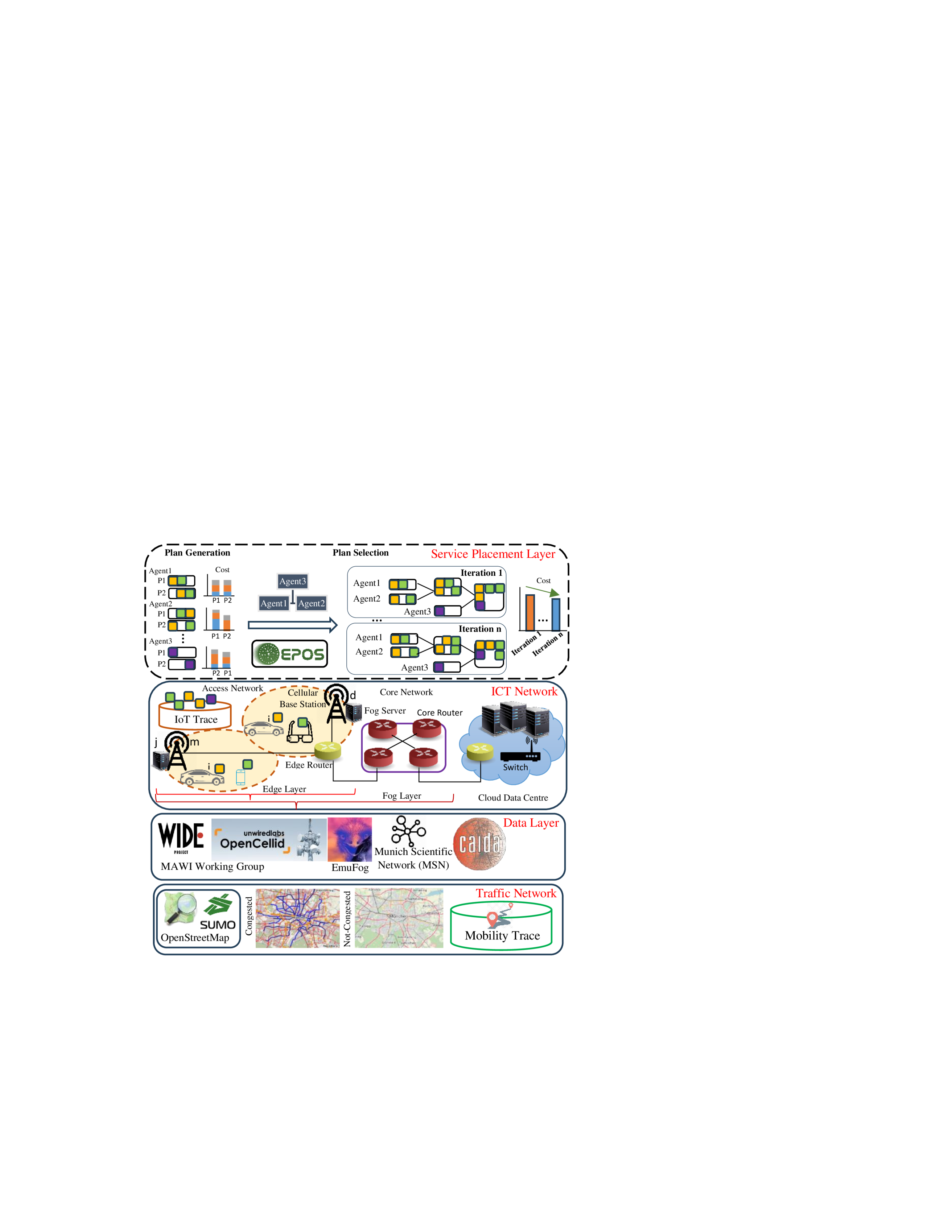

0
When `Computing follows Vehicles': Decentralized Mobility-Aware Resource Allocation in the Edge-to-Cloud Continuum
Zeinab Nezami, Emmanouil Chaniotakis, Evangelos Pournaras
The transformation of smart mobility is unprecedented--Autonomous, shared and electric connected vehicles, along with the urgent need to meet ambitious net-zero targets by shifting to low-carbon transport modalities result in new traffic patterns and requirements for real-time computation at large-scale, for instance, augmented reality applications. The cloud computing paradigm can neither respond to such low-latency requirements nor adapt resource allocation to such dynamic spatio-temporal service requests. This paper addresses this grand challenge by introducing a novel decentralized optimization framework for mobility-aware edge-to-cloud resource allocation, service offloading, provisioning and load-balancing. In contrast to related work, this framework comes with superior efficiency and cost-effectiveness under evaluation in real-world traffic settings and mobility datasets. This breakthrough capability of 'computing follows vehicles' proves able to reduce utilization variance by more than 40 times, while preventing service deadline violations by 14%-34%.
Read more5/7/2024
📉

0
End-to-End Orchestration of NextG Media Services over the Distributed Compute Continuum
Alessandro Mauro, Antonia Maria Tulino, Jaime Llorca
NextG (5G and beyond) networks, through the increasing integration of cloud/edge computing technologies, are becoming highly distributed compute platforms ideally suited to host emerging resource-intensive and latency-sensitive applications (e.g., industrial automation, extended reality, distributed AI). The end-to-end orchestration of such demanding applications, which involves function/data placement, flow routing, and joint communication/computation/storage resource allocation, requires new models and algorithms able to capture: (i) their disaggregated microservice-based architecture, (ii) their complex processing graph structures, including multiple-input multiple-output processing stages, and (iii) the opportunities for efficiently sharing and replicating data streams that may be useful for multiple functions and/or end users. To this end, we first identify the technical gaps in existing literature that prevent efficiently addressing the optimal orchestration of emerging applications described by information-aware directed acyclic graphs (DAGs). We then leverage the recently proposed Cloud Network Flow optimization framework and a novel functionally-equivalent DAG-to-Forest graph transformation procedure to design IDAGO (Information-Aware DAG Orchestration), a polynomial-time multi-criteria approximation algorithm for the optimal orchestration of NextG media services over NextG compute-integrated networks.
Read more7/12/2024