AcuVR: Enhancing Acupuncture Training Workflow with Virtual Reality

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper, "AcuVR: Enhancing Acupuncture Training Workflow with Virtual Reality," explores the use of virtual reality (VR) technology to improve the training and education of acupuncture practitioners.
- The researchers developed a VR-based system called AcuVR that allows learners to practice acupuncture techniques on a virtual human body and receive real-time feedback and guidance.
- The goal is to provide a safe, accessible, and engaging way for students to develop their acupuncture skills before practicing on real patients.
Plain English Explanation
The paper describes a new virtual reality (VR) system called AcuVR that is designed to help train people in the practice of acupuncture. Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese medical practice that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to promote healing and well-being.
Learning acupuncture can be challenging, as it requires a deep understanding of the human body and extensive hands-on practice to develop the necessary skills. The AcuVR system aims to make this training process more accessible and effective by allowing students to practice acupuncture techniques in a virtual environment.
Using VR headsets and controllers, students can interact with a realistic 3D model of the human body and try inserting virtual needles into the appropriate acupuncture points. The system provides real-time feedback and guidance to help students learn proper needle placement and technique. This allows them to make mistakes and learn from them in a risk-free, simulated setting before trying their skills on real patients.
The researchers believe that this VR-based approach can enhance the traditional acupuncture training workflow by offering a more engaging, accessible, and efficient learning experience. By mastering the basics in a virtual environment, students may be better prepared to apply their skills in the real world, ultimately improving patient care and outcomes.
Technical Explanation
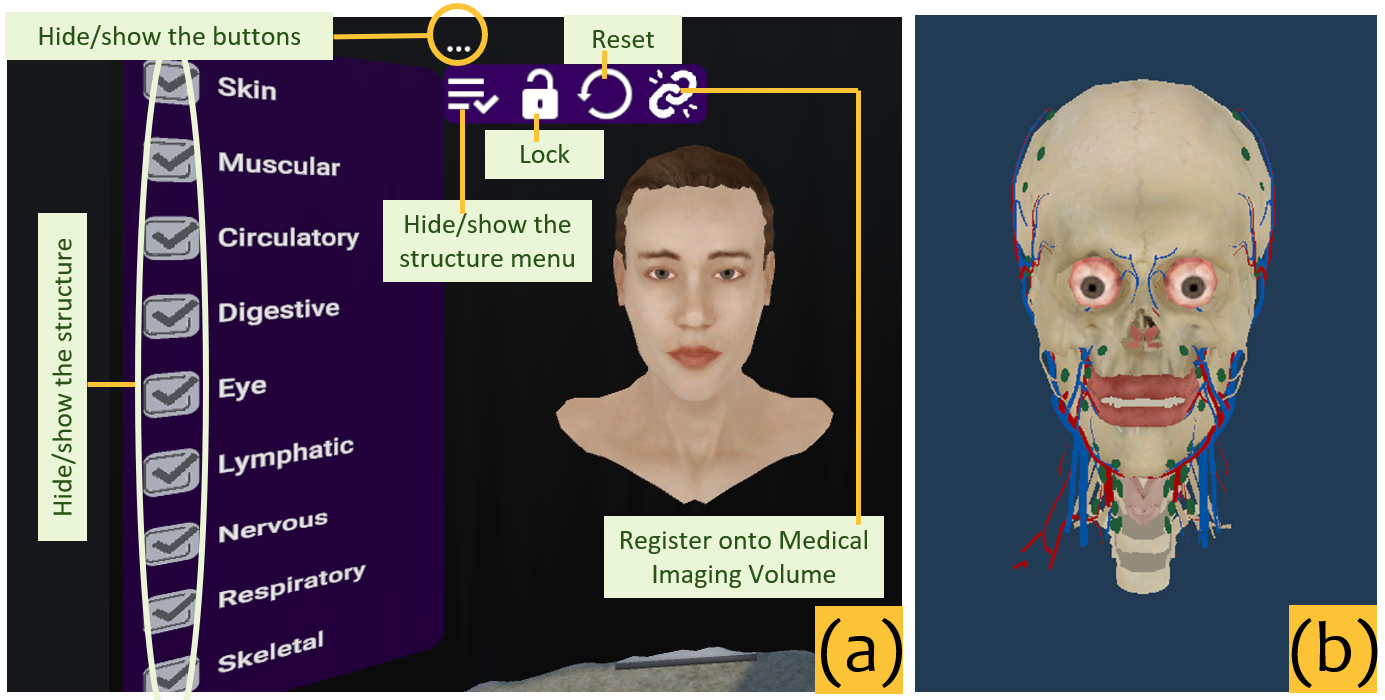
The AcuVR system developed by the researchers combines VR technology with a detailed 3D model of the human body to create an interactive acupuncture training environment. The virtual human model includes accurate representations of the skin, muscles, bones, and acupuncture points, allowing learners to practice needle insertion at the correct locations.
The system is built using the Unity game engine and integrates with commercially available VR headsets and hand controllers. Learners can use the controllers to manipulate virtual acupuncture needles and insert them into the body model, while receiving real-time feedback on their performance.
This feedback is generated through a machine learning-based algorithm that evaluates the trainee's needle placement and provides guidance on proper technique. The algorithm is trained on data from experienced acupuncturists, enabling it to recognize correct needle insertion and provide meaningful feedback to the learner.
By creating a safe, simulated environment for practicing acupuncture, the AcuVR system aims to address several challenges in traditional acupuncture training. These include the limited availability of hands-on practice opportunities, the risk of harming patients during early training, and the difficulty of providing personalized feedback and guidance to every student.
The researchers conducted user studies to evaluate the effectiveness of the AcuVR system, gathering feedback from both acupuncture students and experienced practitioners. The results suggest that the VR-based training can improve learners' understanding of acupuncture anatomy, increase their confidence in needle insertion, and provide a more engaging and enjoyable learning experience compared to traditional methods.
Critical Analysis
The AcuVR system presented in this paper offers a promising approach to enhancing acupuncture training, but there are a few potential limitations and areas for further research:
-
The current system focuses on teaching needle insertion techniques, but acupuncture practice also involves other important skills, such as palpation and the interpretation of subtle patient responses. Future iterations of AcuVR could expand to incorporate these additional aspects of acupuncture training.
-
The user studies were conducted with a relatively small sample size, and the long-term impact of VR-based training on learners' clinical competence and patient outcomes is not yet clear. Larger-scale, longitudinal studies would be needed to better understand the system's real-world effectiveness.
-
While the VR environment aims to be as realistic as possible, it may still lack some of the tactile and sensory cues present in actual acupuncture practice. Integrating additional haptic feedback or other sensory modalities could further improve the fidelity of the training experience.
-
The current version of AcuVR is focused on general acupuncture training, but it could potentially be adapted to address the specific needs of different acupuncture specialties or practice settings, such as traditional Chinese medicine, auricular acupuncture, or veterinary acupuncture.
Overall, the AcuVR system represents a promising step towards leveraging VR technology to enhance acupuncture education and training. As the field of VR-based medical education continues to evolve, further research and development in this area could lead to even more effective and engaging learning experiences for aspiring acupuncture practitioners.
Conclusion
The "AcuVR: Enhancing Acupuncture Training Workflow with Virtual Reality" paper presents a novel VR-based system that aims to improve the training and education of acupuncture practitioners. By creating a safe, interactive virtual environment for practicing acupuncture techniques, the AcuVR system offers a more accessible and engaging way for students to develop their skills before working with real patients.
The key innovation of AcuVR is its ability to provide real-time feedback and guidance to learners, helping them master proper needle insertion and technique. This could lead to better-prepared acupuncture practitioners and, ultimately, improved patient care and outcomes.
While the current system has some limitations, the researchers' work highlights the potential of VR technology to transform medical education and training, not just for acupuncture but potentially for other healthcare disciplines as well. As VR capabilities continue to advance, we may see more innovative solutions like AcuVR emerge to make specialized skills more accessible and learnable.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
AcuVR: Enhancing Acupuncture Training Workflow with Virtual Reality
Menghe Zhang, Chen Chen, Matin Yarmand, Anish Rajeshkumar, Nadir Weibel
Acupuncture is a widely adopted medical practice that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to alleviate pain and treat various health conditions. Current learning practices heavily rely on 2D atlases and practice on peers, which are notably less intuitive and pose risks, particularly in sensitive areas such as the eyes. To address these challenges, we introduce AcuVR, a Virtual Reality (VR) based system designed to add a layer of interactivity and realism. This innovation aims to reduce the risks associated with practicing acupuncture techniques while offering more effective learning strategies. Furthermore, AcuVR incorporates medical imaging and standardized anatomy models, enabling the simulation of customized acupuncture scenarios. This feature represents a significant advancement beyond the limitations of conventional resources such as atlases and textbooks, facilitating a more immersive and personalized learning experience. The evaluation study with eight acupuncture students and practitioners revealed high participant satisfaction and pointed to the effectiveness and potential of AcuVR as a valuable addition to acupuncture training.
Read more7/4/2024
👁️

0
AI-Enhanced Virtual Reality in Medicine: A Comprehensive Survey
Yixuan Wu, Kaiyuan Hu, Danny Z. Chen, Jian Wu
With the rapid advance of computer graphics and artificial intelligence technologies, the ways we interact with the world have undergone a transformative shift. Virtual Reality (VR) technology, aided by artificial intelligence (AI), has emerged as a dominant interaction media in multiple application areas, thanks to its advantage of providing users with immersive experiences. Among those applications, medicine is considered one of the most promising areas. In this paper, we present a comprehensive examination of the burgeoning field of AI-enhanced VR applications in medical care and services. By introducing a systematic taxonomy, we meticulously classify the pertinent techniques and applications into three well-defined categories based on different phases of medical diagnosis and treatment: Visualization Enhancement, VR-related Medical Data Processing, and VR-assisted Intervention. This categorization enables a structured exploration of the diverse roles that AI-powered VR plays in the medical domain, providing a framework for a more comprehensive understanding and evaluation of these technologies. To our best knowledge, this is the first systematic survey of AI-powered VR systems in medical settings, laying a foundation for future research in this interdisciplinary domain.
Read more7/12/2024


0
VR Isle Academy: A VR Digital Twin Approach for Robotic Surgical Skill Development
Achilleas Filippidis, Nikolaos Marmaras, Michael Maravgakis, Alexandra Plexousaki, Manos Kamarianakis, George Papagiannakis
Contemporary progress in the field of robotics, marked by improved efficiency and stability, has paved the way for the global adoption of surgical robotic systems (SRS). While these systems enhance surgeons' skills by offering a more accurate and less invasive approach to operations, they come at a considerable cost. Moreover, SRS components often involve heavy machinery, making the training process challenging due to limited access to such equipment. In this paper we introduce a cost-effective way to facilitate training for a simulator of a SRS via a portable, device-agnostic, ultra realistic simulation with hand tracking and feet tracking support. Error assessment is accessible in both real-time and offline, which enables the monitoring and tracking of users' performance. The VR application has been objectively evaluated by several untrained testers showcasing significant reduction in error metrics as the number of training sessions increases. This indicates that the proposed VR application denoted as VR Isle Academy operates efficiently, improving the robot - controlling skills of the testers in an intuitive and immersive way towards reducing the learning curve at minimal cost.
Read more7/2/2024
⛏️

0
New!Virtual Reality for Immersive Education in Orthopedic Surgery Digital Twins
Jonas Hein, Jan Grunder, Lilian Calvet, Fr'ed'eric Giraud, Nicola Alessandro Cavalcanti, Fabio Carrillo, Philipp Furnstahl
Virtual Reality technology, when integrated with Surgical Digital Twins (SDTs), offers significant potential in medical training and surgical planning. We present SurgTwinVR, a VR application that immerses users within an SDT and enables them to navigate a high-fidelity virtual replica of the surgical environment. SurgTwinVR is the first VR application to utilize a dynamic 3D environment that is a clone of a real surgery, encompassing the entire surgical scene, including the surgeon, anatomy, and instruments. Our system utilizes a SDT with important improvements for real-time rendering and features to showcase the potential benefits of such an application in surgical education.
Read more9/18/2024