Addressing Image Hallucination in Text-to-Image Generation through Factual Image Retrieval

0
🖼️
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Provides formatting instructions for papers submitted to the IJCAI-24 conference
- Covers details on layout, formatting, and submission requirements
- Ensures consistent formatting and presentation of research papers
Plain English Explanation
This document outlines the formatting guidelines for papers submitted to the IJCAI-24 (International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence) conference. It covers important aspects such as the layout, typography, and submission process to ensure a consistent and professional presentation of the research work.
The guidelines cover things like the required paper size, margins, font styles and sizes, as well as the structure and organization of the paper. This helps the conference organizers and reviewers process the submissions efficiently and ensures a level playing field for all authors.
By following these guidelines, authors can focus on the content and quality of their research without getting bogged down in the formatting details. This helps the conference maintain high standards and presents the research in the best possible light.
Technical Explanation
The IJCAI-24 formatting instructions document provides detailed guidelines for the layout and formatting of papers submitted to the IJCAI-24 conference. It specifies the required paper size of 8.5 x 11 inches (or A4), with 1-inch margins on all sides.
The document also outlines the typesetting requirements, including the use of 10-point Times New Roman font for the main text, and 8-point for footnotes. It provides guidance on the organization of the paper, including the structure of sections and subsections, as well as the placement of figures, tables, and references.
Additionally, the instructions cover the submission process, including the file formats and size limits for the paper and any supplementary materials. This ensures a consistent and streamlined review process for the conference organizers and reviewers.
By adhering to these formatting guidelines, authors can ensure that their research papers are presented in a clear and professional manner, making it easier for the reviewers to focus on the content and quality of the work.
Critical Analysis
The IJCAI-24 formatting instructions serve an important purpose in maintaining the consistency and quality of the research papers presented at the conference. By providing clear and detailed guidelines, the instructions help ensure that all submissions adhere to the same standards, making it easier for reviewers to compare and evaluate the papers.
However, it's important to note that the formatting requirements, while necessary for the efficient operation of the conference, can sometimes be seen as an unnecessary burden on authors. The time and effort required to properly format a paper according to the guidelines could be better spent on improving the research content and presentation.
Additionally, the guidelines may not always be flexible enough to accommodate more innovative or unconventional paper formats or styles. This could potentially limit the diversity of research presented at the conference and discourage authors from experimenting with new ways of communicating their findings.
Despite these potential drawbacks, the IJCAI-24 formatting instructions are a necessary and important aspect of the conference, as they help maintain the high quality and consistency of the published research. As with any set of guidelines, there may be room for improvement or adaptation to better serve the needs of the research community.
Conclusion
The IJCAI-24 formatting instructions provide a clear and comprehensive set of guidelines for authors submitting papers to the conference. By ensuring a consistent layout and presentation of the research, these instructions help the conference organizers and reviewers process the submissions efficiently and effectively.
While the formatting requirements may be seen as a burden by some authors, they are a necessary part of maintaining the high standards and professional reputation of the IJCAI conference. By adhering to these guidelines, authors can focus on the quality and content of their research, knowing that their work will be presented in the best possible light.
Overall, the IJCAI-24 formatting instructions are an important tool for ensuring the success and impact of the conference, and for promoting the dissemination of high-quality artificial intelligence research to the broader scientific community.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🖼️

0
Addressing Image Hallucination in Text-to-Image Generation through Factual Image Retrieval
Youngsun Lim, Hyunjung Shim
Text-to-image generation has shown remarkable progress with the emergence of diffusion models. However, these models often generate factually inconsistent images, failing to accurately reflect the factual information and common sense conveyed by the input text prompts. We refer to this issue as Image hallucination. Drawing from studies on hallucinations in language models, we classify this problem into three types and propose a methodology that uses factual images retrieved from external sources to generate realistic images. Depending on the nature of the hallucination, we employ off-the-shelf image editing tools, either InstructPix2Pix or IP-Adapter, to leverage factual information from the retrieved image. This approach enables the generation of images that accurately reflect the facts and common sense.
Read more7/16/2024


0
New!Evaluating Image Hallucination in Text-to-Image Generation with Question-Answering
Youngsun Lim, Hojun Choi, Hyunjung Shim
Despite the impressive success of text-to-image (TTI) generation models, existing studies overlook the issue of whether these models accurately convey factual information. In this paper, we focus on the problem of image hallucination, where images created by generation models fail to faithfully depict factual content. To address this, we introduce I-HallA (Image Hallucination evaluation with Question Answering), a novel automated evaluation metric that measures the factuality of generated images through visual question answering (VQA). We also introduce I-HallA v1.0, a curated benchmark dataset for this purpose. As part of this process, we develop a pipeline that generates high-quality question-answer pairs using multiple GPT-4 Omni-based agents, with human judgments to ensure accuracy. Our evaluation protocols measure image hallucination by testing if images from existing text-to-image models can correctly respond to these questions. The I-HallA v1.0 dataset comprises 1.2K diverse image-text pairs across nine categories with 1,000 rigorously curated questions covering various compositional challenges. We evaluate five text-to-image models using I-HallA and reveal that these state-of-the-art models often fail to accurately convey factual information. Moreover, we validate the reliability of our metric by demonstrating a strong Spearman correlation (rho=0.95) with human judgments. We believe our benchmark dataset and metric can serve as a foundation for developing factually accurate text-to-image generation models.
Read more9/20/2024


0
Analysis of Plan-based Retrieval for Grounded Text Generation
Ameya Godbole, Nicholas Monath, Seungyeon Kim, Ankit Singh Rawat, Andrew McCallum, Manzil Zaheer
In text generation, hallucinations refer to the generation of seemingly coherent text that contradicts established knowledge. One compelling hypothesis is that hallucinations occur when a language model is given a generation task outside its parametric knowledge (due to rarity, recency, domain, etc.). A common strategy to address this limitation is to infuse the language models with retrieval mechanisms, providing the model with relevant knowledge for the task. In this paper, we leverage the planning capabilities of instruction-tuned LLMs and analyze how planning can be used to guide retrieval to further reduce the frequency of hallucinations. We empirically evaluate several variations of our proposed approach on long-form text generation tasks. By improving the coverage of relevant facts, plan-guided retrieval and generation can produce more informative responses while providing a higher rate of attribution to source documents.
Read more8/21/2024
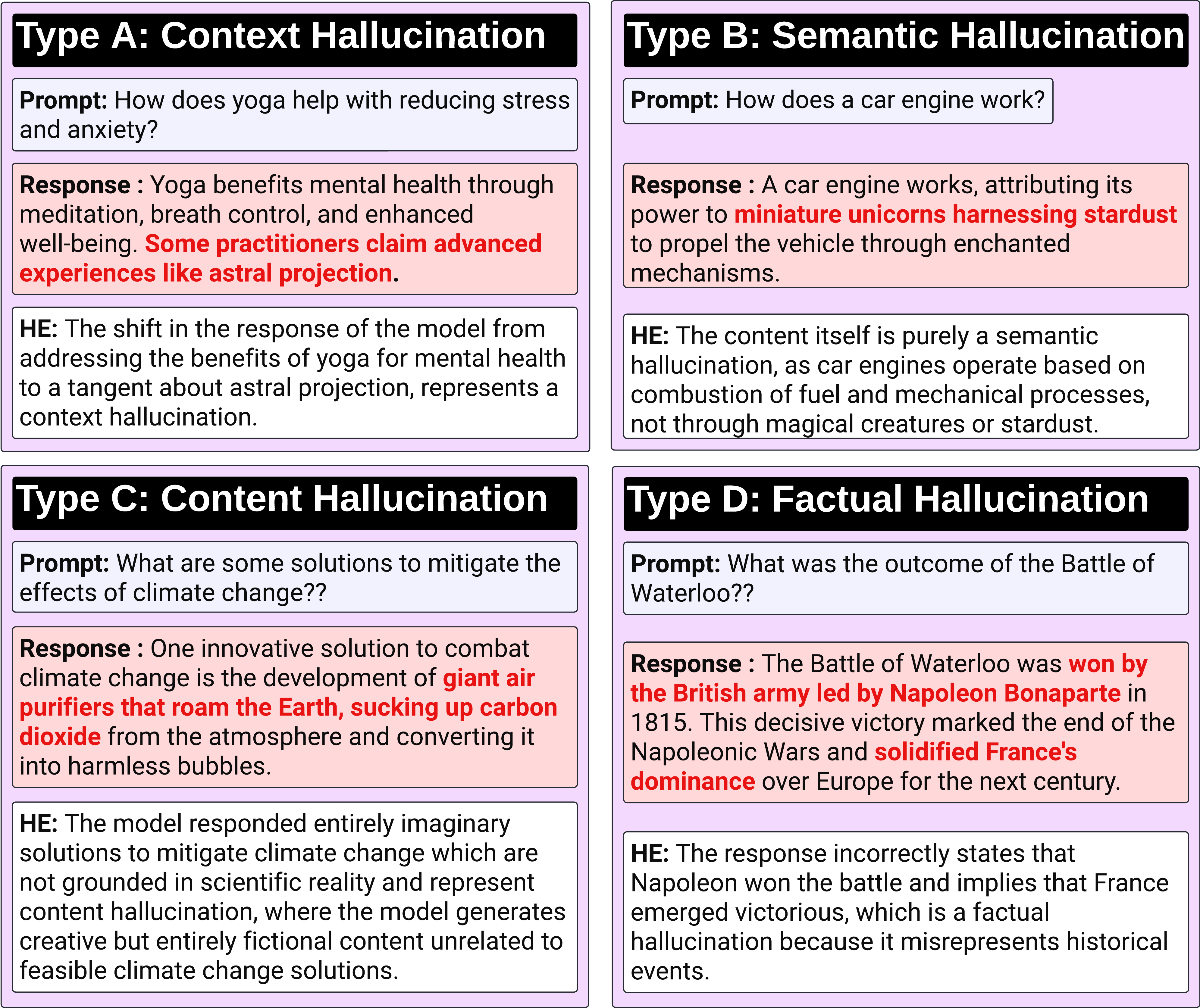

0
Unveiling Hallucination in Text, Image, Video, and Audio Foundation Models: A Comprehensive Review
Pranab Sahoo, Prabhash Meharia, Akash Ghosh, Sriparna Saha, Vinija Jain, Aman Chadha
The rapid advancement of foundation models (FMs) across language, image, audio, and video domains has shown remarkable capabilities in diverse tasks. However, the proliferation of FMs brings forth a critical challenge: the potential to generate hallucinated outputs, particularly in high-stakes applications. The tendency of foundation models to produce hallucinated content arguably represents the biggest hindrance to their widespread adoption in real-world scenarios, especially in domains where reliability and accuracy are paramount. This survey paper presents a comprehensive overview of recent developments that aim to identify and mitigate the problem of hallucination in FMs, spanning text, image, video, and audio modalities. By synthesizing recent advancements in detecting and mitigating hallucination across various modalities, the paper aims to provide valuable insights for researchers, developers, and practitioners. Essentially, it establishes a clear framework encompassing definition, taxonomy, and detection strategies for addressing hallucination in multimodal foundation models, laying the foundation for future research in this pivotal area.
Read more5/21/2024