Antenna Selection in Polarization Reconfigurable MIMO (PR-MIMO) Communication Systems
2112.00931

0
0
🗣️
Abstract
Adaptation of a wireless system to the polarization state of the propagation channel can improve reliability and throughput. This paper in particular considers polarization reconfigurable multiple input multiple output (PR-MIMO) systems, where both transmitter and receiver can change the (linear) polarization orientation at each element of their antenna arrays. We first introduce joint polarization pre-post coding to maximize bounds on the capacity and the maximum eigenvalue of the channel matrix. For this we first derive approximate closed form equations of optimal polarization vectors at one link end, and then use iterative joint polarization pre-post coding to pursue joint optimal polarization vectors at both link ends. Next we investigate the combination of PR-MIMO with hybrid antenna selection / maximum ratio transmission (PR-HS/MRT), which can achieve a remarkable improvement of channel capacity and symbol error rate (SER). Further, two novel schemes of element wise and global polarization reconfiguration are presented for PR-HS/MRT. Comprehensive simulation results indicate that the proposed schemes provide 3 to 5 dB SNR gain in PR-MIMO spatial multiplexing and approximately 3 dB SNR gain in PRHS/ MRT, with concomitant improvements of channel capacity and SER.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Wireless systems can be made more reliable and efficient by adapting to the polarization state of the communication channel.
- This paper explores polarization reconfigurable multiple-input multiple-output (PR-MIMO) systems, where both the transmitter and receiver can adjust the polarization of their antenna elements.
- The paper proposes techniques for optimizing polarization at both ends of the link to maximize capacity and reduce symbol error rate.
- It also investigates combining PR-MIMO with antenna selection and maximum ratio transmission to further improve performance.
Plain English Explanation
Imagine you're trying to make a phone call, but the connection keeps cutting out. One way to improve the reliability of the call is to adjust the orientation of the antennas on both your phone and the cell tower. This is similar to what the researchers are studying in this paper.
In a typical wireless system, the antennas at the transmitter and receiver have a fixed polarization, meaning the electromagnetic waves they send and receive only travel in one direction. However, as these waves propagate through the environment, their polarization can change due to reflections and other effects.
By allowing the antennas to dynamically adjust their polarization, the researchers show that the wireless link can be optimized for better performance. Specifically, they develop techniques to find the best polarization settings at both the transmitter and receiver to maximize the capacity (how much data can be sent) and minimize the error rate (how often the signal is misinterpreted).
The researchers also combine this polarization reconfigurability with another technique called antenna selection, which chooses the best subset of antennas to use. This hybrid approach can provide an even greater improvement in capacity and error rate compared to using polarization reconfiguration alone.
Overall, these innovations could lead to more reliable and faster wireless communications, which would be beneficial for a wide range of applications, from mobile phones to wireless internet to industrial automation.
Technical Explanation
The core idea behind the research is the observation that wireless channel performance can be improved by adapting to the polarization state of the propagation environment. To explore this, the paper focuses on polarization reconfigurable multiple-input multiple-output (PR-MIMO) systems, where both the transmitter and receiver can dynamically adjust the linear polarization orientation of each antenna element.
The authors first develop a technique called joint polarization pre-post coding, which seeks to optimize the polarization vectors at the transmitter and receiver simultaneously to maximize capacity bounds and the largest eigenvalue of the channel matrix. This involves deriving approximate closed-form equations for the optimal polarization at one end, and then using an iterative algorithm to find the joint optimal polarization vectors.
Next, the paper investigates combining PR-MIMO with hybrid antenna selection and maximum ratio transmission (PR-HS/MRT). Antenna selection chooses a subset of the available antennas to use, while maximum ratio transmission optimally combines the signals from the selected antennas. The authors propose two novel schemes for polarization reconfiguration in this PR-HS/MRT context - element-wise and global reconfiguration.
Comprehensive simulations demonstrate that the proposed PR-MIMO and PR-HS/MRT schemes can provide 3-5 dB SNR gains compared to fixed polarization MIMO, resulting in concomitant improvements in channel capacity and symbol error rate performance.
Critical Analysis
The research presented in this paper makes a valuable contribution by showing how polarization reconfigurability can be leveraged to enhance the performance of MIMO wireless systems. The techniques developed, such as joint polarization pre-post coding and the PR-HS/MRT schemes, provide practical mechanisms for realizing these benefits.
That said, the paper does not address some important practical considerations. For example, the polarization reconfiguration is assumed to be perfect, with no losses or errors. In reality, imperfections in the reconfiguration hardware and control algorithms could degrade the achievable gains. The authors also do not consider the additional complexity and cost that would be introduced by incorporating polarization reconfigurability into the system design.
Additionally, the simulations are based on idealized channel models, and it would be important to validate the performance improvements under more realistic propagation conditions, including the effects of mobility, blockages, and interference from other wireless systems.
Overall, while the research presents promising techniques, further work is needed to fully understand the real-world practicality and limitations of polarization reconfigurable MIMO systems. Careful implementation and extensive field testing would be required before these concepts could be confidently deployed in commercial wireless networks.
Conclusion
This paper explores an innovative approach to improving the reliability and throughput of wireless communication systems by adapting to the polarization state of the propagation channel. The proposed techniques for joint polarization optimization and the combination of polarization reconfigurability with antenna selection show the potential for significant performance gains.
If these concepts can be successfully translated into practical, cost-effective implementations, they could lead to meaningful improvements in a wide range of wireless applications, from mobile broadband to IoT connectivity to mission-critical industrial communications. However, further research is needed to fully understand the real-world limitations and trade-offs involved in deploying polarization reconfigurable MIMO systems at scale.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Multi-Polarization Superposition Beamforming: Novel Scheme of Transmit Power Allocation and Subcarrier Assignment
Paul Oh, Sean Kwon

0
0
The 5th generation (5G) new radio (NR) access technology and the beyond-5G future wireless communication require extremely high data rate and spectrum efficiency. Energy-efficient transmission/reception schemes are also regarded as an important component. The polarization domain has attracted substantial attention in this aspects. This paper is the first to propose textit{multi-polarization superposition beamforming (MPS-Beamforming)} with cross-polarization discrimination (XPD) and cross-polarization ratio (XPR)-aware transmit power allocation utilizing the 5G NR antenna panel structure. The appropriate orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) subcarrier assignment algorithm is also proposed to verify the theoretical schemes via simulations. The detailed theoretical derivation along with comprehensive simulation results illustrate that the proposed novel scheme of MPS-Beamforming is significantly beneficial to the improvement of the performance in terms of the symbol error rate (SER) and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) gain at the user equipment (UE). For instance, a provided practical wireless channel environment in the simulations exhibits 8 dB SNR gain for $10^{-4}$ SER in a deterministic channel, and 4 dB SNR gain for $10^{-5}$ SER in abundant statistical channel realizations.
4/4/2024
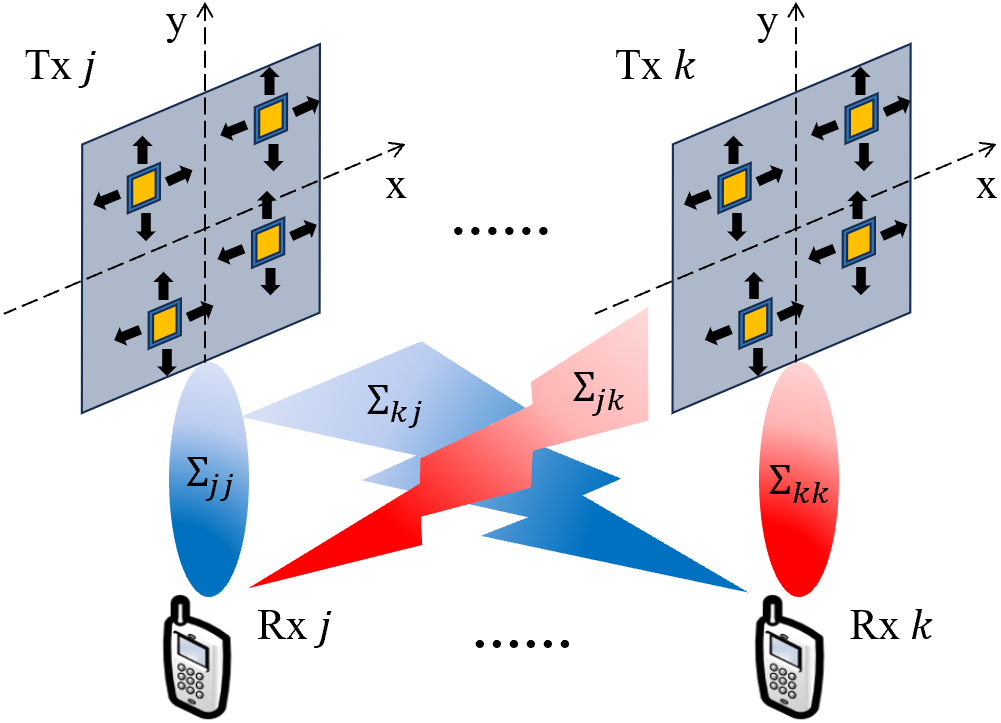
Movable Antenna Enabled Interference Network: Joint Antenna Position and Beamforming Design
Honghao Wang, Qingqing Wu, Wen Chen

0
0
This paper investigates the utility of movable antenna (MA) assistance for the multiple-input single-output (MISO) interference channel. We exploit an additional design degree of freedom provided by MA to enhance the desired signal and suppress interference so as to reduce the total transmit power of interference network. To this end, we jointly optimize the MA positions and transmit beamforming, subject to the signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio constraints of users. To address the non-convex optimization problem, we propose an efficient iterative algorithm to alternately optimize the MA positions via successive convex approximation method and the transmit beamforming via second-order cone program approach. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed MA-enabled MISO interference network outperforms its conventional counterpart without MA, which significantly enhances the capability of inter-cell frequency reuse and reduces the complexity of transmitter design.
4/4/2024
🧪
Cell-Free Massive MIMO with Multi-Antenna Users and Phase Misalignments: A Novel Partially Coherent Transmission Framework
Unnikrishnan Kunnath Ganesan, Tung Thanh Vu, Erik G. Larsson

0
0
Cell-free massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) is a promising technology for next-generation communication systems. This work proposes a novel partially coherent (PC) transmission framework to cope with the challenge of phase misalignment among the access points (APs), which is important for unlocking the full potential of cell-free massive MIMO technology. With the PC operation, the APs are only required to be phase-aligned within clusters. Each cluster transmits the same data stream towards each user equipment (UE), while different clusters send different data streams. We first propose a novel algorithm to group APs into clusters such that the distance between two APs is always smaller than a reference distance ensuring the phase alignment of these APs. Then, we propose new algorithms that optimize the combining at UEs and precoding at APs to maximize the downlink sum data rates. We also propose a novel algorithm for data stream allocation to further improve the sum data rate of the PC operation. Numerical results show that the PC operation using the proposed framework with a sufficiently small reference distance can offer a sum rate close to the sum rate of the ideal fully coherent (FC) operation that requires network-wide phase alignment. This demonstrates the potential of PC operation in practical deployments of cell-free massive MIMO networks.
4/4/2024
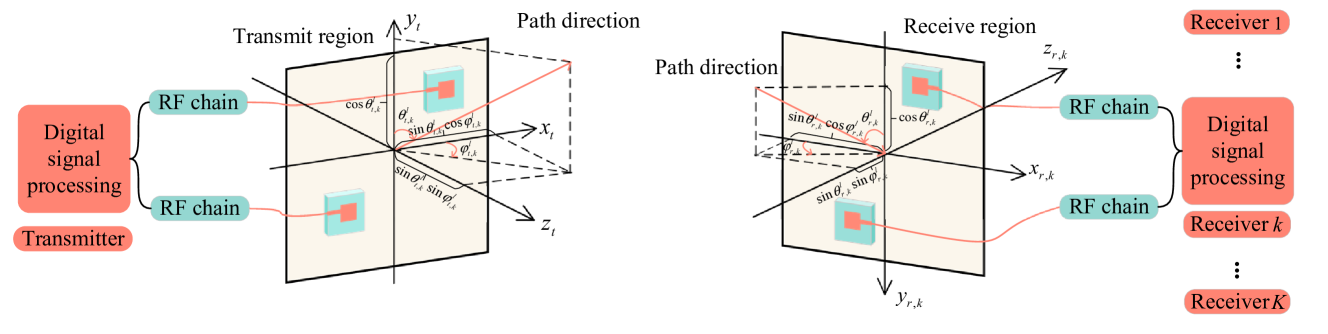
Learning-Based Joint Beamforming and Antenna Movement Design for Movable Antenna Systems
Caihao Weng, Yuanbin Chen, Lipeng Zhu, Ying Wang

0
0
In this paper, we investigate a multi-receiver communication system enabled by movable antennas (MAs). Specifically, the transmit beamforming and the double-side antenna movement at the transceiver are jointly designed to maximize the sum-rate of all receivers under imperfect channel state information (CSI). Since the formulated problem is non-convex with highly coupled variables, conventional optimization methods cannot solve it efficiently. To address these challenges, an effective learning-based algorithm is proposed, namely heterogeneous multi-agent deep deterministic policy gradient (MADDPG), which incorporates two agents to learn policies for beamforming and movement of MAs, respectively. Based on the offline learning under numerous imperfect CSI, the proposed heterogeneous MADDPG can output the solutions for transmit beamforming and antenna movement in real time. Simulation results validate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm, and the MA can significantly improve the sum-rate performance of multiple receivers compared to other benchmark schemes.
4/3/2024