Movable Antenna Enabled Interference Network: Joint Antenna Position and Beamforming Design
2403.13573

0
0
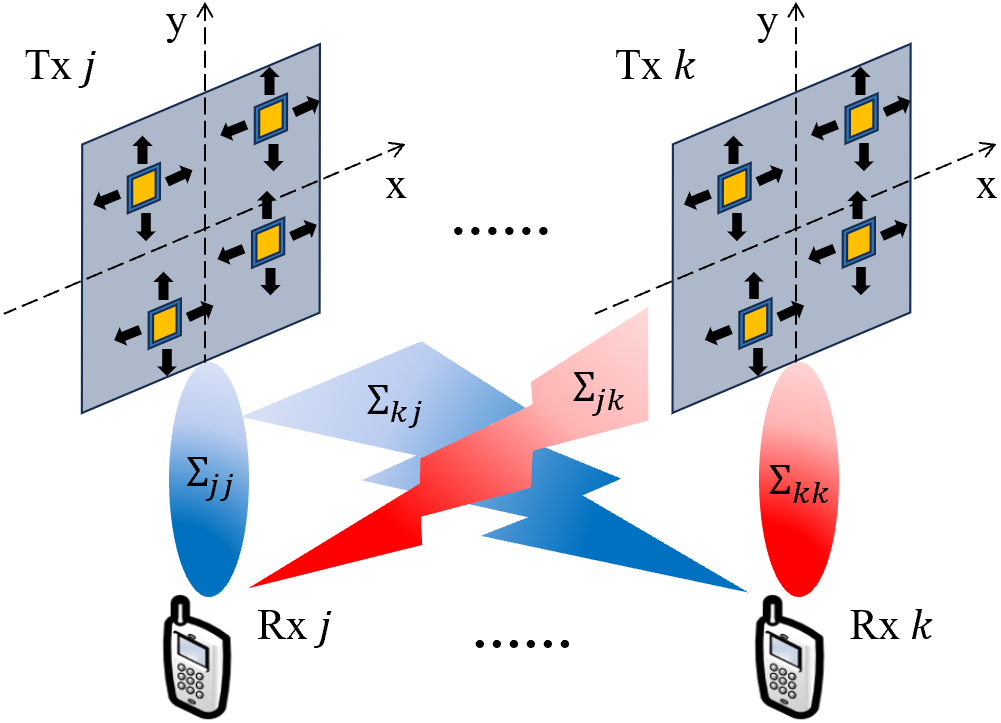
Abstract
This paper investigates the utility of movable antenna (MA) assistance for the multiple-input single-output (MISO) interference channel. We exploit an additional design degree of freedom provided by MA to enhance the desired signal and suppress interference so as to reduce the total transmit power of interference network. To this end, we jointly optimize the MA positions and transmit beamforming, subject to the signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio constraints of users. To address the non-convex optimization problem, we propose an efficient iterative algorithm to alternately optimize the MA positions via successive convex approximation method and the transmit beamforming via second-order cone program approach. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed MA-enabled MISO interference network outperforms its conventional counterpart without MA, which significantly enhances the capability of inter-cell frequency reuse and reduces the complexity of transmitter design.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This research paper explores a method for optimizing the position of movable antennas and their beamforming in a multi-user interference network to minimize power consumption.
- The key ideas involve using the ability to physically move antennas to improve the interference management and energy efficiency in wireless communication systems.
- The paper presents a mathematical optimization framework to jointly optimize antenna positions and beamforming vectors to minimize the total transmit power required.
Plain English Explanation
In wireless communication systems, interference between signals from different devices can be a major challenge. This research explores a novel approach to address this problem by using "movable antennas" - antennas that can physically change their position.
The key insight is that by strategically positioning the antennas, the interference between different signals can be reduced. This allows the transmitters to use less power to achieve the same communication quality, improving the energy efficiency of the system.
The researchers developed a mathematical optimization framework to jointly optimize both the positions of the antennas and the beamforming (the focusing of the transmitted signals). This joint optimization ensures that the antennas are placed in the best locations and the signals are transmitted in the most efficient way possible.
Imagine you have a room with multiple wireless devices, each trying to communicate. If the devices are positioned randomly, their signals may interfere with each other, requiring them to transmit at high power to overcome the interference. However, if you could physically move the antennas on the devices to optimal positions, you could minimize the interference and allow the devices to communicate effectively using much less power.
This concept of using movable antennas to improve interference management and energy efficiency has applications in a variety of wireless systems, from cellular networks to Internet of Things (IoT) devices. By carefully controlling the antenna positions and beamforming, these systems can become more reliable and energy-efficient.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a system model for a multi-user multiple-input, single-output (MISO) interference channel with movable antennas. Each transmitter has multiple antennas that can be physically positioned to optimize the interference management and power consumption.
The researchers formulate a joint optimization problem to determine the optimal antenna positions and beamforming vectors that minimize the total transmit power while satisfying the signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) requirements for each user. This optimization problem is non-convex and challenging to solve directly.
To address this, the authors propose an iterative algorithm that alternates between optimizing the antenna positions and the beamforming vectors. For the antenna position optimization, they use a gradient-based method to move the antennas towards a better configuration. For the beamforming optimization, they use a semidefinite relaxation technique to obtain the optimal beamforming vectors.
Through numerical simulations, the authors demonstrate that their proposed joint optimization approach can significantly reduce the total transmit power compared to a fixed antenna configuration or a scheme that optimizes only the beamforming vectors. The power savings are especially pronounced in scenarios with strong interference.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a promising approach for improving the energy efficiency of wireless communication systems by leveraging the ability to physically move antennas. The joint optimization of antenna positions and beamforming is a novel and potentially impactful contribution.
However, the paper does not address several practical considerations that may limit the feasibility or applicability of this approach. For example, the authors do not discuss the mechanical complexity and cost of implementing movable antennas, or the potential impact on the size and form factor of the devices.
Additionally, the paper assumes perfect knowledge of the channel state information, which may be challenging to obtain in real-world scenarios. The performance of the proposed approach under imperfect or partial channel information is an important area for further research.
The authors also do not consider the potential impact of antenna movement on the reliability or stability of the communication links. Sudden changes in antenna position could disrupt the communication and lead to service interruptions, which would be unacceptable in many practical applications.
Overall, the research presented in this paper is a valuable contribution to the field of reconfigurable antenna systems, but further work is needed to address the practical challenges and limitations before this approach can be widely adopted in real-world wireless networks.
Conclusion
This research paper introduces a novel approach for improving the energy efficiency of wireless communication systems by jointly optimizing the positions of movable antennas and their beamforming. The key idea is to use the ability to physically move the antennas to reduce interference and minimize the total transmit power required.
The authors present a mathematical optimization framework to determine the optimal antenna positions and beamforming vectors, demonstrating significant power savings compared to fixed antenna configurations or schemes that only optimize the beamforming.
While this research shows promise, there are several practical challenges that need to be addressed, such as the mechanical complexity of movable antennas, the impact on device form factors, and the reliability of communication links under dynamic antenna positioning.
Overall, this work represents an important step towards more energy-efficient and interference-resistant wireless communication systems, with potential applications in cellular networks, IoT, and other emerging wireless technologies.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
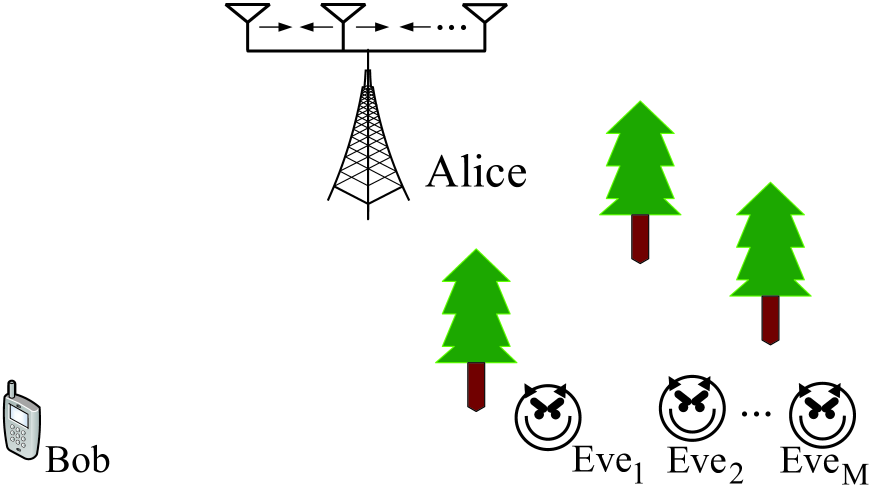
Movable Antennas-Assisted Secure Transmission Without Eavesdroppers' Instantaneous CSI
Guojie Hu, Qingqing Wu, Donghui Xu, Kui Xu, Jiangbo Si, Yunlong Cai, Naofal Al-Dhahir

0
0
Movable antenna (MA) technology is highly promising for improving communication performance, due to its advantage of flexibly adjusting positions of antennas to reconfigure channel conditions. In this paper, we investigate MAs-assisted secure transmission under a legitimate transmitter Alice, a legitimate receiver Bob and multiple eavesdroppers. Specifically, we consider a practical scenario where Alice has no any knowledge about the instantaneous non-line-of-sight component of the wiretap channel. Under this setup, we evaluate the secrecy performance by adopting the secrecy outage probability metric, the tight approximation of which is first derived by interpreting the Rician fading as a special case of Nakagami fading and concurrently exploiting the Laguerre series approximation. Then, we minimize the secrecy outage probability by jointly optimizing the transmit beamforming and positions of antennas at Alice. However, the problem is highly non-convex because the objective includes the complex incomplete gamma function. To tackle this challenge, we, for the first time, effectively approximate the inverse of the incomplete gamma function as a simple linear model. Based on this approximation, we arrive at a simplified problem with a clear structure, which can be solved via the developed alternating projected gradient ascent (APGA) algorithm. Considering the high complexity of the APGA, we further design another scheme where the zero-forcing based beamforming is adopted by Alice, and then we transform the problem into minimizing a simple function which is only related to positions of antennas at Alice.As demonstrated by simulations, our proposed schemes achieve significant performance gains compared to conventional schemes based on fixed-position antennas.
4/5/2024
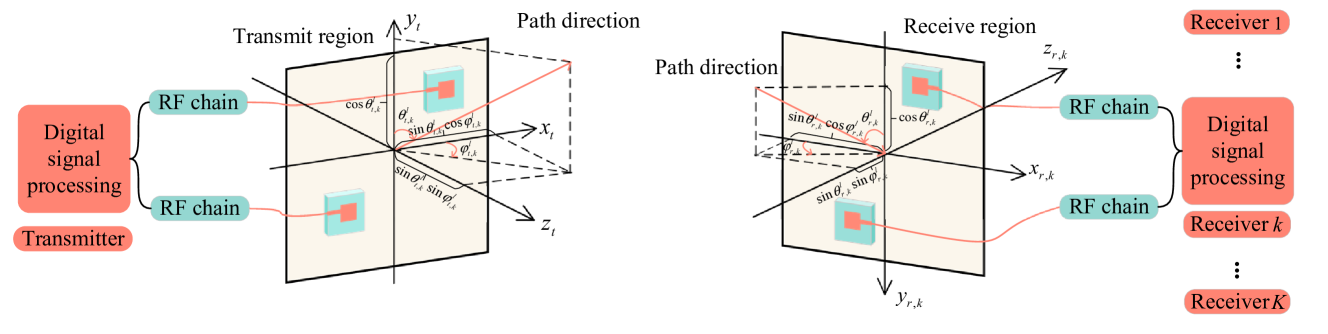
Learning-Based Joint Beamforming and Antenna Movement Design for Movable Antenna Systems
Caihao Weng, Yuanbin Chen, Lipeng Zhu, Ying Wang

0
0
In this paper, we investigate a multi-receiver communication system enabled by movable antennas (MAs). Specifically, the transmit beamforming and the double-side antenna movement at the transceiver are jointly designed to maximize the sum-rate of all receivers under imperfect channel state information (CSI). Since the formulated problem is non-convex with highly coupled variables, conventional optimization methods cannot solve it efficiently. To address these challenges, an effective learning-based algorithm is proposed, namely heterogeneous multi-agent deep deterministic policy gradient (MADDPG), which incorporates two agents to learn policies for beamforming and movement of MAs, respectively. Based on the offline learning under numerous imperfect CSI, the proposed heterogeneous MADDPG can output the solutions for transmit beamforming and antenna movement in real time. Simulation results validate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm, and the MA can significantly improve the sum-rate performance of multiple receivers compared to other benchmark schemes.
4/3/2024
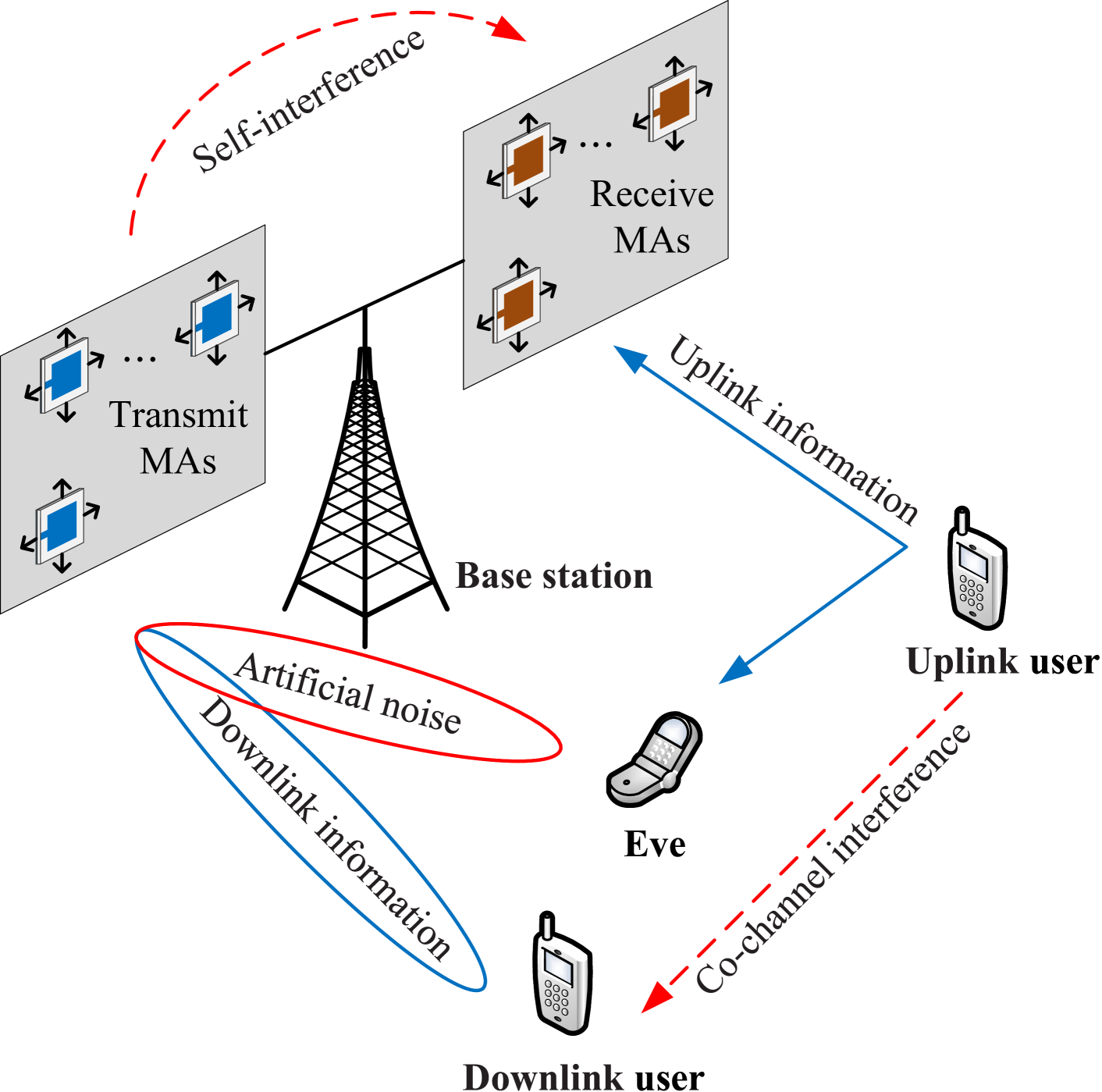
Secure Full-Duplex Communication via Movable Antennas
Jingze Ding, Zijian Zhou, Chenbo Wang, Wenyao Li, Lifeng Lin, Bingli Jiao

0
0
This paper investigates physical layer security (PLS) for a movable antenna (MA)-assisted full-duplex (FD) system. In this system, an FD base station (BS) with multiple MAs for transmission and reception provides services for an uplink (UL) user and a downlink (DL) user. Each user operates in half-duplex (HD) mode and is equipped with a single fixed-position antenna (FPA), in the presence of a single-FPA eavesdropper (Eve). To ensure secure communication, artificial noise (AN) is transmitted to obstruct the interception of Eve. The objective of this paper is to maximize the sum secrecy rate (SSR) of the UL and DL users by jointly optimizing the beamformers of the BS and the positions of MAs. This paper also proposes an alternating optimization (AO) method to address the non-convex problem, which decomposes the optimization problem into three subproblems and solves them iteratively. Simulation results demonstrate a significant performance gain in the SSR achieved by the proposed scheme compared to the benchmark schemes.
4/1/2024
Deep Learning Based Joint Multi-User MISO Power Allocation and Beamforming Design
Cemil Vahapoglu, Timothy J. O'Shea, Tamoghna Roy, Sennur Ulukus

0
0
The evolution of fifth generation (5G) wireless communication networks has led to an increased need for wireless resource management solutions that provide higher data rates, wide coverage, low latency, and power efficiency. Yet, many of existing traditional approaches remain non-practical due to computational limitations, and unrealistic presumptions of static network conditions and algorithm initialization dependencies. This creates an important gap between theoretical analysis and real-time processing of algorithms. To bridge this gap, deep learning based techniques offer promising solutions with their representational capabilities for universal function approximation. We propose a novel unsupervised deep learning based joint power allocation and beamforming design for multi-user multiple-input single-output (MU-MISO) system. The objective is to enhance the spectral efficiency by maximizing the sum-rate with the proposed joint design framework, NNBF-P while also offering computationally efficient solution in contrast to conventional approaches. We conduct experiments for diverse settings to compare the performance of NNBF-P with zero-forcing beamforming (ZFBF), minimum mean square error (MMSE) beamforming, and NNBF, which is also our deep learning based beamforming design without joint power allocation scheme. Experiment results demonstrate the superiority of NNBF-P compared to ZFBF, and MMSE while NNBF can have lower performances than MMSE and ZFBF in some experiment settings. It can also demonstrate the effectiveness of joint design framework with respect to NNBF.
6/13/2024