On the Application of Egocentric Computer Vision to Industrial Scenarios
2406.07738

0
0
Abstract
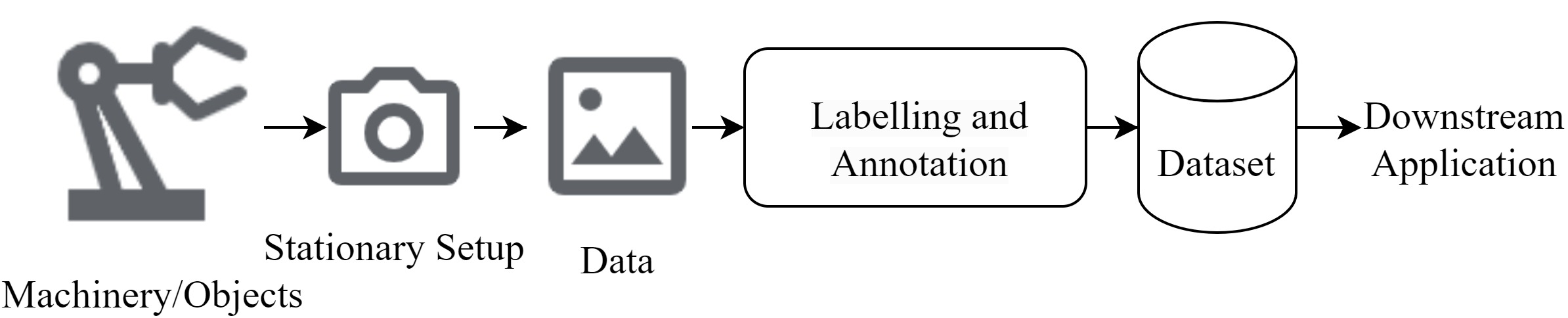
Egocentric vision aims to capture and analyse the world from the first-person perspective. We explore the possibilities for egocentric wearable devices to improve and enhance industrial use cases w.r.t. data collection, annotation, labelling and downstream applications. This would contribute to easier data collection and allow users to provide additional context. We envision that this approach could serve as a supplement to the traditional industrial Machine Vision workflow. Code, Dataset and related resources will be available at: https://github.com/Vivek9Chavan/EgoVis24
Create account to get full access
Overview
- The research paper discusses the application of egocentric computer vision, which involves using cameras mounted on a person's head or clothing, to industrial scenarios.
- It explores the potential benefits and challenges of using this technology in industrial settings, such as manufacturing, maintenance, and training.
- The paper also reviews related work in the field of egocentric computer vision and its applications.
Plain English Explanation
Egocentric computer vision is a technology that uses cameras mounted on a person's head or clothing to capture the wearer's perspective. This can be particularly useful in industrial settings, where workers need to have their hands free to perform tasks while still having access to visual information.
The paper explores how egocentric computer vision can be applied in various industrial scenarios, such as manufacturing, maintenance, and training. For example, workers could use this technology to receive step-by-step instructions or have their actions monitored and analyzed to improve efficiency and safety.
The paper also reviews the existing research in the field of egocentric computer vision, including studies on 3D human pose estimation and identification of conversation partners. This provides context for the current state of the technology and its potential applications.
Technical Explanation
The paper explores the use of egocentric computer vision in industrial settings, which involves using cameras mounted on a person's head or clothing to capture their perspective. The authors review the existing research in this field, including studies on 3D human pose estimation, instance tracking in 3D scenes, and identification of conversation partners from egocentric video.
The researchers discuss the potential benefits of using egocentric computer vision in industrial scenarios, such as providing hands-free access to visual information, monitoring worker performance and safety, and enhancing training and instruction. They also address the challenges, such as the need for robust computer vision algorithms and the integration of the technology into existing industrial workflows.
The paper does not present any new experimental results or technical contributions. Instead, it serves as a review and discussion of the current state of the art in the application of egocentric computer vision to industrial scenarios.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a useful overview of the potential applications of egocentric computer vision in industrial settings, but it does not delve deeply into the specific technical challenges or solutions. The authors acknowledge the need for robust computer vision algorithms and the integration of the technology into existing industrial workflows, but they do not provide detailed insights or proposals on how these challenges could be addressed.
Additionally, the paper does not discuss the potential privacy and ethical concerns that may arise from the use of egocentric cameras in industrial environments, such as worker monitoring and the collection of personal data. These are important considerations that should be addressed in the future research and deployment of this technology.
Overall, the paper serves as a valuable starting point for understanding the potential of egocentric computer vision in industrial scenarios, but more in-depth research and analysis are needed to fully explore the feasibility and implications of this technology.
Conclusion
The research paper provides a high-level overview of the application of egocentric computer vision in industrial scenarios, highlighting the potential benefits and challenges of this technology. By reviewing the existing research in the field, the authors demonstrate the current state of the art and suggest that egocentric computer vision could be a valuable tool for tasks such as manufacturing, maintenance, and training.
However, the paper does not delve deeply into the specific technical and practical challenges that would need to be addressed for the successful deployment of egocentric computer vision in industrial settings. Future research should focus on developing robust computer vision algorithms, addressing privacy and ethical concerns, and integrating the technology seamlessly into existing industrial workflows.
Overall, the paper serves as a valuable starting point for understanding the potential of egocentric computer vision in industrial scenarios and highlights the need for further research and development in this area.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
EgoGen: An Egocentric Synthetic Data Generator
Gen Li, Kaifeng Zhao, Siwei Zhang, Xiaozhong Lyu, Mihai Dusmanu, Yan Zhang, Marc Pollefeys, Siyu Tang

0
0
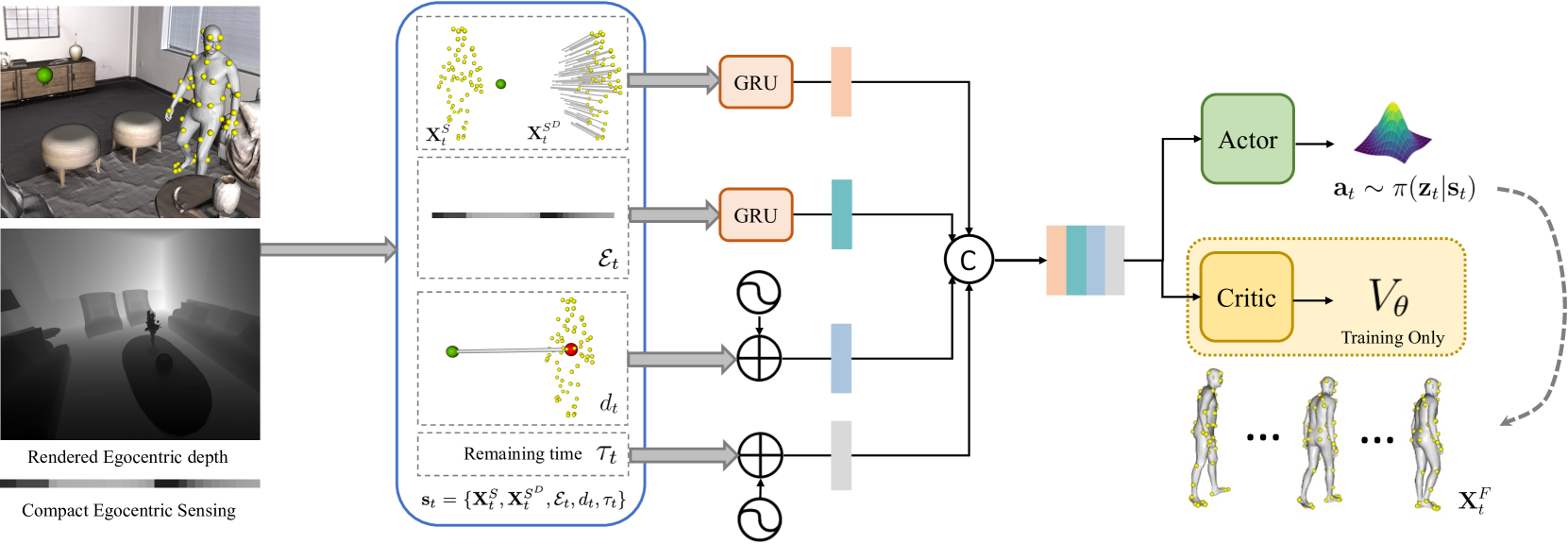
Understanding the world in first-person view is fundamental in Augmented Reality (AR). This immersive perspective brings dramatic visual changes and unique challenges compared to third-person views. Synthetic data has empowered third-person-view vision models, but its application to embodied egocentric perception tasks remains largely unexplored. A critical challenge lies in simulating natural human movements and behaviors that effectively steer the embodied cameras to capture a faithful egocentric representation of the 3D world. To address this challenge, we introduce EgoGen, a new synthetic data generator that can produce accurate and rich ground-truth training data for egocentric perception tasks. At the heart of EgoGen is a novel human motion synthesis model that directly leverages egocentric visual inputs of a virtual human to sense the 3D environment. Combined with collision-avoiding motion primitives and a two-stage reinforcement learning approach, our motion synthesis model offers a closed-loop solution where the embodied perception and movement of the virtual human are seamlessly coupled. Compared to previous works, our model eliminates the need for a pre-defined global path, and is directly applicable to dynamic environments. Combined with our easy-to-use and scalable data generation pipeline, we demonstrate EgoGen's efficacy in three tasks: mapping and localization for head-mounted cameras, egocentric camera tracking, and human mesh recovery from egocentric views. EgoGen will be fully open-sourced, offering a practical solution for creating realistic egocentric training data and aiming to serve as a useful tool for egocentric computer vision research. Refer to our project page: https://ego-gen.github.io/.
4/12/2024
🏷️
3D Human Pose Perception from Egocentric Stereo Videos
Hiroyasu Akada, Jian Wang, Vladislav Golyanik, Christian Theobalt

0
0
While head-mounted devices are becoming more compact, they provide egocentric views with significant self-occlusions of the device user. Hence, existing methods often fail to accurately estimate complex 3D poses from egocentric views. In this work, we propose a new transformer-based framework to improve egocentric stereo 3D human pose estimation, which leverages the scene information and temporal context of egocentric stereo videos. Specifically, we utilize 1) depth features from our 3D scene reconstruction module with uniformly sampled windows of egocentric stereo frames, and 2) human joint queries enhanced by temporal features of the video inputs. Our method is able to accurately estimate human poses even in challenging scenarios, such as crouching and sitting. Furthermore, we introduce two new benchmark datasets, i.e., UnrealEgo2 and UnrealEgo-RW (RealWorld). The proposed datasets offer a much larger number of egocentric stereo views with a wider variety of human motions than the existing datasets, allowing comprehensive evaluation of existing and upcoming methods. Our extensive experiments show that the proposed approach significantly outperforms previous methods. We will release UnrealEgo2, UnrealEgo-RW, and trained models on our project page.
5/16/2024
📉
Instance Tracking in 3D Scenes from Egocentric Videos
Yunhan Zhao, Haoyu Ma, Shu Kong, Charless Fowlkes

0
0
Egocentric sensors such as AR/VR devices capture human-object interactions and offer the potential to provide task-assistance by recalling 3D locations of objects of interest in the surrounding environment. This capability requires instance tracking in real-world 3D scenes from egocentric videos (IT3DEgo). We explore this problem by first introducing a new benchmark dataset, consisting of RGB and depth videos, per-frame camera pose, and instance-level annotations in both 2D camera and 3D world coordinates. We present an evaluation protocol which evaluates tracking performance in 3D coordinates with two settings for enrolling instances to track: (1) single-view online enrollment where an instance is specified on-the-fly based on the human wearer's interactions. and (2) multi-view pre-enrollment where images of an instance to be tracked are stored in memory ahead of time. To address IT3DEgo, we first re-purpose methods from relevant areas, e.g., single object tracking (SOT) -- running SOT methods to track instances in 2D frames and lifting them to 3D using camera pose and depth. We also present a simple method that leverages pretrained segmentation and detection models to generate proposals from RGB frames and match proposals with enrolled instance images. Our experiments show that our method (with no finetuning) significantly outperforms SOT-based approaches in the egocentric setting. We conclude by arguing that the problem of egocentric instance tracking is made easier by leveraging camera pose and using a 3D allocentric (world) coordinate representation.
6/10/2024
A Survey on 3D Egocentric Human Pose Estimation
Md Mushfiqur Azam, Kevin Desai

0
0
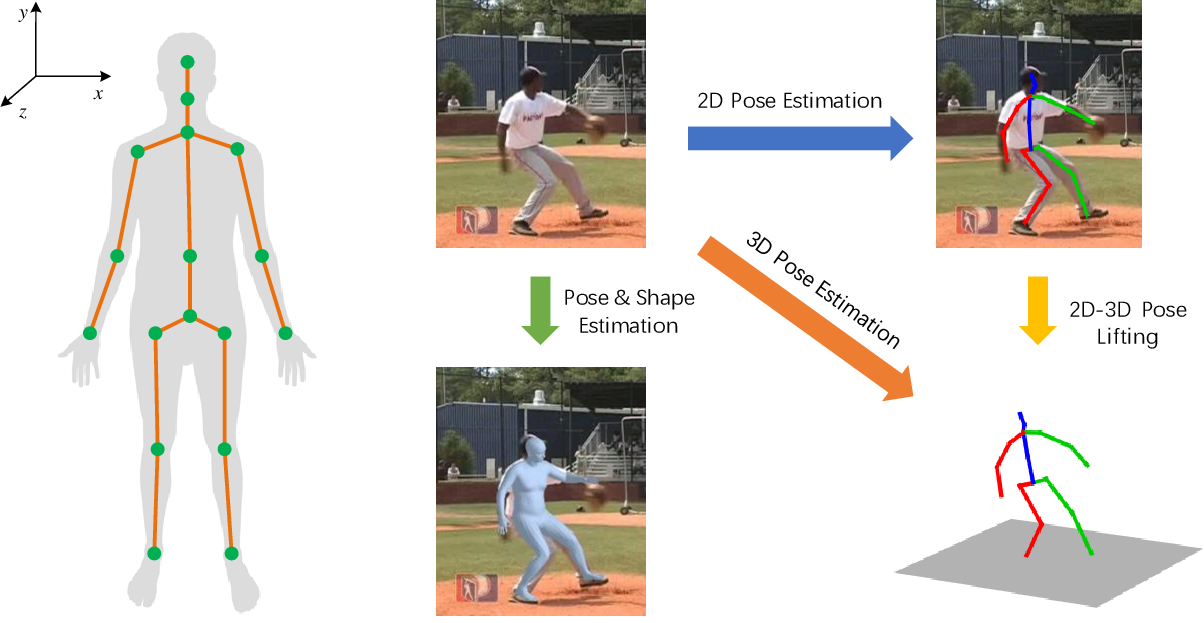
Egocentric human pose estimation aims to estimate human body poses and develop body representations from a first-person camera perspective. It has gained vast popularity in recent years because of its wide range of applications in sectors like XR-technologies, human-computer interaction, and fitness tracking. However, to the best of our knowledge, there is no systematic literature review based on the proposed solutions regarding egocentric 3D human pose estimation. To that end, the aim of this survey paper is to provide an extensive overview of the current state of egocentric pose estimation research. In this paper, we categorize and discuss the popular datasets and the different pose estimation models, highlighting the strengths and weaknesses of different methods by comparative analysis. This survey can be a valuable resource for both researchers and practitioners in the field, offering insights into key concepts and cutting-edge solutions in egocentric pose estimation, its wide-ranging applications, as well as the open problems with future scope.
4/19/2024