A Survey on 3D Egocentric Human Pose Estimation
2403.17893

0
0
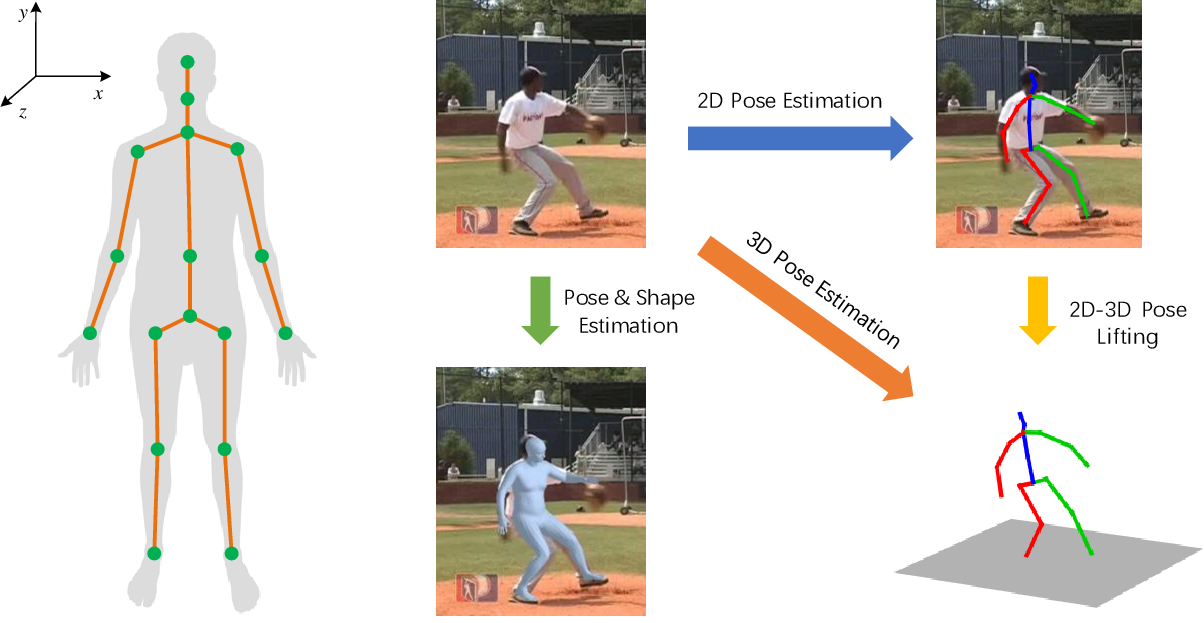
Abstract
Egocentric human pose estimation aims to estimate human body poses and develop body representations from a first-person camera perspective. It has gained vast popularity in recent years because of its wide range of applications in sectors like XR-technologies, human-computer interaction, and fitness tracking. However, to the best of our knowledge, there is no systematic literature review based on the proposed solutions regarding egocentric 3D human pose estimation. To that end, the aim of this survey paper is to provide an extensive overview of the current state of egocentric pose estimation research. In this paper, we categorize and discuss the popular datasets and the different pose estimation models, highlighting the strengths and weaknesses of different methods by comparative analysis. This survey can be a valuable resource for both researchers and practitioners in the field, offering insights into key concepts and cutting-edge solutions in egocentric pose estimation, its wide-ranging applications, as well as the open problems with future scope.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper provides a comprehensive survey of 3D egocentric human pose estimation, which involves using wearable cameras or other sensors to capture a person's body movements and position in 3D space from their own perspective.
- The survey covers the key challenges in this field, the scope of the research, and the various approaches and techniques that have been proposed by researchers.
- It also highlights the potential applications of this technology, such as in virtual and augmented reality, human-computer interaction, and sports and rehabilitation.
Plain English Explanation
3D egocentric human pose estimation is a technology that allows us to capture a person's body movements and position in 3D space from their own perspective. This is typically done using wearable cameras or other sensors that the person carries with them.
This technology has many potential applications, such as in virtual and augmented reality, where it can be used to create more immersive and interactive experiences. It can also be used in human-computer interaction, to allow people to control devices or interact with digital content using natural body movements.
Another potential application is in sports and rehabilitation, where the technology can be used to analyze a person's movements and posture, and provide feedback or guidance to help them improve their performance or recovery.
However, there are also several challenges involved in 3D egocentric human pose estimation. For example, the camera or sensor needs to be able to accurately capture the person's movements, even when they are in complex or occluded environments. There are also challenges in processing and interpreting the data captured by the sensors.
Researchers have been exploring various approaches to address these challenges, such as using machine learning algorithms to analyze the sensor data and reconstruct the person's 3D pose. They have also been exploring new types of sensors, such as event cameras that capture rapid changes in the environment, which can help improve the accuracy and robustness of the 3D pose estimation.
Overall, 3D egocentric human pose estimation is a promising and rapidly evolving field that has the potential to enable a wide range of innovative applications across various domains.
Technical Explanation
The paper provides a comprehensive survey of the state-of-the-art in 3D egocentric human pose estimation. The authors first discuss the key challenges in this field, such as the need to accurately capture the person's movements in complex and dynamic environments, the difficulty of dealing with occlusions and self-occlusions, and the challenges of processing and interpreting the sensor data.
The authors then outline the scope of the survey, which covers a range of approaches and techniques that have been proposed by researchers to address these challenges. This includes methods that use machine learning algorithms to analyze the sensor data and reconstruct the person's 3D pose, as well as approaches that leverage new types of sensors, such as event cameras, to improve the accuracy and robustness of the 3D pose estimation.
The survey also discusses the potential applications of 3D egocentric human pose estimation, such as in virtual and augmented reality, human-computer interaction, and sports and rehabilitation. The authors highlight how this technology can enable more immersive and interactive experiences, allow for natural body-based interactions with digital content, and provide valuable insights into a person's movements and posture.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive and well-researched overview of the field of 3D egocentric human pose estimation. The authors have done a thorough job of identifying the key challenges in this area and highlighting the various approaches and techniques that have been proposed by researchers to address these challenges.
However, the paper does not delve too deeply into the specific limitations or potential issues with the different approaches that are discussed. For example, it does not explore the trade-offs between the accuracy and computational complexity of the various machine learning algorithms that have been proposed, or the potential privacy concerns associated with the use of wearable sensors to capture a person's movements.
Additionally, the paper does not provide much critical analysis or commentary on the overall state of the field and the potential avenues for future research. While it does touch on some emerging trends, such as the use of event cameras, it could have gone further in exploring the potential for new sensing modalities or the need for more comprehensive and diverse datasets to train and evaluate 3D pose estimation models.
Overall, the paper provides a solid foundation for understanding the current state of 3D egocentric human pose estimation, but could benefit from a more critical and forward-looking perspective.
Conclusion
This survey paper provides a comprehensive overview of the field of 3D egocentric human pose estimation, which involves using wearable cameras or other sensors to capture a person's body movements and position in 3D space from their own perspective.
The paper covers the key challenges in this field, such as the need to accurately capture the person's movements in complex and dynamic environments, as well as the various approaches and techniques that have been proposed by researchers to address these challenges. This includes methods that use machine learning algorithms to analyze sensor data and reconstruct 3D pose, as well as approaches that leverage new types of sensors, such as event cameras, to improve accuracy and robustness.
The paper also highlights the potential applications of 3D egocentric human pose estimation, such as in virtual and augmented reality, human-computer interaction, and sports and rehabilitation. While the paper could have provided more critical analysis and commentary on the state of the field, it nonetheless serves as a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners interested in this rapidly evolving area of technology.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🏷️
3D Human Pose Perception from Egocentric Stereo Videos
Hiroyasu Akada, Jian Wang, Vladislav Golyanik, Christian Theobalt

0
0
While head-mounted devices are becoming more compact, they provide egocentric views with significant self-occlusions of the device user. Hence, existing methods often fail to accurately estimate complex 3D poses from egocentric views. In this work, we propose a new transformer-based framework to improve egocentric stereo 3D human pose estimation, which leverages the scene information and temporal context of egocentric stereo videos. Specifically, we utilize 1) depth features from our 3D scene reconstruction module with uniformly sampled windows of egocentric stereo frames, and 2) human joint queries enhanced by temporal features of the video inputs. Our method is able to accurately estimate human poses even in challenging scenarios, such as crouching and sitting. Furthermore, we introduce two new benchmark datasets, i.e., UnrealEgo2 and UnrealEgo-RW (RealWorld). The proposed datasets offer a much larger number of egocentric stereo views with a wider variety of human motions than the existing datasets, allowing comprehensive evaluation of existing and upcoming methods. Our extensive experiments show that the proposed approach significantly outperforms previous methods. We will release UnrealEgo2, UnrealEgo-RW, and trained models on our project page.
5/16/2024

Human Modelling and Pose Estimation Overview
Pawel Knap

0
0
Human modelling and pose estimation stands at the crossroads of Computer Vision, Computer Graphics, and Machine Learning. This paper presents a thorough investigation of this interdisciplinary field, examining various algorithms, methodologies, and practical applications. It explores the diverse range of sensor technologies relevant to this domain and delves into a wide array of application areas. Additionally, we discuss the challenges and advancements in 2D and 3D human modelling methodologies, along with popular datasets, metrics, and future research directions. The main contribution of this paper lies in its up-to-date comparison of state-of-the-art (SOTA) human pose estimation algorithms in both 2D and 3D domains. By providing this comprehensive overview, the paper aims to enhance understanding of 3D human modelling and pose estimation, offering insights into current SOTA achievements, challenges, and future prospects within the field.
6/28/2024

In My Perspective, In My Hands: Accurate Egocentric 2D Hand Pose and Action Recognition
Wiktor Mucha, Martin Kampel

0
0
Action recognition is essential for egocentric video understanding, allowing automatic and continuous monitoring of Activities of Daily Living (ADLs) without user effort. Existing literature focuses on 3D hand pose input, which requires computationally intensive depth estimation networks or wearing an uncomfortable depth sensor. In contrast, there has been insufficient research in understanding 2D hand pose for egocentric action recognition, despite the availability of user-friendly smart glasses in the market capable of capturing a single RGB image. Our study aims to fill this research gap by exploring the field of 2D hand pose estimation for egocentric action recognition, making two contributions. Firstly, we introduce two novel approaches for 2D hand pose estimation, namely EffHandNet for single-hand estimation and EffHandEgoNet, tailored for an egocentric perspective, capturing interactions between hands and objects. Both methods outperform state-of-the-art models on H2O and FPHA public benchmarks. Secondly, we present a robust action recognition architecture from 2D hand and object poses. This method incorporates EffHandEgoNet, and a transformer-based action recognition method. Evaluated on H2O and FPHA datasets, our architecture has a faster inference time and achieves an accuracy of 91.32% and 94.43%, respectively, surpassing state of the art, including 3D-based methods. Our work demonstrates that using 2D skeletal data is a robust approach for egocentric action understanding. Extensive evaluation and ablation studies show the impact of the hand pose estimation approach, and how each input affects the overall performance.
4/16/2024
📊
Multi-person 3D pose estimation from unlabelled data
Daniel Rodriguez-Criado, Pilar Bachiller, George Vogiatzis, Luis J. Manso

0
0
Its numerous applications make multi-human 3D pose estimation a remarkably impactful area of research. Nevertheless, assuming a multiple-view system composed of several regular RGB cameras, 3D multi-pose estimation presents several challenges. First of all, each person must be uniquely identified in the different views to separate the 2D information provided by the cameras. Secondly, the 3D pose estimation process from the multi-view 2D information of each person must be robust against noise and potential occlusions in the scenario. In this work, we address these two challenges with the help of deep learning. Specifically, we present a model based on Graph Neural Networks capable of predicting the cross-view correspondence of the people in the scenario along with a Multilayer Perceptron that takes the 2D points to yield the 3D poses of each person. These two models are trained in a self-supervised manner, thus avoiding the need for large datasets with 3D annotations.
4/10/2024