ARCADE: An Augmented Reality Display Environment for Multimodal Interaction with Conversational Agents

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- ARCADE is an Augmented Reality (AR) system that enables multimodal interaction with conversational agents.
- It combines voice, gesture, and gaze inputs to allow users to engage with virtual characters in an immersive AR environment.
- The system aims to enhance the user experience and facilitate more natural and intuitive interactions with embodied AI agents.
Plain English Explanation
ARCADE: An Augmented Reality Display Environment for Multimodal Interaction with Conversational Agents describes a novel system that uses augmented reality (AR) technology to create an interactive environment for conversing with virtual characters.
The key idea is to allow users to interact with these AI-powered agents in a more natural and intuitive way, leveraging multiple input modalities like voice, gestures, and gaze. By combining these various forms of interaction, the researchers believe they can create a more engaging and seamless user experience compared to traditional text-based or screen-based interfaces.
For example, a user might be able to speak to a virtual character, point at objects in the environment, and make eye contact - all while the character responds and behaves as if it's a real person in the same physical space. This multimodal approach aims to make the interaction feel more immersive and lifelike.
Technical Explanation
ARCADE is an AR system that enables users to interact with conversational agents through voice, gestures, and gaze. It consists of several key components:
- AR Display: A head-mounted display (HMD) or smartphone-based AR system that overlays virtual characters and other content onto the real-world environment.
- Multimodal Input: Sensors that capture the user's voice, hand movements, and eye gaze to enable natural interaction with the virtual agents.
- Conversational Agent: An AI-powered virtual character that can engage in dialogue, respond to the user's inputs, and behave in a lifelike manner.
- Spatial Mapping: Techniques to map the physical environment and track the user's position and orientation, allowing the virtual content to be properly aligned and integrated.
The researchers conducted various experiments to evaluate the ARCADE system, assessing factors like user experience, task performance, and the quality of the conversational interactions. Their results suggest that the multimodal approach can indeed enhance the user's sense of engagement and immersion when interacting with embodied AI agents.
Critical Analysis
The ARCADE system represents an interesting step forward in the field of human-agent interaction, leveraging the capabilities of augmented reality to enable more natural and intuitive forms of communication.
However, the paper acknowledges several limitations and areas for further research. For example, the current system is limited to a relatively small and constrained environment, and the conversational abilities of the virtual agents are still relatively basic compared to human-level dialogue. There are also potential challenges around scalability, robustness, and the long-term effects of this type of interaction on users.
Additionally, while the multimodal approach seems promising, the paper does not provide a thorough comparison to more traditional interface modalities, such as screen-based or voice-only interactions. It would be valuable to understand how ARCADE's performance and user experience compares to these alternative approaches.
Overall, the ARCADE system represents an exciting step forward, but there is still significant work to be done to fully realize the potential of AR-based embodied conversational agents. Continued research and development in this area could lead to more engaging and effective human-AI interaction experiences.
Conclusion
ARCADE is an innovative augmented reality system that aims to enhance the user experience of interacting with conversational agents. By combining voice, gesture, and gaze inputs, the system allows for more natural and immersive interactions, potentially leading to better engagement and more effective communication with embodied AI.
While the current implementation has some limitations, the research demonstrates the promise of this multimodal approach and highlights the potential for AR to transform the way humans and AI-powered virtual characters can collaborate and converse. As the technology continues to evolve, systems like ARCADE may play an increasingly important role in the future of human-agent interaction.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
ARCADE: An Augmented Reality Display Environment for Multimodal Interaction with Conversational Agents
Carolin Schindler, Daiki Mayumi, Yuki Matsuda, Niklas Rach, Keiichi Yasumoto, Wolfgang Minker
Making the interaction with embodied conversational agents accessible in a ubiquitous and natural manner is not only a question of the underlying software but also brings challenges in terms of the technical system that is used to display them. To this end, we present our spatial augmented reality system ARCADE, which can be utilized like a conventional monitor for displaying virtual agents as well as additional content. With its optical-see-through display, ARCADE creates the illusion of the agent being in the room similarly to a human. The applicability of our system is demonstrated in two different dialogue scenarios, which are included in the video accompanying this paper at https://youtu.be/9nH4c4Q-ooE.
Read more8/13/2024

0
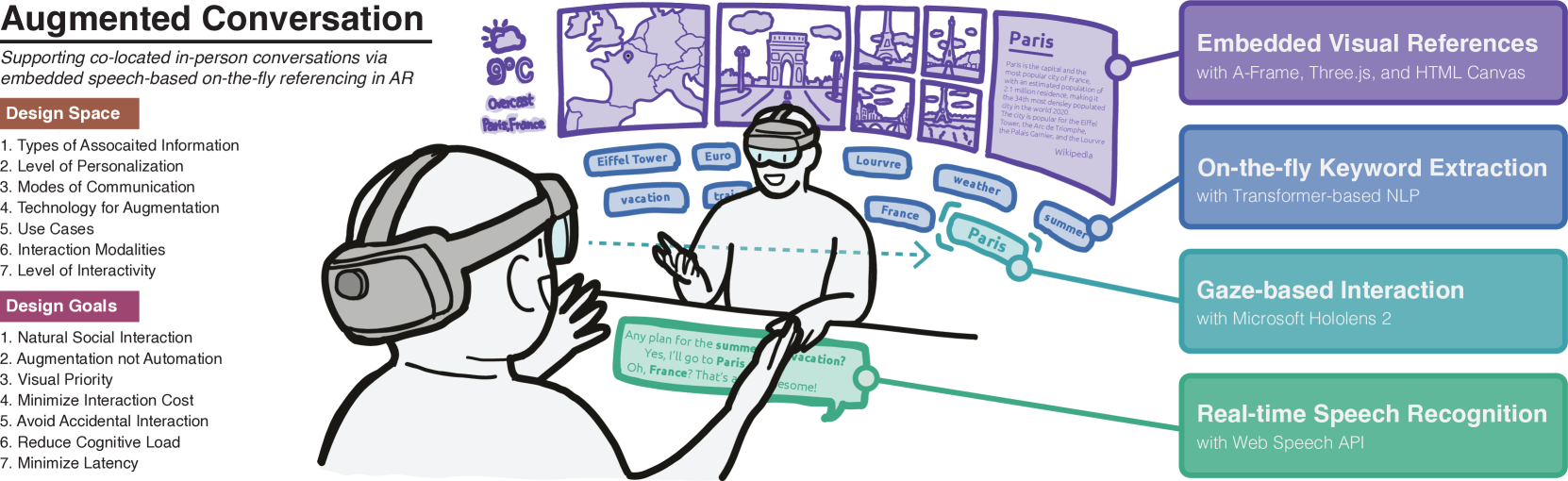
Augmented Conversation with Embedded Speech-Driven On-the-Fly Referencing in AR
Shivesh Jadon, Mehrad Faridan, Edward Mah, Rajan Vaish, Wesley Willett, Ryo Suzuki
This paper introduces the concept of augmented conversation, which aims to support co-located in-person conversations via embedded speech-driven on-the-fly referencing in augmented reality (AR). Today computing technologies like smartphones allow quick access to a variety of references during the conversation. However, these tools often create distractions, reducing eye contact and forcing users to focus their attention on phone screens and manually enter keywords to access relevant information. In contrast, AR-based on-the-fly referencing provides relevant visual references in real-time, based on keywords extracted automatically from the spoken conversation. By embedding these visual references in AR around the conversation partner, augmented conversation reduces distraction and friction, allowing users to maintain eye contact and supporting more natural social interactions. To demonstrate this concept, we developed system, a Hololens-based interface that leverages real-time speech recognition, natural language processing and gaze-based interactions for on-the-fly embedded visual referencing. In this paper, we explore the design space of visual referencing for conversations, and describe our our implementation -- building on seven design guidelines identified through a user-centered design process. An initial user study confirms that our system decreases distraction and friction in conversations compared to smartphone searches, while providing highly useful and relevant information.
Read more5/30/2024
🔎

0
Leveraging Artificial Intelligence to Promote Awareness in Augmented Reality Systems
Wangfan Li, Rohit Mallick, Carlos Toxtli-Hernandez, Christopher Flathmann, Nathan J. McNeese
Recent developments in artificial intelligence (AI) have permeated through an array of different immersive environments, including virtual, augmented, and mixed realities. AI brings a wealth of potential that centers on its ability to critically analyze environments, identify relevant artifacts to a goal or action, and then autonomously execute decision-making strategies to optimize the reward-to-risk ratio. However, the inherent benefits of AI are not without disadvantages as the autonomy and communication methodology can interfere with the human's awareness of their environment. More specifically in the case of autonomy, the relevant human-computer interaction literature cites that high autonomy results in an out-of-the-loop experience for the human such that they are not aware of critical artifacts or situational changes that require their attention. At the same time, low autonomy of an AI system can limit the human's own autonomy with repeated requests to approve its decisions. In these circumstances, humans enter into supervisor roles, which tend to increase their workload and, therefore, decrease their awareness in a multitude of ways. In this position statement, we call for the development of human-centered AI in immersive environments to sustain and promote awareness. It is our position then that we believe with the inherent risk presented in both AI and AR/VR systems, we need to examine the interaction between them when we integrate the two to create a new system for any unforeseen risks, and that it is crucial to do so because of its practical application in many high-risk environments.
Read more5/10/2024


0
Augmented Library: Toward Enriching Physical Library Experience Using HMD-Based Augmented Reality
Qianjie Wei, Jingling Zhang, Pengqi Wang, Xiaofu Jin, Mingming Fan
Despite the rise of digital libraries and online reading platforms, physical libraries still offer unique benefits for education and community engagement. However, due to the convenience of digital resources, physical library visits, especially by college students, have declined. This underscores the need to better engage these users. Augmented Reality (AR) could potentially bridge the gap between the physical and digital worlds. In this paper, we present textit{Augmented Library}, an HMD-based AR system designed to revitalize the physical library experience. By creating interactive features that enhance book discovery, encourage community engagement, and cater to diverse user needs, textit{Augmented Library} combines digital convenience with physical libraries' rich experiences. This paper discusses the development of the system and preliminary user feedback on its impact on student engagement in physical libraries.
Read more8/13/2024