Leveraging Artificial Intelligence to Promote Awareness in Augmented Reality Systems
2405.05916

0
0
🔎
Abstract
Recent developments in artificial intelligence (AI) have permeated through an array of different immersive environments, including virtual, augmented, and mixed realities. AI brings a wealth of potential that centers on its ability to critically analyze environments, identify relevant artifacts to a goal or action, and then autonomously execute decision-making strategies to optimize the reward-to-risk ratio. However, the inherent benefits of AI are not without disadvantages as the autonomy and communication methodology can interfere with the human's awareness of their environment. More specifically in the case of autonomy, the relevant human-computer interaction literature cites that high autonomy results in an out-of-the-loop experience for the human such that they are not aware of critical artifacts or situational changes that require their attention. At the same time, low autonomy of an AI system can limit the human's own autonomy with repeated requests to approve its decisions. In these circumstances, humans enter into supervisor roles, which tend to increase their workload and, therefore, decrease their awareness in a multitude of ways. In this position statement, we call for the development of human-centered AI in immersive environments to sustain and promote awareness. It is our position then that we believe with the inherent risk presented in both AI and AR/VR systems, we need to examine the interaction between them when we integrate the two to create a new system for any unforeseen risks, and that it is crucial to do so because of its practical application in many high-risk environments.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have been integrated into immersive environments like virtual, augmented, and mixed reality.
- AI offers benefits such as analyzing environments, identifying relevant artifacts, and executing autonomous decision-making strategies to optimize outcomes.
- However, the autonomy and communication methods of AI can interfere with the human user's awareness of their surroundings, leading to an "out-of-the-loop" experience.
- Human-computer interaction research shows that high AI autonomy can make users unaware of critical changes, while low autonomy can increase their workload as supervisors.
Plain English Explanation
Artificial intelligence (AI) has been integrated into immersive environments like virtual and augmented reality. AI can analyze these environments, identify important things, and make decisions to optimize outcomes. This is beneficial, but the autonomy and communication of AI can also interfere with the human user's awareness of what's happening around them.
For example, if the AI system has a lot of autonomy, the human user may not be aware of critical changes in the environment that require their attention. On the other hand, if the AI system has low autonomy, the human may have to constantly approve its decisions, increasing their workload and reducing their awareness. In these cases, humans end up in a "supervisor" role, which can further decrease their overall awareness.
The researchers believe we need to develop "human-centered AI" for these immersive environments. This means designing AI systems that sustain and promote the human user's awareness, rather than interfering with it. It's crucial to examine the interaction between AI and immersive technologies to identify and address any unforeseen risks, especially in high-risk applications.
Technical Explanation
The paper discusses the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into virtual, augmented, and mixed reality environments. AI brings benefits such as the ability to analyze environments, identify relevant artifacts, and execute autonomous decision-making strategies to optimize outcomes.
However, the researchers highlight that the inherent autonomy and communication methodology of AI can interfere with the human user's awareness of their surroundings. Specifically, they cite human-computer interaction literature showing that high AI autonomy can result in an "out-of-the-loop" experience where the user is unaware of critical changes. Conversely, low AI autonomy can increase the human's workload as they have to constantly approve the system's decisions, again decreasing their overall awareness.
In these situations, humans effectively become supervisors of the AI system, which can further reduce their situational awareness across multiple dimensions. The paper calls for the development of "human-centered AI" in immersive environments to sustain and promote user awareness, rather than diminish it.
Critical Analysis
The paper raises valid concerns about the potential pitfalls of integrating highly autonomous AI systems into immersive environments. The cited research on the "out-of-the-loop" phenomenon and increased human workload as supervisors is well-supported and highlights important tradeoffs to consider.
However, the paper does not provide specific solutions or a roadmap for designing the proposed "human-centered AI" systems. More research is needed to understand the ideal balance of autonomy, transparency, and human involvement for different immersive applications and user tasks.
Additionally, the paper could have explored other potential issues, such as AI-induced cognitive attacks or challenges in establishing situational awareness in these complex, dynamic environments. Addressing proactive interventions and telepresence awareness could also be important considerations.
Overall, the paper provides a solid foundation for understanding the challenges of integrating AI into immersive technologies, but more research is needed to develop practical solutions that truly prioritize human awareness in these environments.
Conclusion
This paper highlights the need to carefully consider the relationship between artificial intelligence (AI) and immersive technologies like virtual and augmented reality. While AI offers many benefits in these environments, the autonomy and communication methods of AI systems can interfere with the human user's awareness of their surroundings.
The researchers call for the development of "human-centered AI" that sustains and promotes user awareness, rather than diminishing it. Addressing the tradeoffs between AI autonomy and human involvement is crucial, especially in high-risk applications where situational awareness is paramount.
Overall, this paper serves as an important starting point for further research and design considerations to ensure the integration of AI and immersive environments enhances, rather than hinders, the human user's experience and safety.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
📉
Protecting Human Users Against Cognitive Attacks in Immersive Environments
Yan-Ming Chiou, Bob Price, Chien-Chung Shen, Syed Ali Asif

0
0
Integrating mixed reality (MR) with artificial intelligence (AI) technologies, including vision, language, audio, reasoning, and planning, enables the AI-powered MR assistant [1] to substantially elevate human efficiency. This enhancement comes from situational awareness, quick access to essential information, and support in learning new skills in the right context throughout everyday tasks. This blend transforms interactions with both the virtual and physical environments, catering to a range of skill levels and personal preferences. For instance, computer vision enables the understanding of the user's environment, allowing for the provision of timely and relevant digital overlays in MR systems. At the same time, language models enhance comprehension of contextual information and support voice-activated dialogue to answer user questions. However, as AI-driven MR systems advance, they also unveil new vulnerabilities, posing a threat to user safety by potentially exposing them to grave dangers [5, 6].
5/10/2024
📶
Human-Modeling in Sequential Decision-Making: An Analysis through the Lens of Human-Aware AI
Silvia Tulli, Stylianos Loukas Vasileiou, Sarath Sreedharan

0
0
Human-aware has become a popular keyword used to describe a particular class of AI systems that are designed to work and interact with humans. While there exists a surprising level of consistency among the works that use the label human-aware, the term itself mostly remains poorly understood. In this work, we retroactively try to provide an account of what constitutes a human-aware AI system. We see that human-aware AI is a design-oriented paradigm, one that focuses on the need for modeling the humans it may interact with. Additionally, we see that this paradigm offers us intuitive dimensions to understand and categorize the kinds of interactions these systems might have with humans. We show the pedagogical value of these dimensions by using them as a tool to understand and review the current landscape of work related to human-AI systems that purport some form of human modeling. To fit the scope of a workshop paper, we specifically narrowed our review to papers that deal with sequential decision-making and were published in a major AI conference in the last three years. Our analysis helps identify the space of potential research problems that are currently being overlooked. We perform additional analysis on the degree to which these works make explicit reference to results from social science and whether they actually perform user-studies to validate their systems. We also provide an accounting of the various AI methods used by these works.
5/14/2024

Developing Situational Awareness for Joint Action with Autonomous Vehicles
Robert Kaufman, David Kirsh, Nadir Weibel

0
0
Unanswered questions about how human-AV interaction designers can support rider's informational needs hinders Autonomous Vehicles (AV) adoption. To achieve joint human-AV action goals - such as safe transportation, trust, or learning from an AV - sufficient situational awareness must be held by the human, AV, and human-AV system collectively. We present a systems-level framework that integrates cognitive theories of joint action and situational awareness as a means to tailor communications that meet the criteria necessary for goal success. This framework is based on four components of the shared situation: AV traits, action goals, subject-specific traits and states, and the situated driving context. AV communications should be tailored to these factors and be sensitive when they change. This framework can be useful for understanding individual, shared, and distributed human-AV situational awareness and designing for future AV communications that meet the informational needs and goals of diverse groups and in diverse driving contexts.
4/19/2024
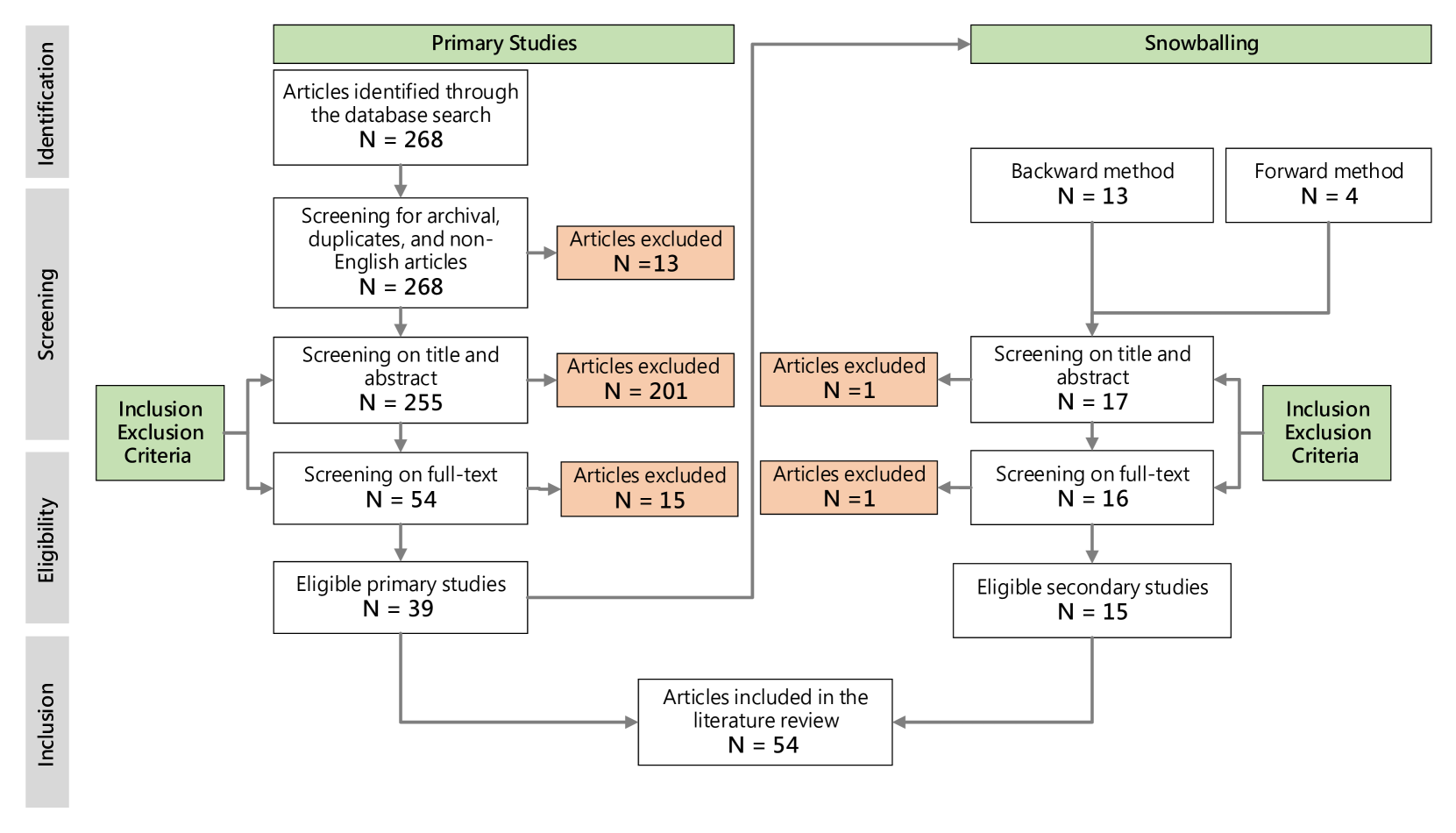
From Explainable to Interactive AI: A Literature Review on Current Trends in Human-AI Interaction
Muhammad Raees, Inge Meijerink, Ioanna Lykourentzou, Vassilis-Javed Khan, Konstantinos Papangelis

0
0
AI systems are increasingly being adopted across various domains and application areas. With this surge, there is a growing research focus and societal concern for actively involving humans in developing, operating, and adopting these systems. Despite this concern, most existing literature on AI and Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) primarily focuses on explaining how AI systems operate and, at times, allowing users to contest AI decisions. Existing studies often overlook more impactful forms of user interaction with AI systems, such as giving users agency beyond contestability and enabling them to adapt and even co-design the AI's internal mechanics. In this survey, we aim to bridge this gap by reviewing the state-of-the-art in Human-Centered AI literature, the domain where AI and HCI studies converge, extending past Explainable and Contestable AI, delving into the Interactive AI and beyond. Our analysis contributes to shaping the trajectory of future Interactive AI design and advocates for a more user-centric approach that provides users with greater agency, fostering not only their understanding of AI's workings but also their active engagement in its development and evolution.
5/27/2024