Are We There Yet? Unravelling Usability Challenges and Opportunities in Collaborative Immersive Analytics for Domain Experts
2406.13918

0
0
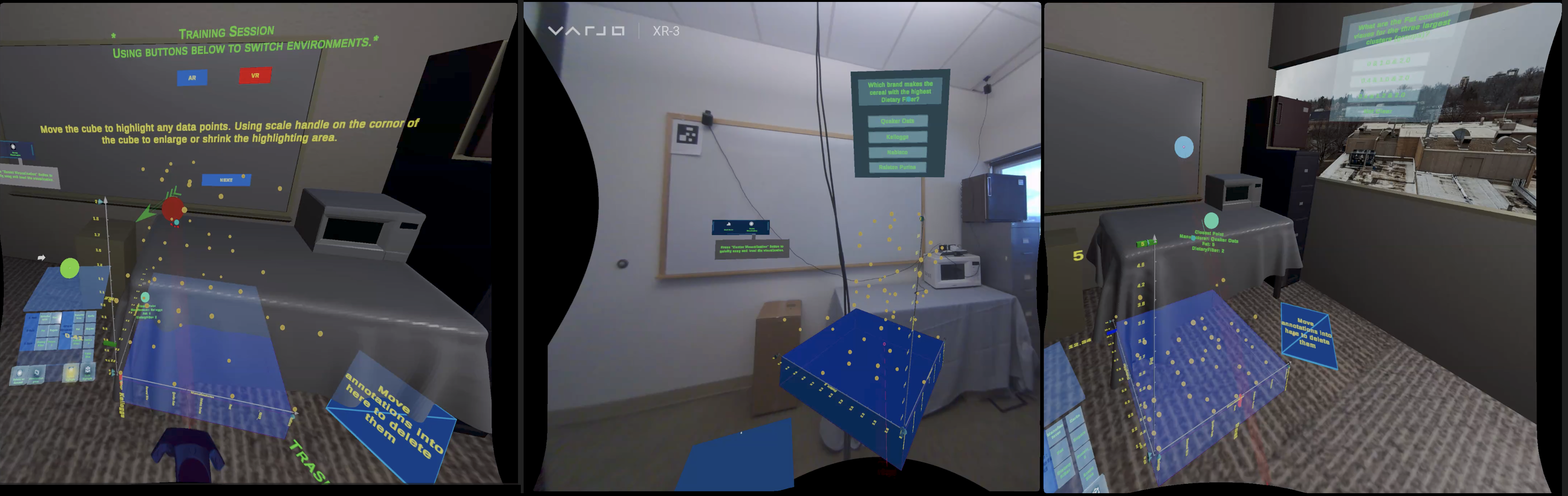
Abstract
In the ever-evolving discipline of high-dimensional scientific data, collaborative immersive analytics (CIA) offers a promising frontier for domain experts in complex data visualization and interpretation. This research presents a comprehensive framework for conducting usability studies on the extended reality (XR) interface of ParaView, an open-source CIA system. By employing established human-computer interaction (HCI) principles, including Jakob Nielsen's Usability Heuristics, Cognitive Load Theory, NASA Task Load Index, System Usability Scale, Affordance Theory, and Gulf of Execution and Evaluation, this study aims to identify underlying usability issues and provide guidelines for enhancing user experience in scientific domains. Our findings reveal significant usability challenges in the ParaView XR interface that impede effective teamwork and collaboration. For instance, the lack of synchronous collaboration, limited communication methods, and the absence of role-based data access are critical areas that need attention. Additionally, inadequate error handling, insufficient feedback mechanisms, and limited support resources during application use require extensive improvement to fully utilize the system's potential. Our study suggests potential improvements to overcome the existing usability barriers of the collaborative immersive system.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores the usability challenges and opportunities in collaborative immersive analytics for domain experts.
- Immersive analytics refers to the use of virtual and augmented reality technologies to enhance data visualization and analysis.
- The study investigates how domain experts, such as scientists and researchers, can effectively collaborate using immersive analytics tools.
Plain English Explanation
Immersive analytics is a new way of interacting with data using virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies. Instead of looking at data on a flat screen, users can experience it in a 3D, immersive environment. This can help domain experts, like scientists and researchers, better understand complex data and work together more effectively.
However, there are still many challenges in making these immersive analytics tools easy to use, especially when multiple people need to collaborate. This paper explores these usability issues and identifies opportunities to improve the design of collaborative immersive analytics systems.
The researchers conducted user studies to understand how domain experts currently use data visualization tools and what barriers they face when trying to work together in an immersive setting. They then used this feedback to identify design principles and features that could make collaborative immersive analytics more accessible and effective for these expert users.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a qualitative study that investigated the usability challenges and opportunities in collaborative immersive analytics for domain experts. The researchers conducted semi-structured interviews and observational studies with 18 domain experts from various fields, including biology, physics, and urban planning.
During the sessions, the participants were asked to complete collaborative data analysis tasks using both 2D visualization tools and an immersive, VR-based analytics system. The researchers observed the participants' behaviors, interactions, and pain points, and conducted follow-up interviews to gather their feedback and insights.
The study identified several key usability challenges, such as difficulties in transitioning between 2D and 3D environments, challenges in coordinating with remote collaborators, and a lack of familiarity with immersive interaction techniques. The paper also highlights opportunities to improve the design of collaborative immersive analytics tools, such as enhancing spatial awareness, supporting flexible collaboration modes, and providing better mechanisms for knowledge sharing and sensemaking.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides valuable insights into the current state of collaborative immersive analytics and the barriers that domain experts face when trying to leverage these technologies. The researchers' methodical approach of combining observational studies and user interviews allows them to uncover a nuanced understanding of the usability challenges.
However, the study is limited by its relatively small sample size and the specific domains represented. It would be beneficial to replicate the study with a larger and more diverse group of domain experts to validate the findings and identify any additional usability concerns or opportunities.
Additionally, the paper does not delve deeply into the technical and design implications of addressing the identified challenges. More details on potential solutions, their feasibility, and the trade-offs involved would help inform the development of more effective collaborative immersive analytics systems.
Conclusion
This paper highlights the significant potential of immersive analytics to enhance data exploration and collaboration for domain experts, but also underscores the substantial usability challenges that must be addressed. By unpacking the barriers faced by users, the researchers provide a valuable foundation for future work in designing more accessible and effective collaborative immersive analytics tools.
As the field of immersive analytics continues to evolve, it will be crucial for researchers and developers to deeply engage with domain experts to ensure that these technologies truly meet their needs and enable more efficient and productive data-driven workflows. The insights from this study can serve as a starting point for further innovation and progress in this emerging and promising area of research.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
I Did Not Notice: A Comparison of Immersive Analytics with Augmented and Virtual Reality
Xiaoyan Zhou, Anil Ufuk Batmaz, Adam S. Williams, Dylan Schreiber, Francisco Ortega

0
0
Immersive environments enable users to engage in embodied interaction, enhancing the sensemaking processes involved in completing tasks such as immersive analytics. Previous comparative studies on immersive analytics using augmented and virtual realities have revealed that users employ different strategies for data interpretation and text-based analytics depending on the environment. Our study seeks to investigate how augmented and virtual reality influences sensemaking processes in quantitative immersive analytics. Our results, derived from a diverse group of participants, indicate that users demonstrate comparable performance in both environments. However, it was observed that users exhibit a higher tolerance for cognitive load in VR and travel further in AR. Based on our findings, we recommend providing users with the option to switch between AR and VR, thereby enabling them to select an environment that aligns with their preferences and task requirements.
4/8/2024
📊
Reimagining TaxiVis through an Immersive Space-Time Cube metaphor and reflecting on potential benefits of Immersive Analytics for urban data exploration
Jorge Wagner, Claudio T. Silva, Wolfgang Stuerzlinger, Luciana Nedel

0
0
Current visualization research has identified the potential of more immersive settings for data exploration, leveraging VR and AR technologies. To explore how a traditional visualization system could be adapted into an immersive framework, and how it could benefit from this, we decided to revisit a landmark paper presented ten years ago at IEEE VIS. TaxiVis, by Ferreira et al., enabled interactive spatio-temporal querying of a large dataset of taxi trips in New York City. Here, we reimagine how TaxiVis' functionalities could be implemented and extended in a 3D immersive environment. Among the unique features we identify as being enabled by the Immersive TaxiVis prototype are alternative uses of the additional visual dimension, a fully visual 3D spatio-temporal query framework, and the opportunity to explore the data at different scales and frames of reference. By revisiting the case studies from the original paper, we demonstrate workflows that can benefit from this immersive perspective. Through reporting on our experience, and on the vision and reasoning behind our design decisions, we hope to contribute to the debate on how conventional and immersive visualization paradigms can complement each other and on how the exploration of urban datasets can be facilitated in the coming years.
5/24/2024
🤖
Harder, Better, Faster, Stronger: Interactive Visualization for Human-Centered AI Tools
Md Naimul Hoque, Sungbok Shin, Niklas Elmqvist

0
0
Human-centered AI (HCAI), rather than replacing the human, puts the human user in the driver's seat of so-called human-centered AI-infused tools (HCAI tools): interactive software tools that amplify, augment, empower, and enhance human performance using AI models; often novel generative or foundation AI ones. In this paper, we discuss how interactive visualization can be a key enabling technology for creating such human-centered AI tools. Visualization has already been shown to be a fundamental component in explainable AI models, and coupling this with data-driven, semantic, and unified interaction feedback loops will enable a human-centered approach to integrating AI models in the loop with human users. We present several examples of our past and current work on such HCAI tools, including for creative writing, temporal prediction, and user experience analysis. We then draw parallels between these tools to suggest common themes on how interactive visualization can support the design of future HCAI tools.
4/3/2024
🖼️
Multisensory extended reality applications offer benefits for volumetric biomedical image analysis in research and medicine
Kathrin Krieger, Jan Egger, Jens Kleesiek, Matthias Gunzer, Jianxu Chen

0
0
3D data from high-resolution volumetric imaging is a central resource for diagnosis and treatment in modern medicine. While the fast development of AI enhances imaging and analysis, commonly used visualization methods lag far behind. Recent research used extended reality (XR) for perceiving 3D images with visual depth perception and touch but used restrictive haptic devices. While unrestricted touch benefits volumetric data examination, implementing natural haptic interaction with XR is challenging. The research question is whether a multisensory XR application with intuitive haptic interaction adds value and should be pursued. In a study, 24 experts for biomedical images in research and medicine explored 3D medical shapes with 3 applications: a multisensory virtual reality (VR) prototype using haptic gloves, a simple VR prototype using controllers, and a standard PC application. Results of standardized questionnaires showed no significant differences between all application types regarding usability and no significant difference between both VR applications regarding presence. Participants agreed to statements that VR visualizations provide better depth information, using the hands instead of controllers simplifies data exploration, the multisensory VR prototype allows intuitive data exploration, and it is beneficial over traditional data examination methods. While most participants mentioned manual interaction as best aspect, they also found it the most improvable. We conclude that a multisensory XR application with improved manual interaction adds value for volumetric biomedical data examination. We will proceed with our open-source research project ISH3DE (Intuitive Stereoptic Haptic 3D Data Exploration) to serve medical education, therapeutic decisions, surgery preparations, or research data analysis.
6/17/2024