I Did Not Notice: A Comparison of Immersive Analytics with Augmented and Virtual Reality
2404.03814

0
0
Abstract
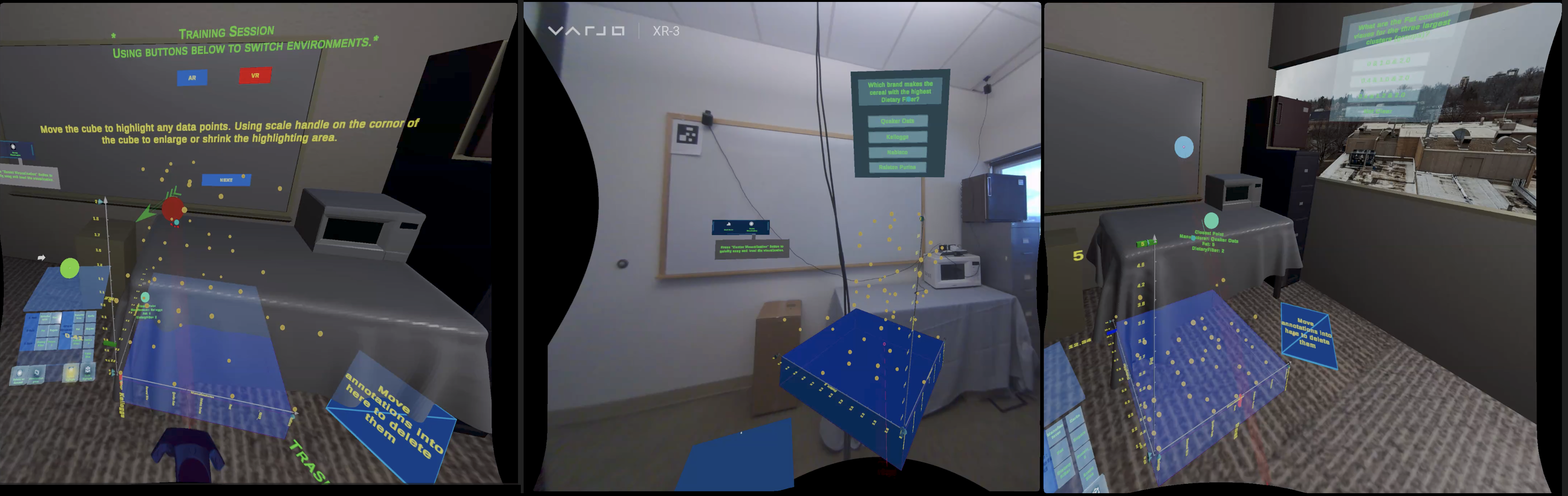
Immersive environments enable users to engage in embodied interaction, enhancing the sensemaking processes involved in completing tasks such as immersive analytics. Previous comparative studies on immersive analytics using augmented and virtual realities have revealed that users employ different strategies for data interpretation and text-based analytics depending on the environment. Our study seeks to investigate how augmented and virtual reality influences sensemaking processes in quantitative immersive analytics. Our results, derived from a diverse group of participants, indicate that users demonstrate comparable performance in both environments. However, it was observed that users exhibit a higher tolerance for cognitive load in VR and travel further in AR. Based on our findings, we recommend providing users with the option to switch between AR and VR, thereby enabling them to select an environment that aligns with their preferences and task requirements.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper compares the use of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) for immersive analytics, which is the study of data exploration and sensemaking in immersive environments.
- The researchers conducted a user study to investigate how people interact with and navigate data in AR versus VR settings.
- The findings provide insights into the strengths and limitations of each technology for different data analysis tasks and user preferences.
Plain English Explanation
In this study, the researchers wanted to understand how people interact with and make sense of data when using augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies. AR blends digital information with the real world, while VR completely immerses the user in a simulated environment.
The researchers had participants perform various data analysis tasks in both AR and VR settings. They observed how the participants navigated the data, what they noticed, and how they made decisions. By comparing the experiences in AR versus VR, the researchers gained insights into the unique benefits and drawbacks of each technology for different types of data exploration and analysis.
For example, the study found that participants were more likely to notice important details in the VR environment, but they also felt more overwhelmed by the amount of information presented. In contrast, the AR setup allowed participants to focus on the data while still being aware of their physical surroundings, which some found helpful.
The findings from this research can inform the design of future immersive analytics tools, helping developers and data analysts choose the most appropriate technology for the task at hand. By understanding the strengths and limitations of AR and VR, we can create more effective and user-friendly data exploration experiences.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a comparative study of immersive analytics in augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) environments. Immersive analytics is the field of study that explores how people can use immersive technologies to make sense of complex data.
The researchers conducted a user study with 24 participants, who were asked to perform various data analysis tasks in both an AR and a VR setup. The AR environment integrated data visualizations into the physical world, while the VR environment completely immersed participants in a virtual data landscape.
The researchers observed the participants' interactions, navigation patterns, and insights gained during the tasks. They found that participants were more likely to notice important details in the VR environment, but also felt more overwhelmed by the amount of information presented. In contrast, the AR setup allowed participants to focus on the data while still being aware of their physical surroundings, which some found helpful.
The paper also discusses the trade-offs between the two technologies, such as the impact on spatial awareness, cognitive load, and social interaction. The findings suggest that the choice between AR and VR for immersive analytics should be based on the specific data analysis tasks, user preferences, and contextual factors.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a well-designed and insightful comparison of AR and VR for immersive analytics, but there are a few potential limitations that could be addressed in future research.
First, the study had a relatively small sample size of 24 participants, which may limit the generalizability of the findings. Expanding the study to include a larger and more diverse participant pool could help validate the results.
Additionally, the paper does not delve deeply into the specific factors that contributed to the participants' preferences and performance in each environment. Further research could explore the cognitive and perceptual mechanisms underlying the observed differences, such as the role of spatial awareness, visual attention, and mental workload.
Another area for future work could be to investigate the impact of different data complexity and visualization types on the relative strengths of AR and VR. The current study used a single dataset and visualization, but immersive analytics often involves exploring diverse data sources and representations.
Finally, the paper does not address the potential long-term implications of using AR and VR for data analysis, such as the effects on user well-being, collaboration, and decision-making. Longitudinal studies could shed light on the broader societal and organizational impacts of these technologies.
Conclusion
This study provides valuable insights into the comparative advantages and disadvantages of using augmented reality and virtual reality for immersive data analysis and sensemaking. The findings suggest that the choice between AR and VR should be tailored to the specific needs of the data analysis task and user preferences.
By understanding the unique strengths and limitations of each technology, researchers and developers can design more effective and user-friendly immersive analytics tools. This, in turn, can lead to improved data exploration, decision-making, and problem-solving across a wide range of domains, from scientific research to business intelligence.
As the field of immersive analytics continues to evolve, further research on the cognitive and perceptual factors underlying the AR and VR user experiences will be crucial for unlocking the full potential of these transformative technologies.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
Are We There Yet? Unravelling Usability Challenges and Opportunities in Collaborative Immersive Analytics for Domain Experts
Fahim Arsad Nafis, Alexander Rose, Simon Su, Songqing Chen, Bo Han

0
0
In the ever-evolving discipline of high-dimensional scientific data, collaborative immersive analytics (CIA) offers a promising frontier for domain experts in complex data visualization and interpretation. This research presents a comprehensive framework for conducting usability studies on the extended reality (XR) interface of ParaView, an open-source CIA system. By employing established human-computer interaction (HCI) principles, including Jakob Nielsen's Usability Heuristics, Cognitive Load Theory, NASA Task Load Index, System Usability Scale, Affordance Theory, and Gulf of Execution and Evaluation, this study aims to identify underlying usability issues and provide guidelines for enhancing user experience in scientific domains. Our findings reveal significant usability challenges in the ParaView XR interface that impede effective teamwork and collaboration. For instance, the lack of synchronous collaboration, limited communication methods, and the absence of role-based data access are critical areas that need attention. Additionally, inadequate error handling, insufficient feedback mechanisms, and limited support resources during application use require extensive improvement to fully utilize the system's potential. Our study suggests potential improvements to overcome the existing usability barriers of the collaborative immersive system.
6/21/2024
📉
The Impact of Social Environment and Interaction Focus on User Experience and Social Acceptability of an Augmented Reality Game
Lorenzo Cocchia, Maurizio Vergari, Tanja Kojic, Francesco Vona, Sebastian Moller, Franca Garzotto, Jan-Niklas Voigt-Antons

0
0
One of the most promising technologies inside the Extended Reality (XR) spectrum is Augmented Reality. This technology is already in people's pockets regarding Mobile Augmented Reality with their smartphones. The scientific community still needs answers about how humans could and should interact in environments where perceived stimuli are different from fully physical or digital circumstances. Moreover, it is still being determined if people accept these new technologies in different social environments and interaction settings or if some obstacles could exist. This paper explores the impact of the Social Environment and the Focus of social interaction on users while playing a location-based augmented reality game, measuring it with user experience and social acceptance indicators. An empirical study in a within-subject fashion was performed in different social environments and under different settings of social interaction focus with N = 28 participants compiling self-reported questionnaires after playing a Scavenger Hunt in Augmented Reality. The measures from two different Social Environments (Crowded vs. Uncrowded) resulted in statistically relevant mean differences with indicators from the Social Acceptability dimension. Moreover, the analyses show statistically relevant differences between the variances from different degrees of Social Interaction Focus with Overall Social Presence, Perceived Psychological Engagement, Perceived Attentional Engagement, and Perceived Emotional Contagion. The results suggest that a location-based AR game played in different social environments and settings can influence the user experience's social dimension. Therefore, they should be carefully considered while designing immersive technological experiences in public spaces involving social interactions between players.
4/26/2024
🤿
From Virtual Gains to Real Pains: Potential Harms of Immersive Exergames
Sebastian Cmentowski, Sukran Karaosmanoglu, Frank Steinicke

0
0
Digitalization and virtualization are parts of our everyday lives in almost all aspects ranging from work, education, and communication to entertainment. A novel step in this direction is the widespread interest in extended reality (XR) [2]. The newest consumer-ready head-mounted displays (HMD) such as Meta Quest 3 or Apple Vision Pro, have reached unprecedented levels of visual fidelity, interaction capabilities, and computational power. The built-in pass-through features of these headsets enable both virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) with the same devices. However, the immersive nature of these experiences is not the only groundbreaking difference from established forms of media.
5/10/2024
🔎
Leveraging Artificial Intelligence to Promote Awareness in Augmented Reality Systems
Wangfan Li, Rohit Mallick, Carlos Toxtli-Hernandez, Christopher Flathmann, Nathan J. McNeese

0
0
Recent developments in artificial intelligence (AI) have permeated through an array of different immersive environments, including virtual, augmented, and mixed realities. AI brings a wealth of potential that centers on its ability to critically analyze environments, identify relevant artifacts to a goal or action, and then autonomously execute decision-making strategies to optimize the reward-to-risk ratio. However, the inherent benefits of AI are not without disadvantages as the autonomy and communication methodology can interfere with the human's awareness of their environment. More specifically in the case of autonomy, the relevant human-computer interaction literature cites that high autonomy results in an out-of-the-loop experience for the human such that they are not aware of critical artifacts or situational changes that require their attention. At the same time, low autonomy of an AI system can limit the human's own autonomy with repeated requests to approve its decisions. In these circumstances, humans enter into supervisor roles, which tend to increase their workload and, therefore, decrease their awareness in a multitude of ways. In this position statement, we call for the development of human-centered AI in immersive environments to sustain and promote awareness. It is our position then that we believe with the inherent risk presented in both AI and AR/VR systems, we need to examine the interaction between them when we integrate the two to create a new system for any unforeseen risks, and that it is crucial to do so because of its practical application in many high-risk environments.
5/10/2024