Reimagining TaxiVis through an Immersive Space-Time Cube metaphor and reflecting on potential benefits of Immersive Analytics for urban data exploration
2402.00344

0
0
📊
Abstract
Current visualization research has identified the potential of more immersive settings for data exploration, leveraging VR and AR technologies. To explore how a traditional visualization system could be adapted into an immersive framework, and how it could benefit from this, we decided to revisit a landmark paper presented ten years ago at IEEE VIS. TaxiVis, by Ferreira et al., enabled interactive spatio-temporal querying of a large dataset of taxi trips in New York City. Here, we reimagine how TaxiVis' functionalities could be implemented and extended in a 3D immersive environment. Among the unique features we identify as being enabled by the Immersive TaxiVis prototype are alternative uses of the additional visual dimension, a fully visual 3D spatio-temporal query framework, and the opportunity to explore the data at different scales and frames of reference. By revisiting the case studies from the original paper, we demonstrate workflows that can benefit from this immersive perspective. Through reporting on our experience, and on the vision and reasoning behind our design decisions, we hope to contribute to the debate on how conventional and immersive visualization paradigms can complement each other and on how the exploration of urban datasets can be facilitated in the coming years.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Current visualization research suggests the potential of more immersive settings like virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) for data exploration.
- This paper revisits a landmark 10-year-old paper on TaxiVis, a system for interactive spatio-temporal querying of taxi trip data in New York City.
- The authors reimagine how TaxiVis' functionalities could be implemented and extended in a 3D immersive environment, called Immersive TaxiVis.
Plain English Explanation
Researchers have found that more immersive technologies like VR and AR could be useful for exploring and understanding data. In this paper, the authors look back at a previous system called TaxiVis, which allowed people to interactively analyze a large dataset of taxi trips in New York City.
The authors wondered how they could take the features of TaxiVis and adapt them to work in a 3D immersive environment. They wanted to see how this could change and improve the way people explore and make sense of the taxi trip data.
Some of the key ideas they explore include:
- Using the extra 3D space in new ways to visualize the data
- Creating a fully 3D interface for querying and filtering the data
- Allowing people to explore the data at different scales and perspectives
By revisiting the original TaxiVis system, the authors hope to contribute to the ongoing discussion about how traditional data visualization tools and immersive technologies can work together. They also want to show how 3D environments could help people better understand urban datasets like taxi trips.
Technical Explanation
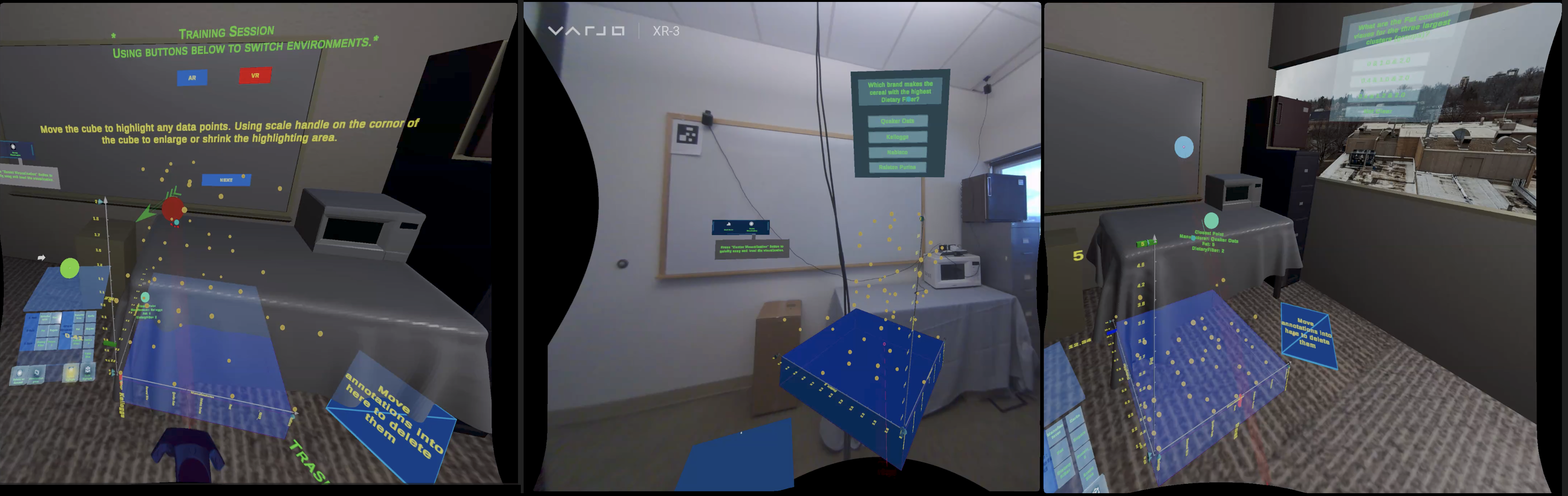
The paper focuses on reimagining the TaxiVis system, a previous landmark visualization tool for exploring a large dataset of taxi trips in New York City, in the context of a 3D immersive environment.
The authors identify several unique features enabled by their Immersive TaxiVis prototype, including:
- Alternative uses of the additional visual dimension provided by a 3D space
- A fully visual 3D spatio-temporal query framework
- The ability to explore the data at different scales and frames of reference
By revisiting the case studies from the original TaxiVis paper, the authors demonstrate how certain workflows and analyses could benefit from this immersive perspective. For example, they show how the 3D spatio-temporal view and ability to seamlessly transition between scales could provide new insights into urban mobility patterns.
The paper contributes to the ongoing debate on how conventional data visualization approaches and emerging immersive analytics paradigms can complement each other. It also explores how the exploration of geospatial urban datasets can be facilitated in the coming years.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a compelling vision for how a landmark data visualization system can be reimagined and extended in the context of 3D immersive environments. The authors make a convincing case for the potential benefits of this approach, such as the ability to leverage the extra visual dimension and provide more seamless multi-scale exploration.
However, the paper does not address some potential limitations or challenges that may arise when transitioning a 2D visualization tool to a 3D immersive setting. For example, issues around occlusion, depth perception, and user disorientation in complex 3D spaces are not discussed in depth.
Additionally, the paper focuses on the design and conceptual aspects of Immersive TaxiVis, but does not provide any empirical user evaluation or comparison to the original TaxiVis system. It would be valuable to understand how the immersive approach impacts the users' ability to perform typical data exploration tasks compared to the traditional 2D interface.
Overall, the paper presents an interesting and well-reasoned exploration of how a seminal data visualization system can be adapted to take advantage of emerging immersive technologies. However, further research is needed to fully understand the practical implications and trade-offs of this approach.
Conclusion
This paper revisits the TaxiVis system, a landmark data visualization tool for exploring taxi trip data, and reimagines how its functionalities could be implemented and extended in a 3D immersive environment. The authors identify several unique features of their Immersive TaxiVis prototype, including alternative uses of the 3D space, a fully visual 3D spatio-temporal query framework, and the ability to explore the data at different scales and perspectives.
By demonstrating how certain workflows and analyses from the original TaxiVis paper could benefit from an immersive approach, the authors contribute to the ongoing discussion on how traditional data visualization and emerging immersive analytics paradigms can complement each other. The paper also explores how the exploration of geospatial urban datasets, such as taxi trip data, can be facilitated in the coming years.
While the paper presents a compelling vision, further research is needed to fully understand the practical implications and trade-offs of transitioning a 2D visualization system to a 3D immersive setting. Nonetheless, this work represents an important step in understanding how the combination of conventional and immersive visualization techniques can enhance our ability to make sense of complex urban datasets.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
Are We There Yet? Unravelling Usability Challenges and Opportunities in Collaborative Immersive Analytics for Domain Experts
Fahim Arsad Nafis, Alexander Rose, Simon Su, Songqing Chen, Bo Han

0
0
In the ever-evolving discipline of high-dimensional scientific data, collaborative immersive analytics (CIA) offers a promising frontier for domain experts in complex data visualization and interpretation. This research presents a comprehensive framework for conducting usability studies on the extended reality (XR) interface of ParaView, an open-source CIA system. By employing established human-computer interaction (HCI) principles, including Jakob Nielsen's Usability Heuristics, Cognitive Load Theory, NASA Task Load Index, System Usability Scale, Affordance Theory, and Gulf of Execution and Evaluation, this study aims to identify underlying usability issues and provide guidelines for enhancing user experience in scientific domains. Our findings reveal significant usability challenges in the ParaView XR interface that impede effective teamwork and collaboration. For instance, the lack of synchronous collaboration, limited communication methods, and the absence of role-based data access are critical areas that need attention. Additionally, inadequate error handling, insufficient feedback mechanisms, and limited support resources during application use require extensive improvement to fully utilize the system's potential. Our study suggests potential improvements to overcome the existing usability barriers of the collaborative immersive system.
6/21/2024
I Did Not Notice: A Comparison of Immersive Analytics with Augmented and Virtual Reality
Xiaoyan Zhou, Anil Ufuk Batmaz, Adam S. Williams, Dylan Schreiber, Francisco Ortega

0
0
Immersive environments enable users to engage in embodied interaction, enhancing the sensemaking processes involved in completing tasks such as immersive analytics. Previous comparative studies on immersive analytics using augmented and virtual realities have revealed that users employ different strategies for data interpretation and text-based analytics depending on the environment. Our study seeks to investigate how augmented and virtual reality influences sensemaking processes in quantitative immersive analytics. Our results, derived from a diverse group of participants, indicate that users demonstrate comparable performance in both environments. However, it was observed that users exhibit a higher tolerance for cognitive load in VR and travel further in AR. Based on our findings, we recommend providing users with the option to switch between AR and VR, thereby enabling them to select an environment that aligns with their preferences and task requirements.
4/8/2024

Metaverse for Safer Roadways: An Immersive Digital Twin Framework for Exploring Human-Autonomy Coexistence in Urban Transportation Systems
Tanmay Vilas Samak, Chinmay Vilas Samak, Venkat Narayan Krovi

0
0
Societal-scale deployment of autonomous vehicles requires them to coexist with human drivers, necessitating mutual understanding and coordination among these entities. However, purely real-world or simulation-based experiments cannot be employed to explore such complex interactions due to safety and reliability concerns, respectively. Consequently, this work presents an immersive digital twin framework to explore and experiment with the interaction dynamics between autonomous and non-autonomous traffic participants. Particularly, we employ a mixed-reality human-machine interface to allow human drivers and autonomous agents to observe and interact with each other for testing edge-case scenarios while ensuring safety at all times. To validate the versatility of the proposed framework's modular architecture, we first present a discussion on a set of user experience experiments encompassing 4 different levels of immersion with 4 distinct user interfaces. We then present a case study of uncontrolled intersection traversal to demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed framework in validating the interactions of a primary human-driven, autonomous, and connected autonomous vehicle with a secondary semi-autonomous vehicle. The proposed framework has been openly released to guide the future of autonomy-oriented digital twins and research on human-autonomy coexistence.
6/11/2024
➖
Unveiling the Era of Spatial Computing
Hanzhong Cao

0
0
The evolution of User Interfaces marks a significant transition from traditional command-line interfaces to more intuitive graphical and touch-based interfaces, largely driven by the emergence of personal computing devices. The advent of spatial computing and Extended Reality technologies further pushes the boundaries, promising a fusion of physical and digital realms through interactive environments. This paper delves into the progression from All Realities technologies encompassing Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality, and Mediated Reality to spatial computing, highlighting their conceptual differences and applications. We explore enabling technologies such as Artificial Intelligence, the Internet of Things, 5G, cloud and edge computing, and blockchain that underpin the development of spatial computing. We further scrutinize the initial forays into commercial spatial computing devices, with a focus on Apple's Vision Pro, evaluating its technological advancements alongside the challenges it faces. Through this examination, we aim to provide insights into the potential of spatial computing to revolutionize our interaction with digital information and the physical world.
5/14/2024