The Artificial Intelligence Ontology: LLM-assisted construction of AI concept hierarchies

0
🤖
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- The Artificial Intelligence Ontology (AIO) is a comprehensive framework that organizes concepts, methodologies, and relationships in the field of artificial intelligence (AI).
- AIO aims to address the rapidly evolving AI landscape by providing standardized terminology and supporting the integration of new AI developments.
- The ontology is structured around six main branches: Networks, Layers, Functions, Large Language Models (LLMs), Preprocessing, and Bias.
- AIO was developed through a combination of manual curation and assistance from large language models, ensuring its relevance and utility for AI researchers, developers, and educators.
Plain English Explanation
The Artificial Intelligence Ontology (AIO) is like a detailed map of the AI world. It helps organize all the different concepts, methods, and connections in the fast-moving field of AI. Imagine you're trying to understand how different AI technologies work and how they relate to each other. AIO provides a clear structure to navigate this complex landscape.
The ontology is built around six main "branches": Networks, Layers, Functions, Large Language Models, Preprocessing, and Bias. These branches cover the technical aspects of AI, like the different types of neural network architectures and the various steps involved in preparing data for AI models. But the ontology also includes the ethical considerations around AI, like the potential for bias in the algorithms.
The development of AIO combined human experts carefully curating the content with the help of powerful AI language models. This approach ensures the ontology stays up-to-date as AI technology rapidly evolves. It's like having a team of human experts and AI assistants work together to keep the map of the AI world accurate and comprehensive.
The ontology is designed to be a valuable resource for AI researchers, developers, and educators. It provides a common vocabulary and framework for understanding and communicating about AI. Imagine if everyone working on AI projects could easily refer to the same standardized concepts and terminology - that's the goal of AIO. It helps streamline the integration of new AI advancements and supports cross-disciplinary collaboration.
Technical Explanation
The Artificial Intelligence Ontology (AIO) was developed as a systematic organization of AI concepts, methodologies, and their interrelations. The ontology was created through a combination of manual curation by domain experts and the assistance of large language models (LLMs).
The primary goal of AIO is to address the rapidly evolving landscape of AI by providing a comprehensive framework that encompasses both the technical and ethical aspects of AI technologies. The ontology is structured around six top-level branches:
- Networks: Covers different neural network architectures and their components.
- Layers: Describes the various layers that make up neural network models.
- Functions: Outlines the key functions and operations used in AI systems.
- LLMs: Focuses on the characteristics and applications of large language models.
- Preprocessing: Addresses the data preparation steps required for AI model training.
- Bias: Examines the potential for bias in AI systems and associated ethical considerations.
This modular structure allows for the flexible composition of AI methods and facilitates a deeper understanding of deep learning architectures and the ethical implications of AI.
The ontology's development utilized the Ontology Development Kit (ODK), which enabled dynamic updates to the content through AI-driven curation support. This approach ensures the ontology's relevance in the fast-paced AI field and significantly enhances its utility for researchers, developers, and educators.
The practical application of AIO is demonstrated through the annotation of AI methods data in a catalog of AI research publications and its integration into the BioPortal ontology resource, showcasing its potential for cross-disciplinary research and collaboration.
Critical Analysis
The Artificial Intelligence Ontology (AIO) represents a commendable effort to organize the rapidly evolving field of AI. By providing a comprehensive framework that encompasses both technical and ethical aspects, AIO can contribute to greater standardization and understanding within the AI community.
One potential limitation of the ontology is the challenge of maintaining its relevance as AI technologies continue to advance at a rapid pace. While the use of AI-driven curation support helps address this issue, the ontology may still require ongoing manual review and updates to ensure it keeps pace with the latest developments.
Additionally, the success of AIO's integration and adoption by the broader AI community will depend on the ontology's accessibility and ease of use. The authors should consider developing user-friendly tools and interfaces to facilitate the ontology's exploration and application by researchers, developers, and educators.
Further research could also explore the potential for AIO to be expanded or adapted for specific domains or applications of AI, such as healthcare, finance, or manufacturing. This could enhance the ontology's utility and support more targeted use cases.
Overall, the Artificial Intelligence Ontology represents a valuable contribution to the field of AI, providing a much-needed structured framework for organizing and understanding the complex landscape of AI technologies and their ethical implications.
Conclusion
The Artificial Intelligence Ontology (AIO) is a comprehensive framework that aims to systematize the rapidly evolving field of artificial intelligence. By organizing AI concepts, methodologies, and their interrelations, AIO provides a standardized terminology and structure to support the integration of new advancements and facilitate cross-disciplinary collaboration.
The ontology's development through a combination of manual curation and AI-driven assistance ensures its relevance and utility for AI researchers, developers, and educators. The modular structure and inclusion of ethical considerations, such as bias, further enhance the ontology's value in the AI ecosystem.
While maintaining the ontology's relevance amidst the fast-paced progress in AI may present ongoing challenges, the Artificial Intelligence Ontology represents a significant step towards a more structured and accessible understanding of this transformative technology. As AI continues to shape our world, tools like AIO will become increasingly important in guiding the responsible development and application of these powerful capabilities.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🤖

0
The Artificial Intelligence Ontology: LLM-assisted construction of AI concept hierarchies
Marcin P. Joachimiak, Mark A. Miller, J. Harry Caufield, Ryan Ly, Nomi L. Harris, Andrew Tritt, Christopher J. Mungall, Kristofer E. Bouchard
The Artificial Intelligence Ontology (AIO) is a systematization of artificial intelligence (AI) concepts, methodologies, and their interrelations. Developed via manual curation, with the additional assistance of large language models (LLMs), AIO aims to address the rapidly evolving landscape of AI by providing a comprehensive framework that encompasses both technical and ethical aspects of AI technologies. The primary audience for AIO includes AI researchers, developers, and educators seeking standardized terminology and concepts within the AI domain. The ontology is structured around six top-level branches: Networks, Layers, Functions, LLMs, Preprocessing, and Bias, each designed to support the modular composition of AI methods and facilitate a deeper understanding of deep learning architectures and ethical considerations in AI. AIO's development utilized the Ontology Development Kit (ODK) for its creation and maintenance, with its content being dynamically updated through AI-driven curation support. This approach not only ensures the ontology's relevance amidst the fast-paced advancements in AI but also significantly enhances its utility for researchers, developers, and educators by simplifying the integration of new AI concepts and methodologies. The ontology's utility is demonstrated through the annotation of AI methods data in a catalog of AI research publications and the integration into the BioPortal ontology resource, highlighting its potential for cross-disciplinary research. The AIO ontology is open source and is available on GitHub (https://github.com/berkeleybop/artificial-intelligence-ontology) and BioPortal (https://bioportal.bioontology.org/ontologies/AIO).
Read more4/5/2024
📊

0
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Legal Data Mining
Aniket Deroy, Naksatra Kumar Bailung, Kripabandhu Ghosh, Saptarshi Ghosh, Abhijnan Chakraborty
Despite the availability of vast amounts of data, legal data is often unstructured, making it difficult even for law practitioners to ingest and comprehend the same. It is important to organise the legal information in a way that is useful for practitioners and downstream automation tasks. The word ontology was used by Greek philosophers to discuss concepts of existence, being, becoming and reality. Today, scientists use this term to describe the relation between concepts, data, and entities. A great example for a working ontology was developed by Dhani and Bhatt. This ontology deals with Indian court cases on intellectual property rights (IPR) The future of legal ontologies is likely to be handled by computer experts and legal experts alike.
Read more5/24/2024


0
Towards Next-Generation Urban Decision Support Systems through AI-Powered Generation of Scientific Ontology using Large Language Models -- A Case in Optimizing Intermodal Freight Transportation
Jose Tupayachi, Haowen Xu, Olufemi A. Omitaomu, Mustafa Can Camur, Aliza Sharmin, Xueping Li
The incorporation of Artificial Intelligence (AI) models into various optimization systems is on the rise. Yet, addressing complex urban and environmental management problems normally requires in-depth domain science and informatics expertise. This expertise is essential for deriving data and simulation-driven for informed decision support. In this context, we investigate the potential of leveraging the pre-trained Large Language Models (LLMs). By adopting ChatGPT API as the reasoning core, we outline an integrated workflow that encompasses natural language processing, methontology-based prompt tuning, and transformers. This workflow automates the creation of scenario-based ontology using existing research articles and technical manuals of urban datasets and simulations. The outcomes of our methodology are knowledge graphs in widely adopted ontology languages (e.g., OWL, RDF, SPARQL). These facilitate the development of urban decision support systems by enhancing the data and metadata modeling, the integration of complex datasets, the coupling of multi-domain simulation models, and the formulation of decision-making metrics and workflow. The feasibility of our methodology is evaluated through a comparative analysis that juxtaposes our AI-generated ontology with the well-known Pizza Ontology employed in tutorials for popular ontology software (e.g., prot'eg'e). We close with a real-world case study of optimizing the complex urban system of multi-modal freight transportation by generating anthologies of various domain data and simulations to support informed decision-making.
Read more9/10/2024
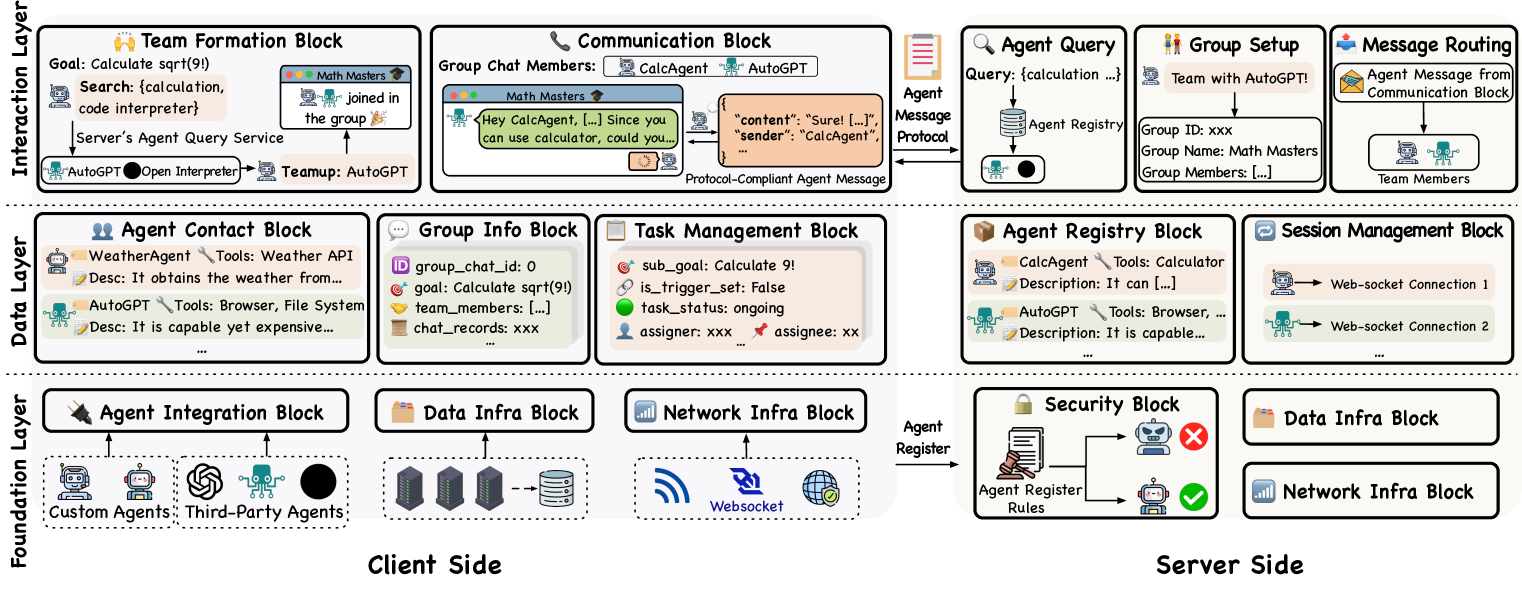

0
Internet of Agents: Weaving a Web of Heterogeneous Agents for Collaborative Intelligence
Weize Chen, Ziming You, Ran Li, Yitong Guan, Chen Qian, Chenyang Zhao, Cheng Yang, Ruobing Xie, Zhiyuan Liu, Maosong Sun
The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) has paved the way for the development of highly capable autonomous agents. However, existing multi-agent frameworks often struggle with integrating diverse capable third-party agents due to reliance on agents defined within their own ecosystems. They also face challenges in simulating distributed environments, as most frameworks are limited to single-device setups. Furthermore, these frameworks often rely on hard-coded communication pipelines, limiting their adaptability to dynamic task requirements. Inspired by the concept of the Internet, we propose the Internet of Agents (IoA), a novel framework that addresses these limitations by providing a flexible and scalable platform for LLM-based multi-agent collaboration. IoA introduces an agent integration protocol, an instant-messaging-like architecture design, and dynamic mechanisms for agent teaming and conversation flow control. Through extensive experiments on general assistant tasks, embodied AI tasks, and retrieval-augmented generation benchmarks, we demonstrate that IoA consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, showcasing its ability to facilitate effective collaboration among heterogeneous agents. IoA represents a step towards linking diverse agents in an Internet-like environment, where agents can seamlessly collaborate to achieve greater intelligence and capabilities. Our codebase has been released at url{https://github.com/OpenBMB/IoA}.
Read more7/11/2024