Artificial Intelligence and Strategic Decision-Making: Evidence from Entrepreneurs and Investors

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This study examines how entrepreneurs and investors use artificial intelligence (AI) to make strategic decisions.
- The researchers conducted experiments to understand how AI tools influence decision-making processes and outcomes.
- The findings provide insights into the potential benefits and challenges of using AI for strategic decision-making.
Plain English Explanation
The researchers wanted to understand how entrepreneurs and investors use artificial intelligence (AI) to make important business decisions. They ran experiments to see how different AI tools and capabilities affect the decision-making process and the outcomes.
The key findings suggest that AI can potentially provide valuable insights and recommendations to help entrepreneurs and investors make better strategic choices. However, there are also some challenges in fully trusting and relying on AI for critical decisions. The researchers found that humans tend to be skeptical of AI recommendations, especially when they conflict with their own intuitions or experiences.
Overall, the study highlights the complex relationship between humans and AI in the context of strategic decision-making. While AI can be a powerful tool, there are still important considerations around how to effectively integrate it into the decision-making process in a way that complements human judgment and expertise.
Technical Explanation
The researchers conducted a series of experiments to investigate how entrepreneurs and investors make strategic decisions with the support of AI tools.
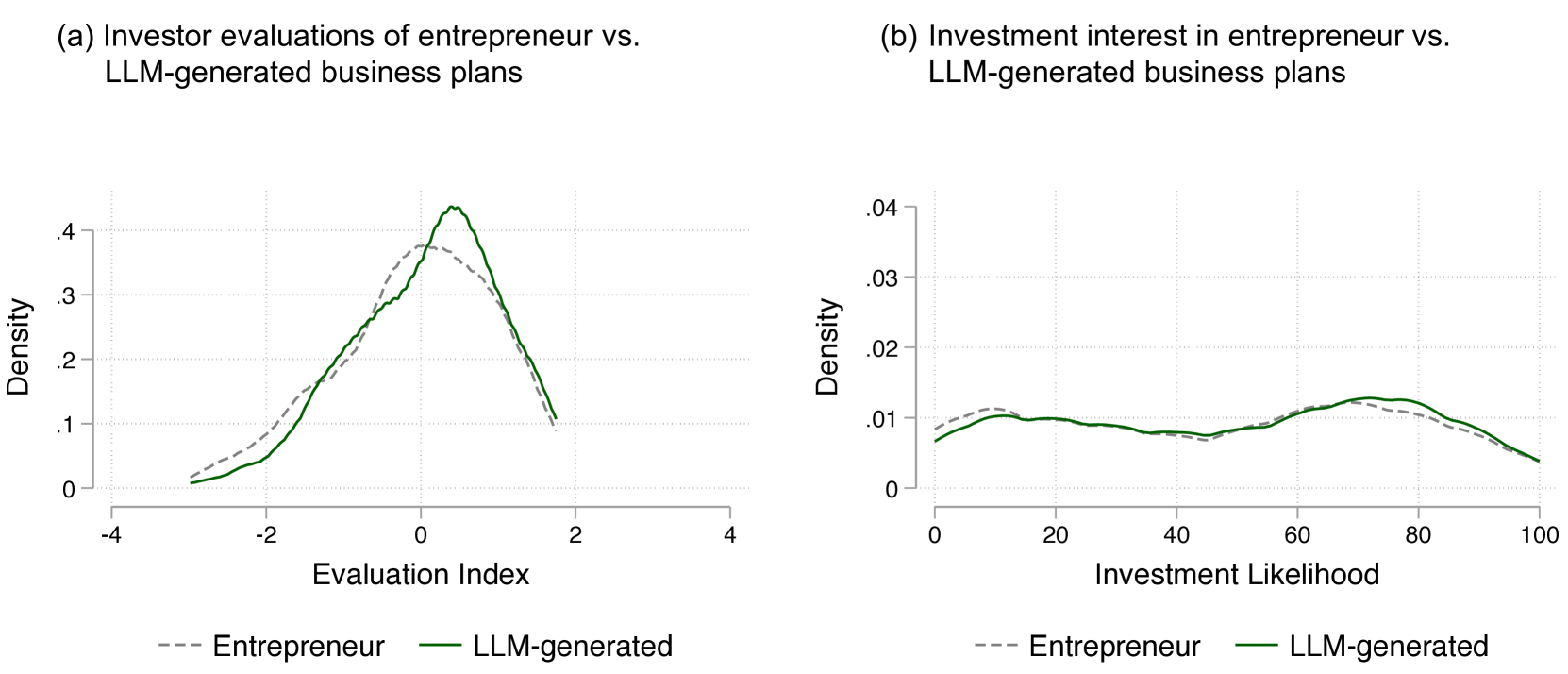
In the first experiment, participants were asked to make investment decisions based on a set of startup profiles. Some participants received AI-generated recommendations, while others made decisions without AI support. The researchers found that participants who received AI recommendations were more likely to make investments, but they also tended to be more skeptical of the recommendations, especially when they conflicted with their own intuitions.
In the second experiment, the researchers examined how the level of AI capability influenced decision-making. Participants were presented with startup profiles and asked to make investment decisions, with some receiving recommendations from a basic AI system and others from a more advanced AI system. The results showed that participants were more likely to follow the recommendations of the more advanced AI system, but they also expressed greater uncertainty about the reliability of the recommendations.
The findings from these experiments suggest that AI can be a valuable tool for strategic decision-making, but there are still important challenges in fully integrating it into the decision-making process. Entrepreneurs and investors may be hesitant to fully trust AI recommendations, especially when they conflict with their own expertise and experience.
Critical Analysis
The researchers acknowledge several limitations and areas for further research in their paper.
One key limitation is the relatively small sample size and the use of simulated startup profiles, which may not fully capture the complexity of real-world investment decisions. The researchers note that further studies with larger, more diverse samples and real-world data would be valuable to corroborate and expand on the findings.
Additionally, the paper does not delve deeply into the specific design and capabilities of the AI systems used in the experiments. More detailed information about the AI models, their training data, and their decision-making processes could provide valuable insights into the strengths, weaknesses, and potential biases of the AI tools.
Another area for further research highlighted in the paper is the role of trust and transparency in the human-AI decision-making relationship. The researchers suggest that a better understanding of the factors that influence trust in AI recommendations could lead to more effective integration of AI into strategic decision-making processes.
Overall, the paper provides a valuable contribution to the understanding of how AI can be leveraged in strategic decision-making, while also highlighting the need for continued research and experimentation in this rapidly evolving field.
Conclusion
This study offers important insights into the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in strategic decision-making by entrepreneurs and investors. The key findings suggest that AI can provide valuable recommendations and insights, but there are also significant challenges in fully trusting and integrating AI into the decision-making process.
The research highlights the complex interplay between human judgment, expertise, and the capabilities of AI systems. While AI holds great potential to enhance strategic decision-making, the effective integration of these technologies will require continued innovation, experimentation, and a deeper understanding of the factors that influence human trust and reliance on AI recommendations.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Artificial Intelligence and Strategic Decision-Making: Evidence from Entrepreneurs and Investors
Felipe A. Csaszar, Harsh Ketkar, Hyunjin Kim
This paper explores how artificial intelligence (AI) may impact the strategic decision-making (SDM) process in firms. We illustrate how AI could augment existing SDM tools and provide empirical evidence from a leading accelerator program and a startup competition that current Large Language Models (LLMs) can generate and evaluate strategies at a level comparable to entrepreneurs and investors. We then examine implications for key cognitive processes underlying SDM -- search, representation, and aggregation. Our analysis suggests AI has the potential to enhance the speed, quality, and scale of strategic analysis, while also enabling new approaches like virtual strategy simulations. However, the ultimate impact on firm performance will depend on competitive dynamics as AI capabilities progress. We propose a framework connecting AI use in SDM to firm outcomes and discuss how AI may reshape sources of competitive advantage. We conclude by considering how AI could both support and challenge core tenets of the theory-based view of strategy. Overall, our work maps out an emerging research frontier at the intersection of AI and strategy.
Read more8/19/2024
🤖

0
Strategic AI adoption in SMEs: A Prescriptive Framework
Atif Hussain, Rana Rizwan
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is increasingly acknowledged as a vital component for the advancement and competitiveness of modern organizations, including small and medium enterprises (SMEs). However, the adoption of AI technologies in SMEs faces significant barriers, primarily related to cost, lack of technical skills, and employee acceptance. This study proposes a comprehensive, phased framework designed to facilitate the effective adoption of AI in SMEs by systematically addressing these barriers. The framework begins with raising awareness and securing commitment from leadership, followed by the adoption of low-cost, general-purpose AI tools to build technical competence and foster a positive attitude towards AI. As familiarity with AI technologies increases, the framework advocates for the integration of task-specific AI tools to enhance efficiency and productivity. Subsequently, it guides organizations towards the in-house development of generative AI tools, providing greater customization and control. Finally, the framework addresses the development of discriminative AI models to meet highly specific and precision-oriented tasks. By providing a structured and incremental approach, this framework ensures that SMEs can navigate the complexities of AI integration effectively, driving innovation, efficiency, and competitive advantage. This study contributes to the field by offering a practical, prescriptive framework tailored to the unique needs of SMEs, facilitating the successful adoption of AI technologies and positioning these organizations for sustained growth in a competitive landscape.
Read more8/23/2024
🤯

0
Business and Regulatory Responses to Artificial Intelligence: Dynamic Regulation, Innovation Ecosystems and the Strategic Management of Disruptive Technology
Mark Fenwick, Erik P. M. Vermeulen, Marcelo Corrales Compagnucci
Identifying and then implementing an effective response to disruptive new AI technologies is enormously challenging for any business looking to integrate AI into their operations, as well as regulators looking to leverage AI-related innovation as a mechanism for achieving regional economic growth. These business and regulatory challenges are particularly significant given the broad reach of AI, as well as the multiple uncertainties surrounding such technologies and their future development and effects. This article identifies two promising strategies for meeting the AI challenge, focusing on the example of Fintech. First, dynamic regulation, in the form of regulatory sandboxes and other regulatory approaches that aim to provide a space for responsible AI-related innovation. An empirical study provides preliminary evidence to suggest that jurisdictions that adopt a more proactive approach to Fintech regulation can attract greater investment. The second strategy relates to so-called innovation ecosystems. It is argued that such ecosystems are most effective when they afford opportunities for creative partnerships between well-established corporations and AI-focused startups and that this aspect of a successful innovation ecosystem is often overlooked in the existing discussion. The article suggests that these two strategies are interconnected, in that greater investment is an important element in both fostering and signaling a well-functioning innovation ecosystem and that a well-functioning ecosystem will, in turn, attract more funding. The resulting synergies between these strategies can, therefore, provide a jurisdiction with a competitive edge in becoming a regional hub for AI-related activity.
Read more7/30/2024

0
AI in Manufacturing: Market Analysis and Opportunities
Mohamed Abdelaal
In this paper, we explore the transformative impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the manufacturing sector, highlighting its potential to revolutionize industry practices and enhance operational efficiency. We delve into various applications of AI in manufacturing, with a particular emphasis on human-machine interfaces (HMI) and AI-powered milling machines, showcasing how these technologies contribute to more intuitive operations and precision in production processes. Through rigorous market analysis, the paper presents insightful data on AI adoption rates among German manufacturers, comparing these figures with global trends and exploring the specific uses of AI in production, maintenance, customer service, and more. In addition, the paper examines the emerging field of Generative AI and the potential applications of large language models in manufacturing processes. The findings indicate a significant increase in AI adoption from 6% in 2020 to 13.3% in 2023 among German companies, with a projection of substantial economic impact by 2030. The study also addresses the challenges faced by companies, such as data quality and integration hurdles, providing a balanced view of the opportunities and obstacles in AI implementation.
Read more7/9/2024