Strategic AI adoption in SMEs: A Prescriptive Framework

0
🤖
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is becoming crucial for modern organizations, including small and medium enterprises (SMEs).
- However, SMEs face significant barriers to adopting AI, such as cost, lack of technical skills, and employee acceptance.
- This study proposes a comprehensive, phased framework to help SMEs effectively adopt AI by addressing these barriers.
Plain English Explanation
The paper discusses how Artificial Intelligence (AI) is becoming an essential tool for modern businesses, including small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). However, SMEs often struggle to implement AI due to various challenges, such as the high cost, lack of technical expertise, and concerns from employees.
To address these issues, the researchers have developed a step-by-step framework to guide SMEs through the process of adopting AI technologies. The framework starts by raising awareness and getting buy-in from company leadership. Then, it recommends using low-cost, general-purpose AI tools to build technical skills and foster a positive attitude towards AI within the organization.
As the company becomes more familiar with AI, the framework suggests integrating task-specific AI tools to improve efficiency and productivity. The next step is to develop customized, in-house generative AI models, which provide even greater control and customization. Finally, the framework guides organizations towards creating more advanced, discriminative AI models to tackle highly specific and precise tasks.
By following this structured and incremental approach, the researchers aim to help SMEs navigate the complexities of AI integration effectively. This, in turn, can drive innovation, improve efficiency, and strengthen the company's competitive advantage in the market.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a comprehensive, phased framework to facilitate the effective adoption of AI technologies in small and medium enterprises (SMEs). The framework is designed to systematically address the primary barriers to AI adoption, which include cost, lack of technical skills, and employee acceptance.
The framework consists of four main phases:
-
Awareness and Commitment: This initial phase focuses on raising awareness about the benefits of AI and securing a commitment from the organization's leadership to invest in and support the adoption of AI technologies.
-
Low-cost, General-purpose AI Tools: In this phase, the framework advocates for the adoption of low-cost, general-purpose AI tools. This helps build technical competence within the organization and fosters a positive attitude towards AI among employees.
-
Task-specific AI Integration: As the organization's familiarity with AI increases, the framework guides the integration of task-specific AI tools to enhance efficiency and productivity.
-
In-house Generative and Discriminative AI Development: The final phase involves the development of customized, in-house generative AI models, providing greater control and customization. Additionally, the framework addresses the creation of more advanced, discriminative AI models to tackle highly specific and precision-oriented tasks.
By following this structured and incremental approach, the framework aims to help SMEs navigate the complexities of AI integration effectively, driving innovation, efficiency, and competitive advantage.
Critical Analysis
The framework proposed in the paper provides a well-structured and comprehensive approach to addressing the challenges faced by SMEs in adopting AI technologies. The phased implementation strategy, starting with awareness and commitment, and gradually advancing to more complex AI tools and in-house development, seems well-designed to help SMEs build the necessary skills and infrastructure.
However, the paper does not delve into potential limitations or caveats of the framework. For example, it does not address the specific challenges that may arise in the implementation of each phase, such as the availability of low-cost, general-purpose AI tools that are suitable for SMEs, or the potential hurdles in developing in-house generative and discriminative AI models.
Additionally, the paper could have provided more insights into the evaluation or validation of the proposed framework, such as case studies or pilot deployments within SMEs. This would have strengthened the practical applicability and efficacy of the approach.
Further research could explore the scalability of the framework, its adaptability to different industries or organizational structures, and the long-term impacts on SMEs' innovation, efficiency, and competitiveness.
Conclusion
This study presents a comprehensive, phased framework to facilitate the effective adoption of AI in small and medium enterprises (SMEs). The framework systematically addresses the primary barriers to AI adoption, such as cost, lack of technical skills, and employee acceptance, by guiding SMEs through a structured and incremental process.
By providing a practical and prescriptive approach, the researchers aim to help SMEs navigate the complexities of AI integration and position these organizations for sustained growth and competitive advantage in a rapidly evolving business landscape. While the framework offers a promising solution, further research and validation are needed to fully understand its long-term impacts and potential limitations.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🤖

0
Strategic AI adoption in SMEs: A Prescriptive Framework
Atif Hussain, Rana Rizwan
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is increasingly acknowledged as a vital component for the advancement and competitiveness of modern organizations, including small and medium enterprises (SMEs). However, the adoption of AI technologies in SMEs faces significant barriers, primarily related to cost, lack of technical skills, and employee acceptance. This study proposes a comprehensive, phased framework designed to facilitate the effective adoption of AI in SMEs by systematically addressing these barriers. The framework begins with raising awareness and securing commitment from leadership, followed by the adoption of low-cost, general-purpose AI tools to build technical competence and foster a positive attitude towards AI. As familiarity with AI technologies increases, the framework advocates for the integration of task-specific AI tools to enhance efficiency and productivity. Subsequently, it guides organizations towards the in-house development of generative AI tools, providing greater customization and control. Finally, the framework addresses the development of discriminative AI models to meet highly specific and precision-oriented tasks. By providing a structured and incremental approach, this framework ensures that SMEs can navigate the complexities of AI integration effectively, driving innovation, efficiency, and competitive advantage. This study contributes to the field by offering a practical, prescriptive framework tailored to the unique needs of SMEs, facilitating the successful adoption of AI technologies and positioning these organizations for sustained growth in a competitive landscape.
Read more8/23/2024

0
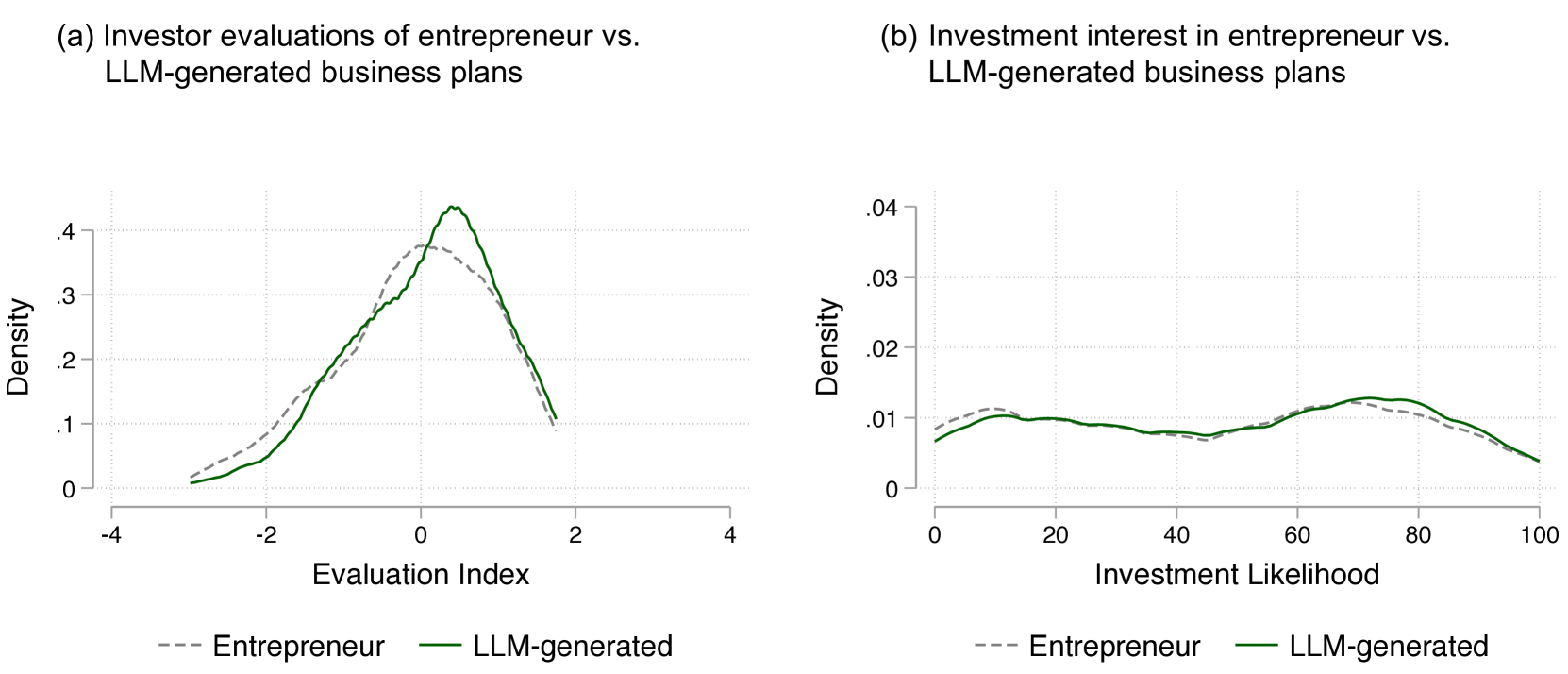
Artificial Intelligence and Strategic Decision-Making: Evidence from Entrepreneurs and Investors
Felipe A. Csaszar, Harsh Ketkar, Hyunjin Kim
This paper explores how artificial intelligence (AI) may impact the strategic decision-making (SDM) process in firms. We illustrate how AI could augment existing SDM tools and provide empirical evidence from a leading accelerator program and a startup competition that current Large Language Models (LLMs) can generate and evaluate strategies at a level comparable to entrepreneurs and investors. We then examine implications for key cognitive processes underlying SDM -- search, representation, and aggregation. Our analysis suggests AI has the potential to enhance the speed, quality, and scale of strategic analysis, while also enabling new approaches like virtual strategy simulations. However, the ultimate impact on firm performance will depend on competitive dynamics as AI capabilities progress. We propose a framework connecting AI use in SDM to firm outcomes and discuss how AI may reshape sources of competitive advantage. We conclude by considering how AI could both support and challenge core tenets of the theory-based view of strategy. Overall, our work maps out an emerging research frontier at the intersection of AI and strategy.
Read more8/19/2024


0
Integrating ESG and AI: A Comprehensive Responsible AI Assessment Framework
Sung Une Lee, Harsha Perera, Yue Liu, Boming Xia, Qinghua Lu, Liming Zhu, Jessica Cairns, Moana Nottage
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a widely developed and adopted technology across entire industry sectors. Integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations with AI investments is crucial for ensuring ethical and sustainable technological advancement. Particularly from an investor perspective, this integration not only mitigates risks but also enhances long-term value creation by aligning AI initiatives with broader societal goals. Yet, this area has been less explored in both academia and industry. To bridge the gap, we introduce a novel ESG-AI framework, which is developed based on insights from engagements with 28 companies and comprises three key components. The framework provides a structured approach to this integration, developed in collaboration with industry practitioners. The ESG-AI framework provides an overview of the environmental and social impacts of AI applications, helping users such as investors assess the materiality of AI use. Moreover, it enables investors to evaluate a company's commitment to responsible AI through structured engagements and thorough assessment of specific risk areas. We have publicly released the framework and toolkit in April 2024, which has received significant attention and positive feedback from the investment community. This paper details each component of the framework, demonstrating its applicability in real-world contexts and its potential to guide ethical AI investments.
Read more8/7/2024

0
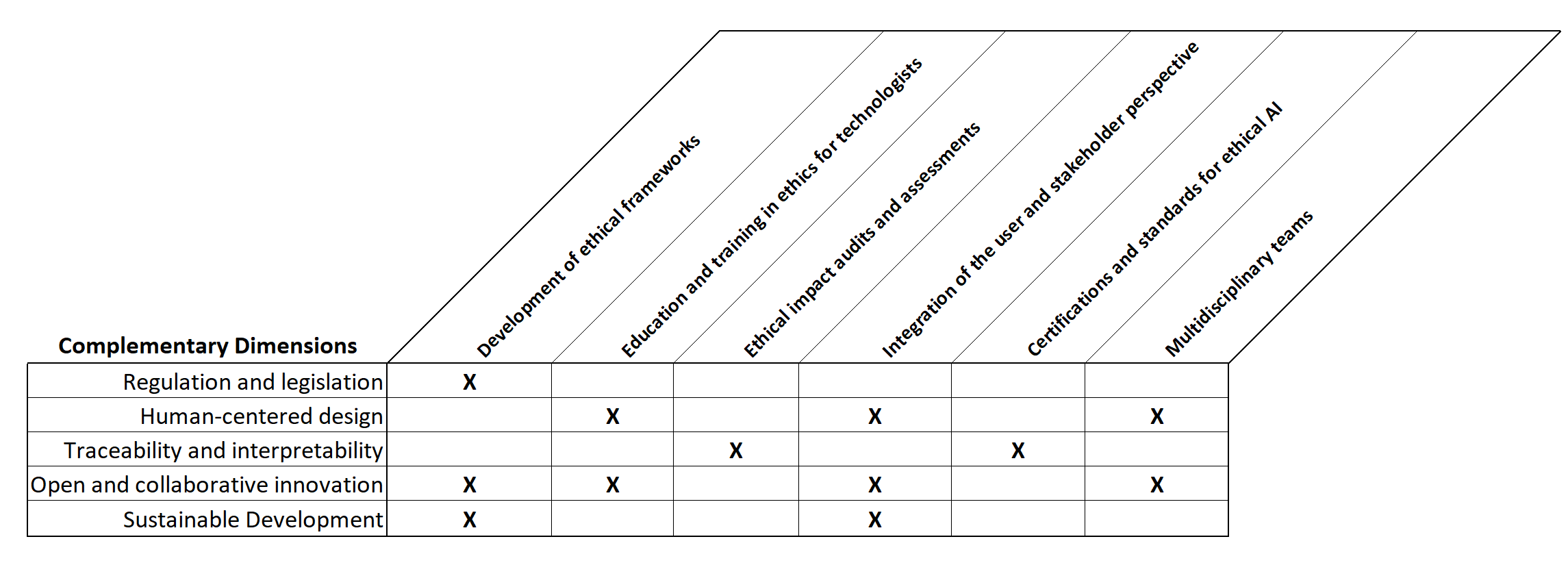
Towards an Ethical and Inclusive Implementation of Artificial Intelligence in Organizations: A Multidimensional Framework
Ernesto Giralt Hern'andez
This article analyzes the impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on contemporary society and the importance of adopting an ethical approach to its development and implementation within organizations. It examines the technocritical perspective of some philosophers and researchers, who warn of the risks of excessive technologization that could undermine human autonomy. However, the article also acknowledges the active role that various actors, such as governments, academics, and civil society, can play in shaping the development of AI aligned with human and social values. A multidimensional approach is proposed that combines ethics with regulation, innovation, and education. It highlights the importance of developing detailed ethical frameworks, incorporating ethics into the training of professionals, conducting ethical impact audits, and encouraging the participation of stakeholders in the design of AI. In addition, four fundamental pillars are presented for the ethical implementation of AI in organizations: 1) Integrated values, 2) Trust and transparency, 3) Empowering human growth, and 4) Identifying strategic factors. These pillars encompass aspects such as alignment with the company's ethical identity, governance and accountability, human-centered design, continuous training, and adaptability to technological and market changes. The conclusion emphasizes that ethics must be the cornerstone of any organization's strategy that seeks to incorporate AI, establishing a solid framework that ensures that technology is developed and used in a way that respects and promotes human values.
Read more5/6/2024