Generative AI in the Wild: Prospects, Challenges, and Strategies
2302.10827

0
0
🤖
Abstract
Automated machine learning (AutoML) is envisioned to make ML techniques accessible to ordinary users. Recent work has investigated the role of humans in enhancing AutoML functionality throughout a standard ML workflow. However, it is also critical to understand how users adopt existing AutoML solutions in complex, real-world settings from a holistic perspective. To fill this gap, this study conducted semi-structured interviews of AutoML users (N=19) focusing on understanding (1) the limitations of AutoML encountered by users in their real-world practices, (2) the strategies users adopt to cope with such limitations, and (3) how the limitations and workarounds impact their use of AutoML. Our findings reveal that users actively exercise user agency to overcome three major challenges arising from customizability, transparency, and privacy. Furthermore, users make cautious decisions about whether and how to apply AutoML on a case-by-case basis. Finally, we derive design implications for developing future AutoML solutions.
Get summaries of the top AI research delivered straight to your inbox:
Overview
- Generative AI (GenAI) technologies are transforming creative industries by enabling new forms of human-AI collaboration.
- While previous research has focused on the technical capabilities of GenAI, this study explores how users perceive and utilize these technologies in real-world scenarios.
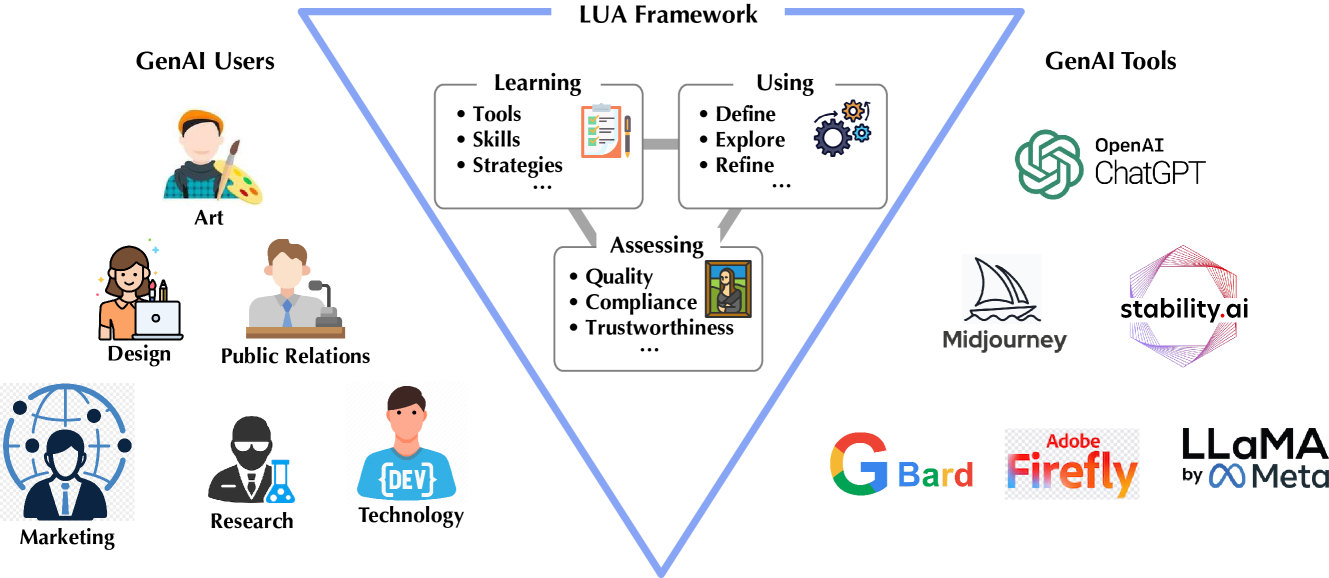
- The study follows a holistic "Learning, Using, and Assessing" (LUA) framework to understand the human-GenAI co-creation process.
Plain English Explanation
Generative AI (GenAI) systems are a new type of technology that can create novel and engaging content, such as text, images, and even music. These systems have the potential to greatly enhance creative workflows by working alongside human experts. However, little is known about how people actually use and experience these tools in their day-to-day work.
To better understand this, researchers interviewed 18 people who use GenAI in creative industries. They wanted to see how these users learn to work with GenAI, how they incorporate it into their creative processes, and how they evaluate the technology's strengths and limitations.
The study found that GenAI can indeed foster productive collaboration between humans and machines. Users reported that GenAI helps them generate new ideas and explore creative avenues they might not have considered otherwise. At the same time, users also face significant challenges, such as managing the resources required to use GenAI, making the tools user-friendly, and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations.
In response, users have developed various strategies to overcome these challenges. For example, they might experiment with different GenAI models to find the best fit for their needs or work closely with developers to improve the tools' usability.
Overall, this research provides valuable insights into the real-world dynamics of human-GenAI collaboration, which can inform the design of future GenAI tools and systems.
Technical Explanation
The researchers conducted semi-structured interviews with 18 users of GenAI technologies in creative industries. They used a holistic "Learning, Using, and Assessing" (LUA) framework to understand the human-GenAI co-creation process from multiple perspectives.
In the "Learning" phase, the researchers explored how users acquire the necessary skills and knowledge to work with GenAI tools. They found that users often engage in self-directed learning, experimenting with different models and techniques to understand the capabilities and limitations of the technology.
During the "Using" phase, the researchers examined how users integrate GenAI into their creative workflows. They discovered that GenAI can greatly facilitate the co-creation process, enabling users to generate novel ideas and explore new creative avenues. However, users also face substantial challenges, such as managing the computational resources required to run GenAI models, ensuring the tools are user-friendly, and maintaining compliance with relevant regulations.
In the "Assessing" phase, the researchers investigated how users evaluate the performance and impact of GenAI technologies. Users reported a range of strategies for overcoming the challenges they encountered, such as experimenting with different GenAI models, collaborating with tool developers, and establishing internal guidelines for responsible use.
The study's findings highlight the complex and multifaceted nature of human-GenAI collaboration in real-world creative settings. The insights gained can inform the design of future GenAI tools and systems to better support users' needs and preferences.
Critical Analysis
The study provides valuable insights into the practical realities of using GenAI technologies in creative industries, an area that has received limited attention in prior research. By adopting a holistic LUA framework, the researchers were able to capture the nuanced interplay between users' learning processes, usage patterns, and assessment strategies.
One potential limitation of the study is the relatively small sample size of 18 participants. While the researchers conducted in-depth interviews, a larger and more diverse sample could have yielded additional insights and perspectives. Additionally, the study focused on creative industries, and the findings may not be generalizable to other domains where GenAI is being applied.
Further research could explore the experiences of GenAI users in different sectors, as well as the potential long-term societal and economic implications of widespread GenAI adoption. Investigating the ethical considerations surrounding the use of these technologies, such as issues of bias, transparency, and accountability, could also be a fruitful area for future inquiry.
Conclusion
This study offers a comprehensive understanding of how users perceive and utilize GenAI technologies in real-world creative settings. The research highlights the complex interplay between the benefits and challenges of human-GenAI collaboration, as well as the diverse strategies users employ to navigate this evolving landscape.
The insights gained can inform the design of future GenAI tools and systems, ensuring they better support users' needs and preferences. As GenAI technologies continue to advance, understanding the human experience will be crucial for unlocking their full potential and steering their development in socially responsible directions.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
Generative AI in the Wild: Prospects, Challenges, and Strategies
Yuan Sun, Eunchae Jang, Fenglong Ma, Ting Wang

0
0
Propelled by their remarkable capabilities to generate novel and engaging content, Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) technologies are disrupting traditional workflows in many industries. While prior research has examined GenAI from a techno-centric perspective, there is still a lack of understanding about how users perceive and utilize GenAI in real-world scenarios. To bridge this gap, we conducted semi-structured interviews with (N=18) GenAI users in creative industries, investigating the human-GenAI co-creation process within a holistic LUA (Learning, Using and Assessing) framework. Our study uncovered an intriguingly complex landscape: Prospects-GenAI greatly fosters the co-creation between human expertise and GenAI capabilities, profoundly transforming creative workflows; Challenges-Meanwhile, users face substantial uncertainties and complexities arising from resource availability, tool usability, and regulatory compliance; Strategies-In response, users actively devise various strategies to overcome many of such challenges. Our study reveals key implications for the design of future GenAI tools.
4/8/2024
📉
Automating Creativity
Ming-Hui Huang, Roland T. Rust

0
0
Generative AI (GenAI) has spurred the expectation of being creative, due to its ability to generate content, yet so far, its creativity has somewhat disappointed, because it is trained using existing data following human intentions to generate outputs. The purpose of this paper is to explore what is required to evolve AI from generative to creative. Based on a reinforcement learning approach and building upon various research streams of computational creativity, we develop a triple prompt-response-reward engineering framework to develop the creative capability of GenAI. This framework consists of three components: 1) a prompt model for expected creativity by developing discriminative prompts that are objectively, individually, or socially novel, 2) a response model for observed creativity by generating surprising outputs that are incrementally, disruptively, or radically innovative, and 3) a reward model for improving creativity over time by incorporating feedback from the AI, the creator/manager, and/or the customers. This framework enables the application of GenAI for various levels of creativity strategically.
5/14/2024
🤖
Crafting Tomorrow's Evaluations: Assessment Design Strategies in the Era of Generative AI
Rajan Kadel, Bhupesh Kumar Mishra, Samar Shailendra, Samia Abid, Maneeha Rani, Shiva Prasad Mahato

0
0
GenAI has gained the attention of a myriad of users in almost every profession. Its advancement has had an intense impact on education, significantly disrupting the assessment design and evaluation methodologies. Despite the potential benefits and possibilities of GenAI in the education sector, there are several concerns primarily centred around academic integrity, authenticity, equity of access, assessment evaluation methodology, and feedback. Consequently, academia is encountering challenges in assessment design that are essential to retaining academic integrity in the age of GenAI. In this article, we discuss the challenges, and opportunities that need to be addressed for the assessment design and evaluation. The article also highlights the importance of clear policy about the usage of GenAI in completing assessment tasks, and also in design approaches to ensure academic integrity and subject learning. Additionally, this article also provides assessment categorisation based on the use of GenAI to cultivate knowledge among students and academic professionals. It also provides information on the skills necessary to formulate and articulate problems and evaluate the task, enabling students and academics to effectively utilise GenAI tools.
5/6/2024
🤖
The collective use and evaluation of generative AI tools in digital humanities research: Survey-based results
Meredith Dedema, Rongqian Ma

0
0
The advent of generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) technologies has revolutionized research, with significant implications for Digital Humanities (DH), a field inherently intertwined with technological progress. This article investigates how digital humanities scholars adopt, practice, as well as critically evaluate, GenAI technologies such as ChatGPT in the research process. Drawing on 76 responses collected from an international survey study, we explored digital humanities scholars' rationale for GenAI adoption in research, identified specific use cases and practices of using GenAI to support various DH research tasks, and analyzed scholars' collective perceptions of GenAI's benefits, risks, and impact on DH research. The survey results suggest that DH research communities hold divisive sentiments towards the value of GenAI in DH scholarship, whereas the actual usage diversifies among individuals and across research tasks. Our survey-based analysis has the potential to serve as a basis for further empirical research on the impact of GenAI on the evolution of DH scholarship.
4/22/2024