Benchmarking and Improving Bird's Eye View Perception Robustness in Autonomous Driving
2405.17426

0
0

Abstract
Recent advancements in bird's eye view (BEV) representations have shown remarkable promise for in-vehicle 3D perception. However, while these methods have achieved impressive results on standard benchmarks, their robustness in varied conditions remains insufficiently assessed. In this study, we present RoboBEV, an extensive benchmark suite designed to evaluate the resilience of BEV algorithms. This suite incorporates a diverse set of camera corruption types, each examined over three severity levels. Our benchmarks also consider the impact of complete sensor failures that occur when using multi-modal models. Through RoboBEV, we assess 33 state-of-the-art BEV-based perception models spanning tasks like detection, map segmentation, depth estimation, and occupancy prediction. Our analyses reveal a noticeable correlation between the model's performance on in-distribution datasets and its resilience to out-of-distribution challenges. Our experimental results also underline the efficacy of strategies like pre-training and depth-free BEV transformations in enhancing robustness against out-of-distribution data. Furthermore, we observe that leveraging extensive temporal information significantly improves the model's robustness. Based on our observations, we design an effective robustness enhancement strategy based on the CLIP model. The insights from this study pave the way for the development of future BEV models that seamlessly combine accuracy with real-world robustness.
Create account to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
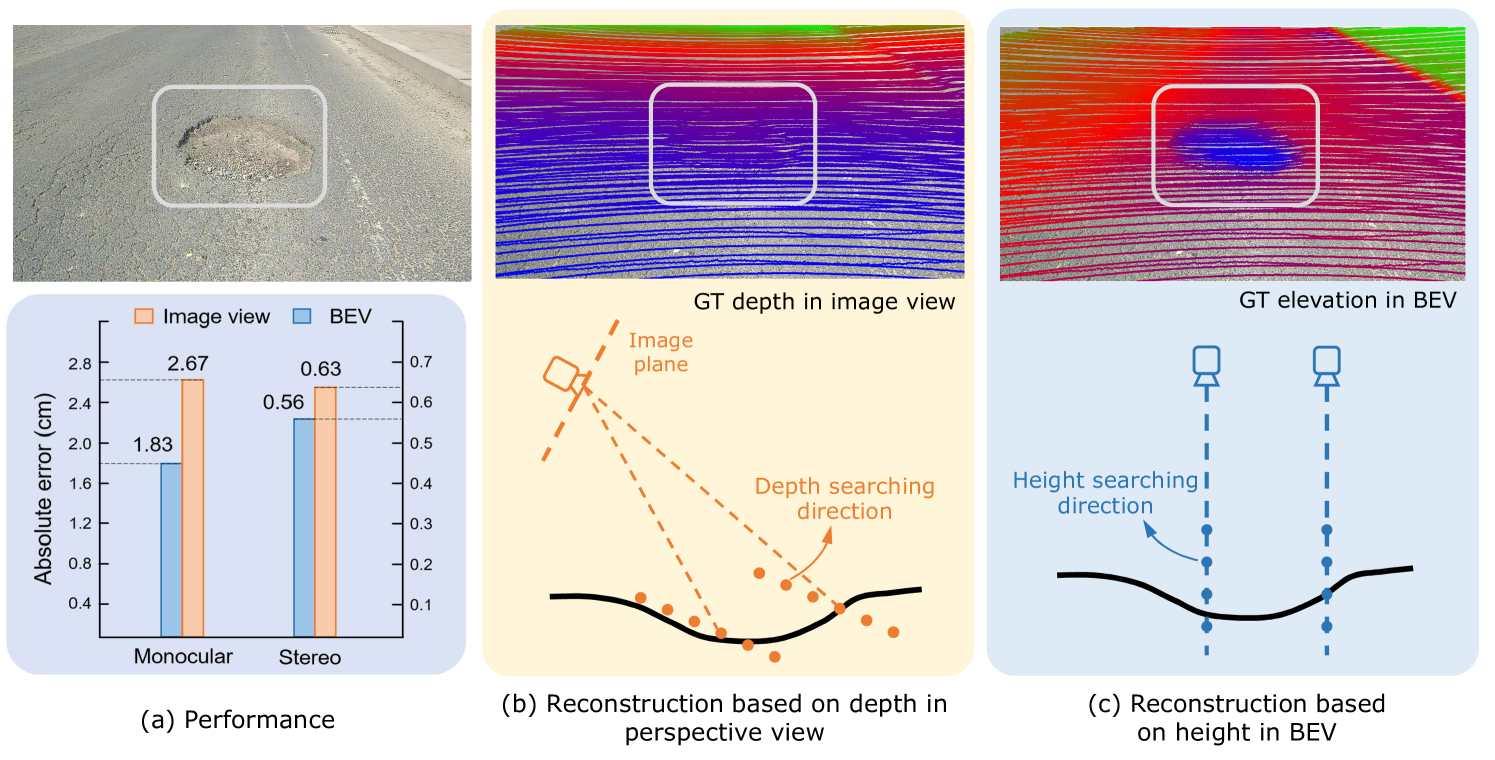
RoadBEV: Road Surface Reconstruction in Bird's Eye View
Tong Zhao, Lei Yang, Yichen Xie, Mingyu Ding, Masayoshi Tomizuka, Yintao Wei

0
0
Road surface conditions, especially geometry profiles, enormously affect driving performance of autonomous vehicles. Vision-based online road reconstruction promisingly captures road information in advance. Existing solutions like monocular depth estimation and stereo matching suffer from modest performance. The recent technique of Bird's-Eye-View (BEV) perception provides immense potential to more reliable and accurate reconstruction. This paper uniformly proposes two simple yet effective models for road elevation reconstruction in BEV named RoadBEV-mono and RoadBEV-stereo, which estimate road elevation with monocular and stereo images, respectively. The former directly fits elevation values based on voxel features queried from image view, while the latter efficiently recognizes road elevation patterns based on BEV volume representing discrepancy between left and right voxel features. Insightful analyses reveal their consistence and difference with perspective view. Experiments on real-world dataset verify the models' effectiveness and superiority. Elevation errors of RoadBEV-mono and RoadBEV-stereo achieve 1.83cm and 0.50cm, respectively. The estimation performance improves by 50% in BEV based on monocular image. Our models are promising for practical applications, providing valuable references for vision-based BEV perception in autonomous driving. The code is released at https://github.com/ztsrxh/RoadBEV.
4/24/2024

Uncertainty Quantification for Bird's Eye View Semantic Segmentation: Methods and Benchmarks
Linlin Yu, Bowen Yang, Tianhao Wang, Kangshuo Li, Feng Chen

0
0
The fusion of raw features from multiple sensors on an autonomous vehicle to create a Bird's Eye View (BEV) representation is crucial for planning and control systems. There is growing interest in using deep learning models for BEV semantic segmentation. Anticipating segmentation errors and improving the explainability of DNNs is essential for autonomous driving, yet it is under-studied. This paper introduces a benchmark for predictive uncertainty quantification in BEV segmentation. The benchmark assesses various approaches across three popular datasets using two representative backbones and focuses on the effectiveness of predicted uncertainty in identifying misclassified and out-of-distribution (OOD) pixels, as well as calibration. Empirical findings highlight the challenges in uncertainty quantification. Our results find that evidential deep learning based approaches show the most promise by efficiently quantifying aleatoric and epistemic uncertainty. We propose the Uncertainty-Focal-Cross-Entropy (UFCE) loss, designed for highly imbalanced data, which consistently improves the segmentation quality and calibration. Additionally, we introduce a vacuity-scaled regularization term that enhances the model's focus on high uncertainty pixels, improving epistemic uncertainty quantification.
6/3/2024

Improving Bird's Eye View Semantic Segmentation by Task Decomposition
Tianhao Zhao, Yongcan Chen, Yu Wu, Tianyang Liu, Bo Du, Peilun Xiao, Shi Qiu, Hongda Yang, Guozhen Li, Yi Yang, Yutian Lin

0
0
Semantic segmentation in bird's eye view (BEV) plays a crucial role in autonomous driving. Previous methods usually follow an end-to-end pipeline, directly predicting the BEV segmentation map from monocular RGB inputs. However, the challenge arises when the RGB inputs and BEV targets from distinct perspectives, making the direct point-to-point predicting hard to optimize. In this paper, we decompose the original BEV segmentation task into two stages, namely BEV map reconstruction and RGB-BEV feature alignment. In the first stage, we train a BEV autoencoder to reconstruct the BEV segmentation maps given corrupted noisy latent representation, which urges the decoder to learn fundamental knowledge of typical BEV patterns. The second stage involves mapping RGB input images into the BEV latent space of the first stage, directly optimizing the correlations between the two views at the feature level. Our approach simplifies the complexity of combining perception and generation into distinct steps, equipping the model to handle intricate and challenging scenes effectively. Besides, we propose to transform the BEV segmentation map from the Cartesian to the polar coordinate system to establish the column-wise correspondence between RGB images and BEV maps. Moreover, our method requires neither multi-scale features nor camera intrinsic parameters for depth estimation and saves computational overhead. Extensive experiments on nuScenes and Argoverse show the effectiveness and efficiency of our method. Code is available at https://github.com/happytianhao/TaDe.
4/3/2024

GraphBEV: Towards Robust BEV Feature Alignment for Multi-Modal 3D Object Detection
Ziying Song, Lei Yang, Shaoqing Xu, Lin Liu, Dongyang Xu, Caiyan Jia, Feiyang Jia, Li Wang

0
0
Integrating LiDAR and camera information into Bird's-Eye-View (BEV) representation has emerged as a crucial aspect of 3D object detection in autonomous driving. However, existing methods are susceptible to the inaccurate calibration relationship between LiDAR and the camera sensor. Such inaccuracies result in errors in depth estimation for the camera branch, ultimately causing misalignment between LiDAR and camera BEV features. In this work, we propose a robust fusion framework called Graph BEV. Addressing errors caused by inaccurate point cloud projection, we introduce a Local Align module that employs neighbor-aware depth features via Graph matching. Additionally, we propose a Global Align module to rectify the misalignment between LiDAR and camera BEV features. Our Graph BEV framework achieves state-of-the-art performance, with an mAP of 70.1%, surpassing BEV Fusion by 1.6% on the nuscenes validation set. Importantly, our Graph BEV outperforms BEV Fusion by 8.3% under conditions with misalignment noise.
4/11/2024