Benchmarking Large Language Models for Persian: A Preliminary Study Focusing on ChatGPT
2404.02403

0
0
Abstract
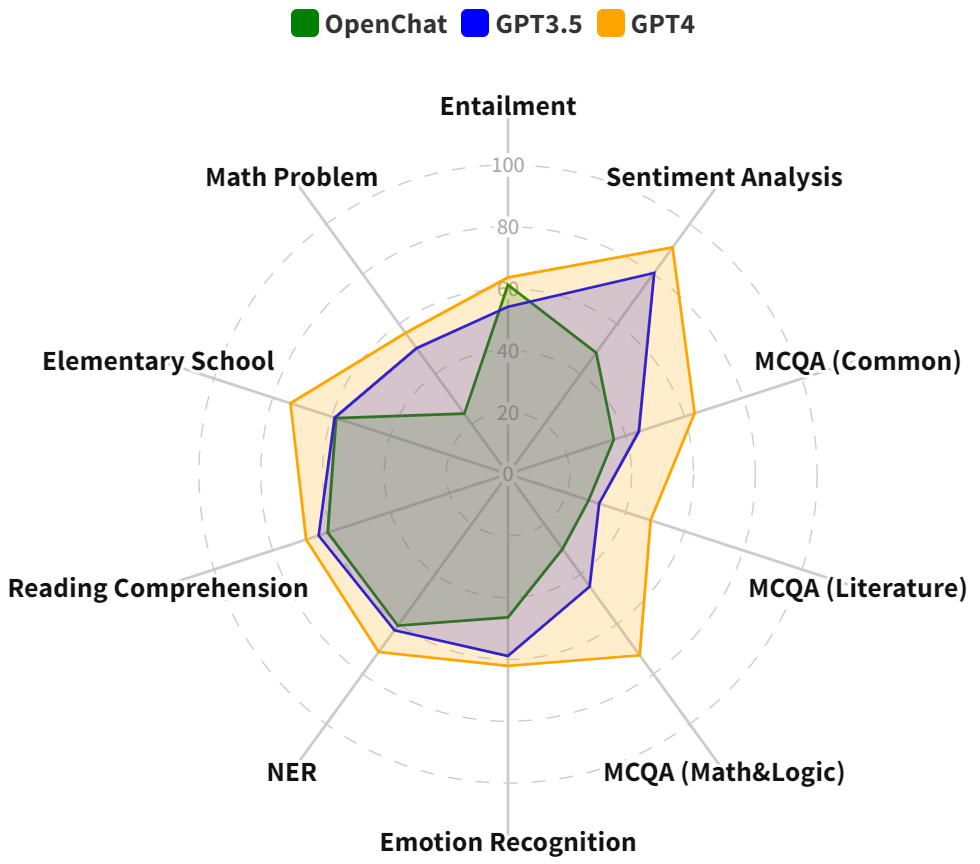
This paper explores the efficacy of large language models (LLMs) for Persian. While ChatGPT and consequent LLMs have shown remarkable performance in English, their efficiency for more low-resource languages remains an open question. We present the first comprehensive benchmarking study of LLMs across diverse Persian language tasks. Our primary focus is on GPT-3.5-turbo, but we also include GPT-4 and OpenChat-3.5 to provide a more holistic evaluation. Our assessment encompasses a diverse set of tasks categorized into classic, reasoning, and knowledge-based domains. To enable a thorough comparison, we evaluate LLMs against existing task-specific fine-tuned models. Given the limited availability of Persian datasets for reasoning tasks, we introduce two new benchmarks: one based on elementary school math questions and another derived from the entrance exams for 7th and 10th grades. Our findings reveal that while LLMs, especially GPT-4, excel in tasks requiring reasoning abilities and a broad understanding of general knowledge, they often lag behind smaller pre-trained models fine-tuned specifically for particular tasks. Additionally, we observe improved performance when test sets are translated to English before inputting them into GPT-3.5. These results highlight the significant potential for enhancing LLM performance in the Persian language. This is particularly noteworthy due to the unique attributes of Persian, including its distinct alphabet and writing styles.
Get summaries of the top AI research delivered straight to your inbox:
Overview
- This paper presents a preliminary study on benchmarking large language models (LLMs) for the Persian language, with a focus on the popular ChatGPT model.
- The researchers evaluate the performance of ChatGPT on various tasks related to Persian, including language generation, translation, and question answering.
- The goal is to provide insights into the capabilities and limitations of ChatGPT when it comes to processing and generating Persian text, which is an important step in understanding the state of LLMs for this language.
Plain English Explanation
Large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT have shown impressive performance on a wide range of tasks, from generating human-like text to answering questions. However, the majority of research and development on these models has focused on English and a few other high-resource languages.
In this study, the researchers wanted to explore how well ChatGPT, one of the most advanced LLMs, performs when it comes to the Persian language. Persian is an important language spoken by millions of people, but it is considered a low-resource language in the field of natural language processing.
The researchers tested ChatGPT on various tasks related to Persian, such as generating coherent Persian text, translating between Persian and English, and answering questions about Persian language and culture. By analyzing ChatGPT's performance on these tasks, the researchers were able to identify the model's strengths and weaknesses when it comes to the Persian language.
The findings of this study provide valuable insights for researchers and developers working on improving LLMs for low-resource languages like Persian. It also highlights the importance of evaluating the capabilities of these models across a diverse range of languages, rather than focusing solely on high-resource languages like English.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a preliminary study on benchmarking the performance of the large language model ChatGPT on various tasks related to the Persian language. The researchers designed a set of experiments to evaluate ChatGPT's capabilities in areas such as Persian text generation, translation, and question answering.
For text generation, the researchers prompted ChatGPT to generate Persian text on a variety of topics and assessed the coherence, fluency, and grammatical correctness of the generated output. They also tested ChatGPT's ability to translate between Persian and English, both in terms of accuracy and fluency.
To evaluate question answering, the researchers curated a set of questions related to Persian language, culture, and history, and examined how well ChatGPT was able to provide relevant and informative responses.
The results of the experiments reveal both the strengths and limitations of ChatGPT when it comes to processing and generating Persian text. While the model demonstrated some ability to handle Persian, it also exhibited challenges in areas like maintaining consistent grammar, producing contextually appropriate responses, and demonstrating a deep understanding of Persian-specific concepts and nuances.
The findings of this study contribute to the growing body of research on the multilingual capabilities of large language models, highlighting the need for further development and evaluation of these models for low-resource languages like Persian.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a valuable initial exploration of ChatGPT's performance on Persian-related tasks, but it acknowledges the preliminary nature of the study and the need for more comprehensive evaluation.
One limitation of the study is the relatively small scale of the experiments, with a limited number of prompts and test cases. Expanding the scope of the evaluation, including a wider range of task types and a larger and more diverse set of test data, would help to provide a more robust assessment of ChatGPT's capabilities.
Additionally, the paper does not delve deeply into the specific challenges and limitations observed in ChatGPT's Persian language processing. A more detailed analysis of the error patterns and the model's weaknesses could yield additional insights that could inform future model development and fine-tuning efforts.
It would also be valuable to compare ChatGPT's performance to that of other large language models, both monolingual and multilingual, to better understand the relative strengths and weaknesses of different approaches to Persian language processing.
Despite these limitations, the paper serves as an important first step in benchmarking the capabilities of state-of-the-art language models for Persian, which is a crucial step in advancing the field of natural language processing for low-resource languages.
Conclusion
This preliminary study on benchmarking ChatGPT for Persian language tasks provides valuable insights into the current capabilities and limitations of large language models when it comes to processing and generating Persian text.
The findings suggest that while ChatGPT demonstrates some ability to handle Persian, it also faces significant challenges in areas like grammar, context-awareness, and deep understanding of Persian-specific concepts. These insights are important for researchers and developers working on improving the multilingual capabilities of LLMs, as they highlight the need for more focused efforts on low-resource languages like Persian.
As the field of natural language processing continues to advance, studies like this one will play a crucial role in driving the development of language models that can truly serve the needs of diverse linguistic communities around the world.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
💬
MEGAVERSE: Benchmarking Large Language Models Across Languages, Modalities, Models and Tasks
Sanchit Ahuja, Divyanshu Aggarwal, Varun Gumma, Ishaan Watts, Ashutosh Sathe, Millicent Ochieng, Rishav Hada, Prachi Jain, Maxamed Axmed, Kalika Bali, Sunayana Sitaram

0
0
There has been a surge in LLM evaluation research to understand LLM capabilities and limitations. However, much of this research has been confined to English, leaving LLM building and evaluation for non-English languages relatively unexplored. Several new LLMs have been introduced recently, necessitating their evaluation on non-English languages. This study aims to perform a thorough evaluation of the non-English capabilities of SoTA LLMs (GPT-3.5-Turbo, GPT-4, PaLM2, Gemini-Pro, Mistral, Llama2, and Gemma) by comparing them on the same set of multilingual datasets. Our benchmark comprises 22 datasets covering 83 languages, including low-resource African languages. We also include two multimodal datasets in the benchmark and compare the performance of LLaVA models, GPT-4-Vision and Gemini-Pro-Vision. Our experiments show that larger models such as GPT-4, Gemini-Pro and PaLM2 outperform smaller models on various tasks, notably on low-resource languages, with GPT-4 outperforming PaLM2 and Gemini-Pro on more datasets. We also perform a study on data contamination and find that several models are likely to be contaminated with multilingual evaluation benchmarks, necessitating approaches to detect and handle contamination while assessing the multilingual performance of LLMs.
4/4/2024
A Systematic Evaluation of Large Language Models for Natural Language Generation Tasks
Xuanfan Ni, Piji Li

0
0
Recent efforts have evaluated large language models (LLMs) in areas such as commonsense reasoning, mathematical reasoning, and code generation. However, to the best of our knowledge, no work has specifically investigated the performance of LLMs in natural language generation (NLG) tasks, a pivotal criterion for determining model excellence. Thus, this paper conducts a comprehensive evaluation of well-known and high-performing LLMs, namely ChatGPT, ChatGLM, T5-based models, LLaMA-based models, and Pythia-based models, in the context of NLG tasks. We select English and Chinese datasets encompassing Dialogue Generation and Text Summarization. Moreover, we propose a common evaluation setting that incorporates input templates and post-processing strategies. Our study reports both automatic results, accompanied by a detailed analysis.
5/17/2024
💬
ChatGPT as an inventor: Eliciting the strengths and weaknesses of current large language models against humans in engineering design
Daniel Nyg{aa}rd Ege, Henrik H. {O}vreb{o}, Vegar Stubberud, Martin Francis Berg, Christer Elverum, Martin Steinert, H{aa}vard Vestad

0
0
This study compares the design practices and performance of ChatGPT 4.0, a large language model (LLM), against graduate engineering students in a 48-hour prototyping hackathon, based on a dataset comprising more than 100 prototypes. The LLM participated by instructing two participants who executed its instructions and provided objective feedback, generated ideas autonomously and made all design decisions without human intervention. The LLM exhibited similar prototyping practices to human participants and finished second among six teams, successfully designing and providing building instructions for functional prototypes. The LLM's concept generation capabilities were particularly strong. However, the LLM prematurely abandoned promising concepts when facing minor difficulties, added unnecessary complexity to designs, and experienced design fixation. Communication between the LLM and participants was challenging due to vague or unclear descriptions, and the LLM had difficulty maintaining continuity and relevance in answers. Based on these findings, six recommendations for implementing an LLM like ChatGPT in the design process are proposed, including leveraging it for ideation, ensuring human oversight for key decisions, implementing iterative feedback loops, prompting it to consider alternatives, and assigning specific and manageable tasks at a subsystem level.
4/30/2024
Comparing the Efficacy of GPT-4 and Chat-GPT in Mental Health Care: A Blind Assessment of Large Language Models for Psychological Support
Birger Moell

0
0
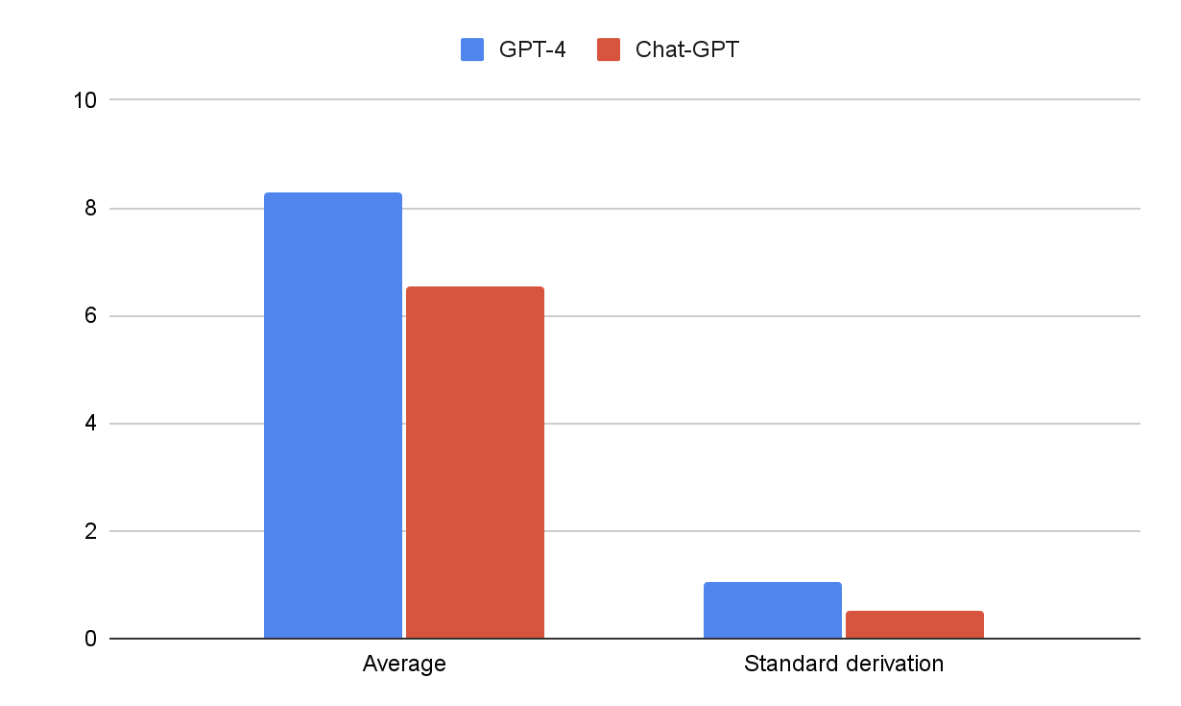
Background: Rapid advancements in natural language processing have led to the development of large language models with the potential to revolutionize mental health care. These models have shown promise in assisting clinicians and providing support to individuals experiencing various psychological challenges. Objective: This study aims to compare the performance of two large language models, GPT-4 and Chat-GPT, in responding to a set of 18 psychological prompts, to assess their potential applicability in mental health care settings. Methods: A blind methodology was employed, with a clinical psychologist evaluating the models' responses without knowledge of their origins. The prompts encompassed a diverse range of mental health topics, including depression, anxiety, and trauma, to ensure a comprehensive assessment. Results: The results demonstrated a significant difference in performance between the two models (p > 0.05). GPT-4 achieved an average rating of 8.29 out of 10, while Chat-GPT received an average rating of 6.52. The clinical psychologist's evaluation suggested that GPT-4 was more effective at generating clinically relevant and empathetic responses, thereby providing better support and guidance to potential users. Conclusions: This study contributes to the growing body of literature on the applicability of large language models in mental health care settings. The findings underscore the importance of continued research and development in the field to optimize these models for clinical use. Further investigation is necessary to understand the specific factors underlying the performance differences between the two models and to explore their generalizability across various populations and mental health conditions.
5/16/2024