Bring Adaptive Binding Prototypes to Generalized Referring Expression Segmentation

0

Sign in to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Bring Adaptive Binding Prototypes to Generalized Referring Expression Segmentation
Weize Li, Zhicheng Zhao, Haochen Bai, Fei Su
Referring Expression Segmentation (RES) has attracted rising attention, aiming to identify and segment objects based on natural language expressions. While substantial progress has been made in RES, the emergence of Generalized Referring Expression Segmentation (GRES) introduces new challenges by allowing expressions to describe multiple objects or lack specific object references. Existing RES methods, usually rely on sophisticated encoder-decoder and feature fusion modules, and are difficult to generate class prototypes that match each instance individually when confronted with the complex referent and binary labels of GRES. In this paper, reevaluating the differences between RES and GRES, we propose a novel Model with Adaptive Binding Prototypes (MABP) that adaptively binds queries to object features in the corresponding region. It enables different query vectors to match instances of different categories or different parts of the same instance, significantly expanding the decoder's flexibility, dispersing global pressure across all queries, and easing the demands on the encoder. Experimental results demonstrate that MABP significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in all three splits on gRefCOCO dataset. Meanwhile, MABP also surpasses state-of-the-art methods on RefCOCO+ and G-Ref datasets, and achieves very competitive results on RefCOCO. Code is available at https://github.com/buptLwz/MABP
Read more5/27/2024


0
3D-GRES: Generalized 3D Referring Expression Segmentation
Changli Wu, Yihang Liu, Jiayi Ji, Yiwei Ma, Haowei Wang, Gen Luo, Henghui Ding, Xiaoshuai Sun, Rongrong Ji
3D Referring Expression Segmentation (3D-RES) is dedicated to segmenting a specific instance within a 3D space based on a natural language description. However, current approaches are limited to segmenting a single target, restricting the versatility of the task. To overcome this limitation, we introduce Generalized 3D Referring Expression Segmentation (3D-GRES), which extends the capability to segment any number of instances based on natural language instructions. In addressing this broader task, we propose the Multi-Query Decoupled Interaction Network (MDIN), designed to break down multi-object segmentation tasks into simpler, individual segmentations. MDIN comprises two fundamental components: Text-driven Sparse Queries (TSQ) and Multi-object Decoupling Optimization (MDO). TSQ generates sparse point cloud features distributed over key targets as the initialization for queries. Meanwhile, MDO is tasked with assigning each target in multi-object scenarios to different queries while maintaining their semantic consistency. To adapt to this new task, we build a new dataset, namely Multi3DRes. Our comprehensive evaluations on this dataset demonstrate substantial enhancements over existing models, thus charting a new path for intricate multi-object 3D scene comprehension. The benchmark and code are available at https://github.com/sosppxo/MDIN.
Read more8/1/2024


0
HDC: Hierarchical Semantic Decoding with Counting Assistance for Generalized Referring Expression Segmentation
Zhuoyan Luo, Yinghao Wu, Yong Liu, Yicheng Xiao, Xiao-Ping Zhang, Yujiu Yang
The newly proposed Generalized Referring Expression Segmentation (GRES) amplifies the formulation of classic RES by involving multiple/non-target scenarios. Recent approaches focus on optimizing the last modality-fused feature which is directly utilized for segmentation and object-existence identification. However, the attempt to integrate all-grained information into a single joint representation is impractical in GRES due to the increased complexity of the spatial relationships among instances and deceptive text descriptions. Furthermore, the subsequent binary target justification across all referent scenarios fails to specify their inherent differences, leading to ambiguity in object understanding. To address the weakness, we propose a $textbf{H}$ierarchical Semantic $textbf{D}$ecoding with $textbf{C}$ounting Assistance framework (HDC). It hierarchically transfers complementary modality information across granularities, and then aggregates each well-aligned semantic correspondence for multi-level decoding. Moreover, with complete semantic context modeling, we endow HDC with explicit counting capability to facilitate comprehensive object perception in multiple/single/non-target settings. Experimental results on gRefCOCO, Ref-ZOM, R-RefCOCO, and RefCOCO benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness and rationality of HDC which outperforms the state-of-the-art GRES methods by a remarkable margin. Code will be available $href{https://github.com/RobertLuo1/HDC}{here}$.
Read more5/27/2024
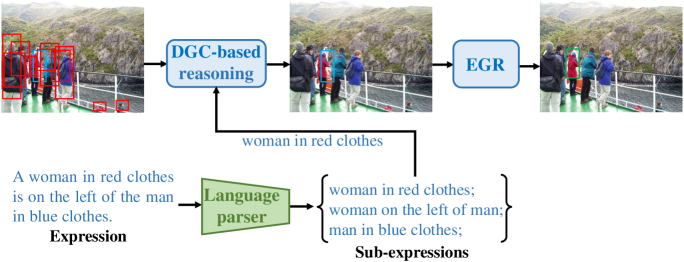

0
Make Graph-based Referring Expression Comprehension Great Again through Expression-guided Dynamic Gating and Regression
Jingcheng Ke, Dele Wang, Jun-Cheng Chen, I-Hong Jhuo, Chia-Wen Lin, Yen-Yu Lin
One common belief is that with complex models and pre-training on large-scale datasets, transformer-based methods for referring expression comprehension (REC) perform much better than existing graph-based methods. We observe that since most graph-based methods adopt an off-the-shelf detector to locate candidate objects (i.e., regions detected by the object detector), they face two challenges that result in subpar performance: (1) the presence of significant noise caused by numerous irrelevant objects during reasoning, and (2) inaccurate localization outcomes attributed to the provided detector. To address these issues, we introduce a plug-and-adapt module guided by sub-expressions, called dynamic gate constraint (DGC), which can adaptively disable irrelevant proposals and their connections in graphs during reasoning. We further introduce an expression-guided regression strategy (EGR) to refine location prediction. Extensive experimental results on the RefCOCO, RefCOCO+, RefCOCOg, Flickr30K, RefClef, and Ref-reasoning datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the DGC module and the EGR strategy in consistently boosting the performances of various graph-based REC methods. Without any pretaining, the proposed graph-based method achieves better performance than the state-of-the-art (SOTA) transformer-based methods.
Read more9/6/2024