ChatGPT Is Here to Help, Not to Replace Anybody -- An Evaluation of Students' Opinions On Integrating ChatGPT In CS Courses
2404.17443

0
0
🌐
Abstract
Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT and Bard are capable of producing code based on textual descriptions, with remarkable efficacy. Such technology will have profound implications for computing education, raising concerns about cheating, excessive dependence, and a decline in computational thinking skills, among others. There has been extensive research on how teachers should handle this challenge but it is also important to understand how students feel about this paradigm shift. In this research, 52 first-year CS students were surveyed in order to assess their views on technologies with code-generation capabilities, both from academic and professional perspectives. Our findings indicate that while students generally favor the academic use of GPT, they don't over rely on it, only mildly asking for its help. Although most students benefit from GPT, some struggle to use it effectively, urging the need for specific GPT training. Opinions on GPT's impact on their professional lives vary, but there is a consensus on its importance in academic practice.
Get summaries of the top AI research delivered straight to your inbox:
Overview
- The paper explores how the code generation capabilities of large language models (LLMs) like GPT and Bard could impact computing education.
- It surveys 52 first-year computer science students to understand their views on using these technologies in academic and professional contexts.
- The findings suggest that while students generally favor the academic use of LLMs, they do not overly rely on them and only mildly ask for their assistance.
- Some students struggle to use LLMs effectively, highlighting the need for specific training on these tools.
- Opinions on the impact of LLMs on students' professional lives vary, but there is a consensus on their importance in academic practice.
Plain English Explanation
Large language models (LLMs) like GPT and Bard have the remarkable ability to generate code based on textual descriptions. This technology could have significant implications for computing education, raising concerns about cheating, over-reliance, and a decline in computational thinking skills.
The researchers surveyed 52 first-year computer science students to understand their perspectives on using these code-generating technologies in academic and professional settings. The findings suggest that while students generally favor using LLMs in their studies, they don't heavily depend on them and only ask for their assistance when needed.
However, some students struggle to use LLMs effectively, which highlights the importance of providing specific training on these tools. Opinions on the impact of LLMs on students' future careers vary, but there is a consensus that these technologies are essential in academic practice.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a study that investigates how first-year computer science students perceive the use of large language models (LLMs) with code-generation capabilities, such as GPT and Bard, in both academic and professional contexts.
The researchers surveyed 52 students to assess their views on the implications of this technology for computing education, including concerns about cheating, over-reliance, and the potential decline in computational thinking skills.
The findings suggest that while students generally favor the academic use of LLMs, they do not overly rely on them and only mildly ask for their assistance. Although most students benefit from using LLMs, some struggle to use them effectively, which highlights the need for specific training on these tools.
Opinions on the impact of LLMs on students' professional lives vary, but there is a consensus that these technologies are essential in academic practice, particularly for tasks like code generation, debugging, and exploring programming concepts.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides valuable insights into how first-year computer science students perceive the use of large language models (LLMs) with code-generation capabilities in academic and professional settings. However, the study has some limitations.
First, the sample size of 52 students is relatively small, and the participants were all from the same university. Expanding the study to include a larger and more diverse sample of students could provide a more comprehensive understanding of the broader student perspective.
Additionally, the paper does not delve deeply into the specific challenges or strategies students employ when using LLMs, such as evaluating the quality and reliability of the generated code. Further research could explore these aspects in more detail to inform the development of effective educational interventions and support systems.
It would also be beneficial to investigate the long-term implications of LLM usage on students' skills, such as the potential decline in computational thinking or problem-solving abilities. Longitudinal studies could shed light on these concerns and help educators develop strategies to mitigate any negative impacts.
Conclusion
The research presented in this paper highlights the complex and multifaceted nature of how first-year computer science students perceive the use of large language models (LLMs) with code-generation capabilities in academic and professional settings.
While the findings suggest that students generally favor the academic use of LLMs, the study also identifies the need for specific training and support to help students effectively leverage these technologies. Additionally, the potential impacts on students' long-term skills and the professional implications of LLM usage warrant further investigation.
As computing education continues to evolve alongside advancements in AI-powered tools, it will be crucial for educators, researchers, and policymakers to collaborate in developing strategies that harness the benefits of LLMs while also addressing the challenges and concerns raised in this paper.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
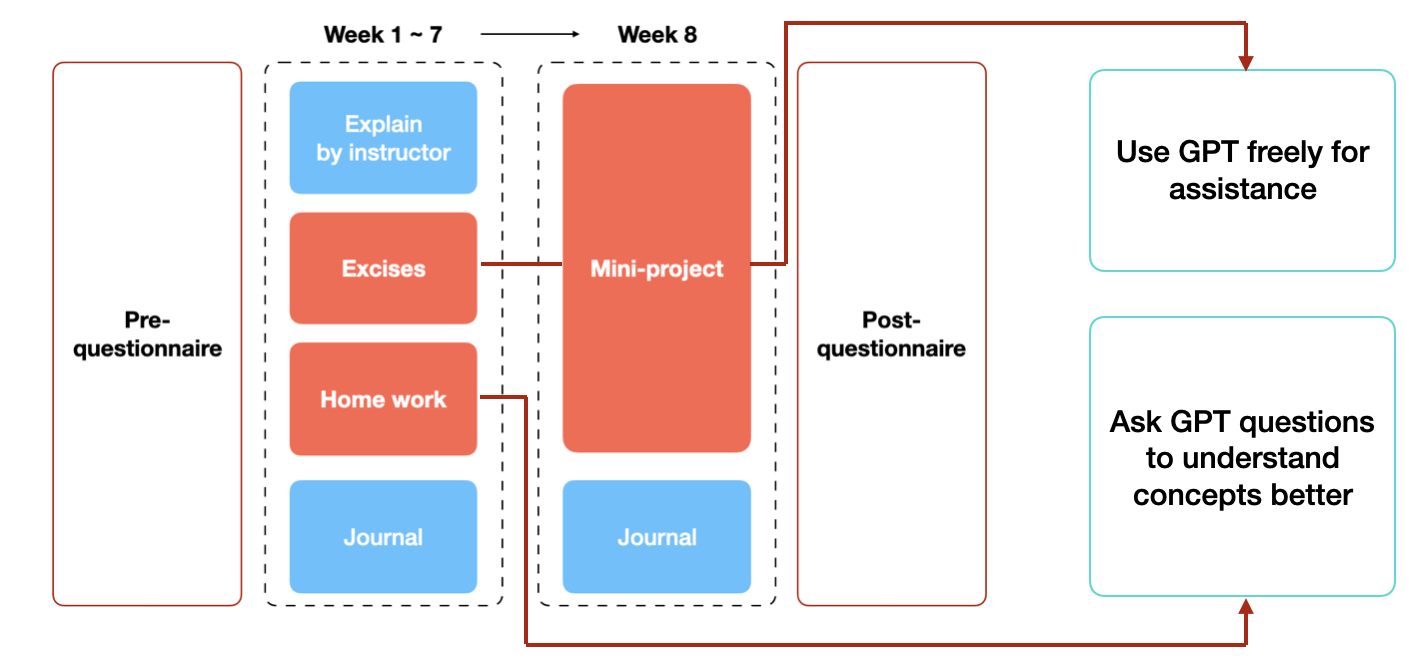
Enhancing Programming Education with ChatGPT: A Case Study on Student Perceptions and Interactions in a Python Course
Boxaun Ma, Li Chen, Shin'ichi Konomi

0
0
The integration of ChatGPT as a supportive tool in education, notably in programming courses, addresses the unique challenges of programming education by providing assistance with debugging, code generation, and explanations. Despite existing research validating ChatGPT's effectiveness, its application in university-level programming education and a detailed understanding of student interactions and perspectives remain limited. This paper explores ChatGPT's impact on learning in a Python programming course tailored for first-year students over eight weeks. By analyzing responses from surveys, open-ended questions, and student-ChatGPT dialog data, we aim to provide a comprehensive view of ChatGPT's utility and identify both its advantages and limitations as perceived by students. Our study uncovers a generally positive reception toward ChatGPT and offers insights into its role in enhancing the programming education experience. These findings contribute to the broader discourse on AI's potential in education, suggesting paths for future research and application.
4/8/2024
📊
ChatGPT in Data Visualization Education: A Student Perspective
Nam Wook Kim, Hyung-Kwon Ko, Grace Myers, Benjamin Bach

0
0
Unlike traditional educational chatbots that rely on pre-programmed responses, large-language model-driven chatbots, such as ChatGPT, demonstrate remarkable versatility and have the potential to serve as a dynamic resource for addressing student needs from understanding advanced concepts to solving complex problems. This work explores the impact of such technology on student learning in an interdisciplinary, project-oriented data visualization course. Throughout the semester, students engaged with ChatGPT across four distinct projects, including data visualizations and implementing them using a variety of tools including Tableau, D3, and Vega-lite. We collected conversation logs and reflection surveys from the students after each assignment. In addition, we conducted interviews with selected students to gain deeper insights into their overall experiences with ChatGPT. Our analysis examined the advantages and barriers of using ChatGPT, students' querying behavior, the types of assistance sought, and its impact on assignment outcomes and engagement. Based on the findings, we discuss design considerations for an educational solution that goes beyond the basic interface of ChatGPT, specifically tailored for data visualization education.
5/3/2024
✨
Beyond Code Generation: An Observational Study of ChatGPT Usage in Software Engineering Practice
Ranim Khojah, Mazen Mohamad, Philipp Leitner, Francisco Gomes de Oliveira Neto

0
0
Large Language Models (LLMs) are frequently discussed in academia and the general public as support tools for virtually any use case that relies on the production of text, including software engineering. Currently there is much debate, but little empirical evidence, regarding the practical usefulness of LLM-based tools such as ChatGPT for engineers in industry. We conduct an observational study of 24 professional software engineers who have been using ChatGPT over a period of one week in their jobs, and qualitatively analyse their dialogues with the chatbot as well as their overall experience (as captured by an exit survey). We find that, rather than expecting ChatGPT to generate ready-to-use software artifacts (e.g., code), practitioners more often use ChatGPT to receive guidance on how to solve their tasks or learn about a topic in more abstract terms. We also propose a theoretical framework for how (i) purpose of the interaction, (ii) internal factors (e.g., the user's personality), and (iii) external factors (e.g., company policy) together shape the experience (in terms of perceived usefulness and trust). We envision that our framework can be used by future research to further the academic discussion on LLM usage by software engineering practitioners, and to serve as a reference point for the design of future empirical LLM research in this domain.
4/24/2024
❗
Google or ChatGPT: Who is the Better Helper for University Students
Mengmeng Zhang, Xiantong Yang

0
0
Using information technology tools for academic help-seeking among college students has become a popular trend. In the evolutionary process between Generation Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) and traditional search engines, when students face academic challenges, do they tend to prefer Google, or are they more inclined to utilize ChatGPT? And what are the key factors influencing learners' preference to use ChatGPT for academic help-seeking? These relevant questions merit attention. The study employed a mixed-methods research design to investigate Taiwanese university students' online academic help-seeking preferences. The results indicated that students tend to prefer using ChatGPT to seek academic assistance, reflecting the potential popularity of GenAI in the educational field. Additionally, in comparing seven machine learning algorithms, the Random Forest and LightGBM algorithms exhibited superior performance. These two algorithms were employed to evaluate the predictive capability of 18 potential factors. It was found that GenAI fluency, GenAI distortions, and age were the core factors influencing how university students seek academic help. Overall, this study underscores that educators should prioritize the cultivation of students' critical thinking skills, while technical personnel should enhance the fluency and reliability of ChatGPT and Google searches and explore the integration of chat and search functions to achieve optimal balance.
5/2/2024