Collaborative Access Control for IoT -- A Blockchain Approach

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Presents a blockchain-based approach for collaborative access control in the Internet of Things (IoT)
- Aims to address the challenges of centralized access control in IoT environments
- Proposes a decentralized, secure, and transparent access control system leveraging blockchain technology
Plain English Explanation
The paper discusses a blockchain-based solution for managing access control in the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT devices are often connected to the internet and can be accessed by multiple users, which can create security and privacy concerns.
Traditionally, access control in IoT has been handled by a central authority, such as a cloud service or a central server. This approach can have limitations, as the central authority represents a single point of failure and may not be able to scale to handle the large number of IoT devices and users.
The researchers propose using a blockchain-based system to decentralize access control. Blockchain technology can provide a secure, transparent, and distributed way to manage access permissions without relying on a central authority.
In this system, IoT devices and users can interact directly to request and grant access permissions, which are then recorded on the blockchain. This decentralized approach can improve security, reduce the risk of a single point of failure, and enable scalable access control for IoT environments.
The researchers also discuss how the blockchain-based system can support collaborative access control, where multiple parties can collectively manage and enforce access policies for IoT devices.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a blockchain-based architecture for collaborative access control in IoT environments. The key components of the system include:
- IoT Devices: The IoT devices that require access control to their resources and functionalities.
- Users: The individuals or entities that need to access the IoT devices.
- Blockchain Network: The decentralized blockchain network that serves as the underlying infrastructure for the access control system.
- Smart Contracts: Automated, self-executing agreements on the blockchain that define and enforce the access control policies.
The access control process involves the following steps:
- Registration: IoT devices and users register with the blockchain network and create their own identities.
- Access Request: A user requests access to an IoT device by sending a transaction to the blockchain.
- Access Verification: The blockchain network, through the execution of smart contracts, verifies the user's identity and access permissions.
- Access Granting: If the access request is valid, the smart contract grants the user the requested access rights.
- Access Logging: All access requests and grants are recorded on the blockchain, providing a transparent and tamper-proof audit trail.
The researchers also discuss mechanisms for collaborative access control, where multiple stakeholders can collectively define and enforce access policies for IoT devices.
Critical Analysis
The proposed blockchain-based approach for collaborative access control in IoT addresses several limitations of traditional centralized access control systems. By decentralizing the access control process and leveraging the transparency and immutability of blockchain, the system can improve security, reduce the risk of single points of failure, and enable scalable access management.
However, the paper does not thoroughly discuss the performance and scalability implications of the blockchain-based system, particularly in terms of transaction processing and network congestion as the number of IoT devices and users increases. Further research is needed to evaluate the system's practical viability in large-scale IoT deployments.
Additionally, the paper does not address potential privacy concerns related to the storage of access control information on the public blockchain. [Techniques like software-based security frameworks may be necessary to mitigate such privacy risks.
Conclusion
The proposed blockchain-based approach for collaborative access control in IoT presents a promising solution to the limitations of centralized access control systems. By leveraging the decentralized, secure, and transparent nature of blockchain, the system can improve the security and scalability of IoT access management.
While the paper provides a solid foundation for the concept, further research is needed to address the performance, scalability, and privacy challenges associated with implementing such a system in real-world IoT environments. Overall, the work demonstrates the potential of blockchain technology to enhance access control and collaboration in the rapidly growing IoT landscape.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Collaborative Access Control for IoT -- A Blockchain Approach
Yongtao Huang, I-Ling Yen, Farokh Bastani
The Internet of Things (IoT) necessitates robust access control mechanisms to secure a vast array of interconnected devices. Most of the existing IoT systems in practice use centralized solutions. We identify the problems in such solutions and adopt the blockchain based decentralized access control approach. Though there are works in the literature that use blockchain for access control, there are some gaps in these works. We develop a blockchain embedded access control (BEAC) framework to bridge the gaps. First, blockchain based solutions for access control require an enabling P2P network while existing P2P overlays do not support some required features. We develop a novel P2P infrastructure to seamlessly support our BEAC framework. Second, most of the works consider blockchain based access control for a single access control model, and we develop a generic blockchain mechanism and show that it can support the embedding of various access control models. Finally, existing works adopt existing blockchain mechanisms which may incur a high communication overhead. We develop a shortcut approach to improve the number of message rounds in the access protocol. Our experiments demonstrate the efficacy of our system, showing that the shortcut mechanism can reduces access time by approximately 43%.
Read more5/27/2024


0
A Blockchain Embedded Peer-to-Peer Access Control Framework for IoT Systems
Yongtao Huang, I-Ling Yen, Farokh Bastani
We consider access control for IoT systems that involves shared accesses to the IoT devices as well as their data. Since IoT devices are dispersed all over the edge of the Internet, traditional centralized access control has problems. Blockchain based decentralized access control is thus the new solution trend. However, existing blockchain based access control methods do not focus on performance issues and may incur a high communication overhead. In this paper, we develop a Pruning Blockchain based Access Control (PBAC) protocol to cutdown the unnecessary message rounds and achieve high efficiency in access validations and policy management. The protocol includes a shortcut and a Role and Device Hierarchy-Based Access Control (R&D-BAC) approaches for different environment settings. To realize the PBAC protocol, it is necessary to carefully engineer the system architecture, which is also discussed in the paper. Experiments demonstrate the efficacy of the PBAC protocol, specifically, the shortcut mechanism reduces access time by approximately 43%, and R&D-BAC outperforms traditional blockchain based RBAC by more than two folds.
Read more7/15/2024
🌐

0
BeACONS: A Blockchain-enabled Authentication and Communications Network for Scalable IoV
Qi Shi, Jingyi Sun, Hanwei Fu, Peizhe Fu, Jiayuan Ma, Hao Xu, Erwu Liu
This paper introduces a novel blockchain-enabled authentication and communications network for scalable Internet of Vehicles, which aims to bolster security and confidentiality, diminish communications latency, and reduce dependence on centralised infrastructures like Certificate Authorities and Public Key Infrastructures by leveraging Blockchain-enabled Domain Name Services and Blockchain-enabled Mutual Authentication. The proposed network is structured into a primary layer, consisting of Road Side Units and edge servers as servers of Blockchain-enabled Domain Name Services for managing inter-vehicle communications identities, and a sub-layer within each vehicle for intra-vehicle communications via the Blockchain-enabled Mutual Authentication Protocol. This design facilitates secure connections across vehicles by coordinating between the layers, significantly improving communications security and efficiency. This study also evaluates Road Side Unit availability against the random distribution of Road Side Units along the route of different vehicles. The proposed model presents a novel pathway towards a decentralised, secure, and efficient Internet of Vehicles ecosystem, contributing to the advancement of autonomous and trustworthy vehicular networks.
Read more5/15/2024
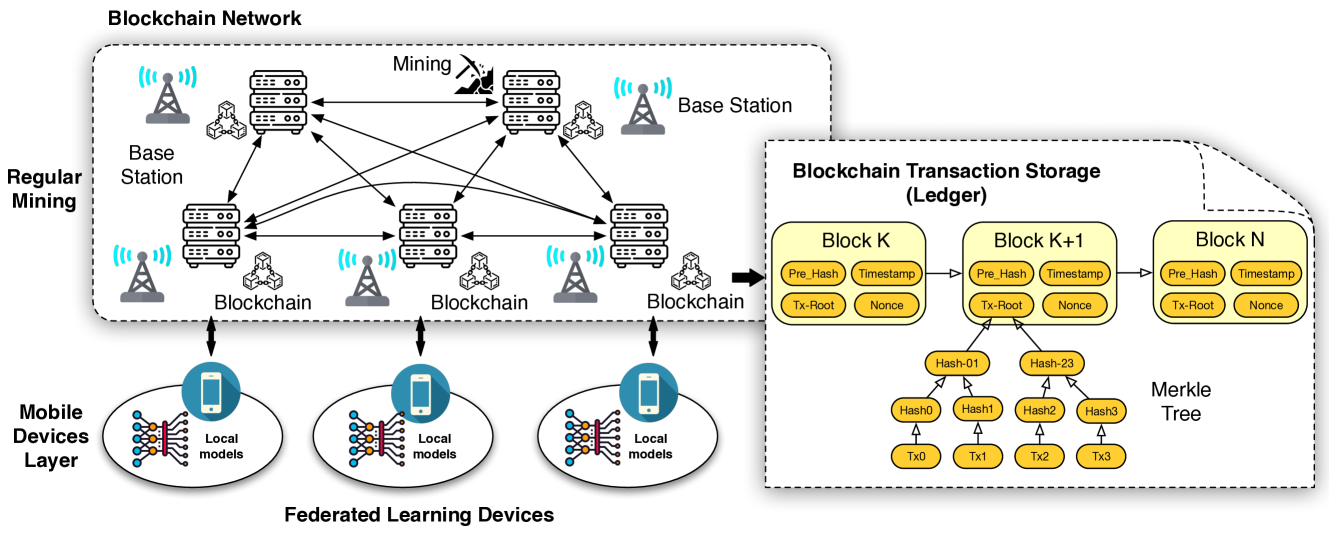

0
Blockchains for Internet of Things: Fundamentals, Applications, and Challenges
Yusen Wu, Ye Hu, Mingzhe Chen, Yelena Yesha, M'erouane Debbah
Internet of Things (IoT) services necessitate the storage, transmission, and analysis of diverse data for inference, autonomy, and control. Blockchains, with their inherent properties of decentralization and security, offer efficient database solutions for these devices through consensus-based data sharing. However, it's essential to recognize that not every blockchain system is suitable for specific IoT applications, and some might be more beneficial when excluded with privacy concerns. For example, public blockchains are not suitable for storing sensitive data. This paper presents a detailed review of three distinct blockchains tailored for enhancing IoT applications. We initially delve into the foundational aspects of three blockchain systems, highlighting their strengths, limitations, and implementation needs. Additionally, we discuss the security issues in different blockchains. Subsequently, we explore the blockchain's application in three pivotal IoT areas: edge AI, communications, and healthcare. We underscore potential challenges and the future directions for integrating different blockchains in IoT. Ultimately, this paper aims to offer a comprehensive perspective on the synergies between blockchains and the IoT ecosystem, highlighting the opportunities and complexities involved.
Read more6/18/2024