Software-based Security Framework for Edge and Mobile IoT
2404.06435

0
0

Abstract
With the proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, ensuring secure communications has become imperative. Due to their low cost and embedded nature, many of these devices operate with computational and energy constraints, neglecting the potential security vulnerabilities that they may bring. This work-in-progress is focused on designing secure communication among remote servers and embedded IoT devices to balance security robustness and energy efficiency. The proposed approach uses lightweight cryptography, optimizing device performance and security without overburdening their limited resources. Our architecture stands out for integrating Edge servers and a central Name Server, allowing secure and decentralized authentication and efficient connection transitions between different Edge servers. This architecture enhances the scalability of the IoT network and reduces the load on each server, distributing the responsibility for authentication and key management.
Get summaries of the top AI research delivered straight to your inbox:
Overview
- Presents a software-based security framework for edge and mobile IoT devices
- Addresses security challenges in IoT environments, including resource-constrained devices and dynamic network topologies
- Proposes a multi-layered approach to enhance security and privacy for edge and mobile IoT systems
Plain English Explanation
The paper discusses a security framework designed to protect edge and mobile Internet of Things (IoT) devices. IoT systems, which connect a wide range of devices to the internet, often face security challenges due to the limited resources of the devices and the dynamic nature of IoT networks.
The proposed framework takes a multi-layered approach to enhance security and privacy for these edge and mobile IoT systems. This approach aligns with research on quarantining malicious IoT devices and remote automotive security. The framework aims to address the unique challenges of IoT environments, such as tailoring authentication protocols for ambient IoT devices and optimizing lightweight malware detection models for IoT devices.
By leveraging a combination of techniques, the researchers hope to improve the overall security and resilience of edge and mobile IoT systems, which are crucial for distributed swarm learning at the edge of the Internet of Things.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a software-based security framework for edge and mobile IoT devices. The framework consists of several key components:
- Device Attestation: This component verifies the integrity and authenticity of IoT devices, ensuring they have not been tampered with or compromised.
- Secure Execution Environment: The framework provides a secure execution environment on the IoT devices, isolating critical security functions and sensitive data from the main operating system.
- Dynamic Security Policy Management: The framework dynamically adjusts security policies based on the device's context, such as location, network connectivity, and detected threats.
- Anomaly Detection and Response: The framework employs machine learning-based anomaly detection to identify and respond to potential security incidents in real-time.
- Secure Communication and Data Protection: The framework ensures secure communication between IoT devices and the cloud, as well as the protection of sensitive data both at rest and in transit.
The researchers evaluate the proposed framework through a combination of analytical models, simulation, and experimental validation, demonstrating its effectiveness in improving the security and resilience of edge and mobile IoT systems.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a comprehensive approach to securing edge and mobile IoT devices, addressing several key challenges in this domain. The multi-layered design of the framework is a strength, as it provides a holistic solution that addresses various security concerns.
However, the paper does not delve deeply into the specific implementation details or trade-offs of the individual components. Additionally, the authors acknowledge that the framework's effectiveness may be dependent on the specific IoT use case and deployment environment, which could limit its generalizability.
Further research may be needed to explore the performance and resource overhead of the proposed framework, especially on resource-constrained IoT devices. The authors also mention the potential for future work to investigate the integration of hardware-based security features to further strengthen the framework.
Conclusion
This paper proposes a software-based security framework that aims to enhance the security and privacy of edge and mobile IoT systems. The multi-layered approach, which includes device attestation, secure execution environments, dynamic security policy management, and anomaly detection, represents a comprehensive effort to address the unique challenges of IoT environments.
The framework's design and evaluation demonstrate its potential to improve the overall security and resilience of edge and mobile IoT devices, which are crucial components of the Internet of Things ecosystem. As IoT continues to permeate various industries and applications, the development of robust security solutions like the one presented in this paper will be essential to ensuring the safe and reliable operation of these systems.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🏅
New!Large-Scale Security Analysis of Real-World Backend Deployments Speaking IoT-Focused Protocols
Carlotta Tagliaro, Martina Komsic, Andrea Continella, Kevin Borgolte, Martina Lindorfer

0
0
Internet-of-Things devices, ranging from smart home assistants to health devices, are pervasive: Forecasts estimate their number to reach 29 billion by 2030. Understanding the security of their machine-to-machine communication is crucial. Prior work focused on identifying devices' vulnerabilities or proposed protocol-specific solutions. Instead, in this paper, we investigate the security of backends speaking Internet-of-Things (IoT) protocols at scale, that is, the backbone of the entire IoT ecosystem. We focus on three real-world protocols used by IoT for our large-scale analysis: MQTT, CoAP, and XMPP. We gather a dataset of over 337,000 backends, augment it with geographical and provider data, and perform non-invasive active measurements to investigate three major security threats: information leakage, weak authentication, and denial of service. Our results provide quantitative evidence of a problematic immaturity in the IoT security ecosystem. Among other issues, we find that 9.44% backends expose information, 30.38% CoAP-speaking backends are vulnerable to denial of service attacks, and 99.84% of MQTT-speaking and XMPP-speaking backends use insecure transport protocols (only 0.16% adopt TLS, of which 70.93% adopt a vulnerable version).
5/17/2024
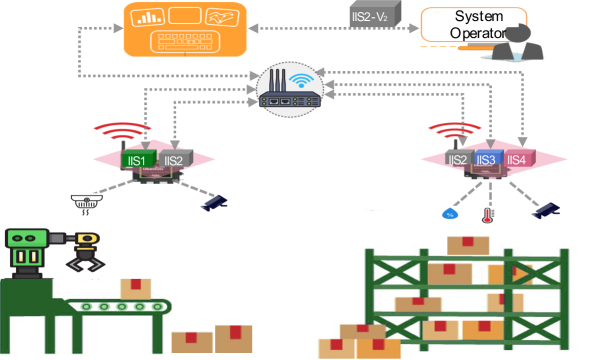
Empowering IoT Applications with Flexible, Energy-Efficient Remote Management of Low-Power Edge Devices
Shadi Attarha, Anna Forster

0
0
In the context of the Internet of Things (IoT), reliable and energy-efficient provision of IoT applications has become critical. Equipping IoT systems with tools that enable a flexible, well-performing, and automated way of monitoring and managing IoT edge devices is an essential prerequisite. In current IoT systems, low-power edge appliances have been utilized in a way that can not be controlled and re-configured in a timely manner. Hence, conducting a trade-off solution between manageability, performance and design requirements are demanded. This paper introduces a novel approach for fine-grained monitoring and managing individual micro-services within low-power edge devices, which improves system reliability and energy efficiency. The proposed method enables operational flexibility for IoT edge devices by leveraging a modularization technique. Following a review of existing solutions for remote-managed IoT services, a detailed description of the suggested approach is presented. Also, to explore the essential design principles that must be considered in this approach, the suggested architecture is elaborated in detail. Finally, the advantages of the proposed solution to deal with disruptions are demonstrated in the proof of concept-based experiments.
5/6/2024
💬
Distributed Threat Intelligence at the Edge Devices: A Large Language Model-Driven Approach
Syed Mhamudul Hasan, Alaa M. Alotaibi, Sajedul Talukder, Abdur R. Shahid

0
0
With the proliferation of edge devices, there is a significant increase in attack surface on these devices. The decentralized deployment of threat intelligence on edge devices, coupled with adaptive machine learning techniques such as the in-context learning feature of large language models (LLMs), represents a promising paradigm for enhancing cybersecurity on low-powered edge devices. This approach involves the deployment of lightweight machine learning models directly onto edge devices to analyze local data streams, such as network traffic and system logs, in real-time. Additionally, distributing computational tasks to an edge server reduces latency and improves responsiveness while also enhancing privacy by processing sensitive data locally. LLM servers can enable these edge servers to autonomously adapt to evolving threats and attack patterns, continuously updating their models to improve detection accuracy and reduce false positives. Furthermore, collaborative learning mechanisms facilitate peer-to-peer secure and trustworthy knowledge sharing among edge devices, enhancing the collective intelligence of the network and enabling dynamic threat mitigation measures such as device quarantine in response to detected anomalies. The scalability and flexibility of this approach make it well-suited for diverse and evolving network environments, as edge devices only send suspicious information such as network traffic and system log changes, offering a resilient and efficient solution to combat emerging cyber threats at the network edge. Thus, our proposed framework can improve edge computing security by providing better security in cyber threat detection and mitigation by isolating the edge devices from the network.
5/15/2024
🖼️
Quarantining Malicious IoT Devices in Intelligent Sliced Mobile Networks
David Candal-Ventureira, Pablo Fondo-Ferreiro, Felipe Gil-Casti~neira, Francisco Javier Gonz'alez-Casta~no

0
0
The unstoppable adoption of the Internet of Things (IoT) is driven by the deployment of new services that require continuous capture of information from huge populations of sensors, or actuating over a myriad of smart objects. Accordingly, next generation networks are being designed to support such massive numbers of devices and connections. For example, the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) is designing the different 5G releases specifically with IoT in mind. Nevertheless, from a security perspective this scenario is a potential nightmare: the attack surface becomes wider and many IoT nodes do not have enough resources to support advanced security protocols. In fact, security is rarely a priority in their design. Thus, including network-level mechanisms for preventing attacks from malware-infected IoT devices is mandatory to avert further damage. In this paper, we propose a novel Software-Defined Networking (SDN)-based architecture to identify suspicious nodes in 4G or 5G networks and redirect their traffic to a secondary network slice where traffic is analyzed in depth before allowing it reaching its destination. The architecture can be easily integrated in any existing deployment due to its interoperability. By following this approach, we can detect potential threats at an early stage and limit the damage by Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks originated in IoT devices.
4/1/2024