A Comprehensive Evaluation of the Impact of ATM QoS Mechanisms on Network Performance for Multimedia and Data Applications

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper evaluates the impact of different quality of service (QoS) mechanisms in Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) networks on the performance of multimedia and data applications.
- The authors investigate how various QoS approaches, such as traffic shaping, policing, and scheduling, affect factors like throughput, delay, and jitter for different application types.
- The research aims to provide insights that can help optimize ATM network performance and support a range of real-time and non-real-time applications.
Plain English Explanation
The paper looks at how different techniques used in ATM networks to manage the quality of service can impact the performance of various types of applications. ATM is a communications standard that was developed to handle a mix of traffic, including video, audio, and regular data.
The researchers tested out different QoS mechanisms, like controlling the flow of data (traffic shaping), enforcing data rate limits (policing), and prioritizing certain types of traffic (scheduling). They measured how these QoS approaches affected important factors for applications, such as the total amount of data that could be transmitted (throughput), how quickly the data arrived (delay), and how consistent the delivery time was (jitter).
The goal was to understand which QoS methods work best for supporting a variety of applications with different needs, from real-time multimedia to regular data transfers. This information can help network operators configure their ATM networks to provide the optimal performance for the mix of applications their users are running.
Technical Explanation
The paper describes an experimental evaluation of several QoS mechanisms in an ATM network environment. The authors set up a testbed with an ATM switch and traffic generators to simulate multimedia and data applications. They tested the impact of traffic shaping, policing, and various scheduling algorithms on metrics like throughput, delay, and jitter for each application type.
The traffic shaping experiments involved regulating the flow of data using leaky bucket and token bucket approaches. Policing experiments enforced peak cell rate and sustainable cell rate limits. The scheduling experiments compared priority queuing, weighted round robin, and weighted fair queuing algorithms.
The results show that the choice of QoS mechanism has a significant effect on application performance. For example, stricter traffic shaping improved delay and jitter for real-time multimedia but reduced overall throughput. Policing had a greater impact on non-real-time data traffic. Scheduling algorithms also demonstrated tradeoffs between fairness, delay, and throughput depending on the mix of application types.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a thorough, quantitative evaluation of common ATM QoS mechanisms and their impact on a range of application performance metrics. The experimental setup and methodology appear rigorous, allowing the authors to draw clear conclusions about the performance trade-offs associated with different QoS approaches.
However, the paper does note some limitations. The testbed only simulated a single ATM switch, whereas real-world networks have multiple interconnected components. The researchers also acknowledge that their results may not generalize perfectly to production network environments with unpredictable real-world traffic patterns.
Additionally, the paper focuses solely on the technical performance impacts of QoS mechanisms. It does not address potential economic, operational, or policy considerations that network operators may need to weigh when implementing QoS controls.
Further research could explore the interaction of QoS with other network management techniques, as well as the end-user experience and broader organizational impacts of different QoS approaches. Longitudinal studies tracking the evolution of QoS requirements and best practices over time would also be valuable.
Conclusion
This paper provides a comprehensive technical evaluation of how various QoS mechanisms in ATM networks can affect the performance of multimedia and data applications. The findings offer network operators valuable insights to help optimize ATM infrastructure for supporting a diverse range of real-time and non-real-time services.
While the results are specific to an ATM context, the general principles around QoS trade-offs and the importance of aligning network controls with application requirements have broader relevance as networks continue to evolve. This research contributes to our understanding of how to engineer resilient, high-performing communication systems capable of meeting the demands of modern digital applications and user experiences.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
A Comprehensive Evaluation of the Impact of ATM QoS Mechanisms on Network Performance for Multimedia and Data Applications
Mahdi Manavi
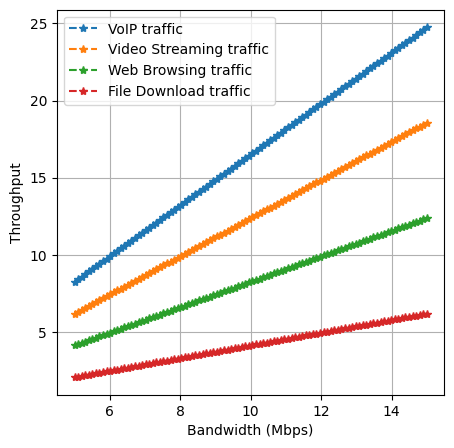
The Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) network is crucial due to its ability to efficiently transmit data, provide reliable connections, and support various service classes with specific Quality of Service (QoS) requirements. In this paper, we utilize the OPNET network simulation software to model an ATM network and analyze the impact of QoS classification on network performance. We investigate the effects of Constant Bit Rate (CBR), Variable Bit Rate (VBR), Available Bit Rate (ABR) and Unspecified Bit Rate (UBR) models on various network traffic types such as voice, video and data. For voice traffic, we examine key QoS parameters including Jitter, Packet Delay Variation and End-to-End Delay. For video traffic, we evaluate Packet Delay Variation and End-to-End Delay. Additionally, we analyze Download Response Time for data traffic to assess the influence of QoS on the ATM network. Our results demonstrate that CBR and VBR are preferred for real-time traffic like voice and video, providing low delay and jitter. The simulation approach enables us to test various configurations and gain insights not possible in hardware tests. Our findings can help network operators determine the optimal QoS settings and tradeoffs when deploying ATM for modern multi-service networks.
Read more4/1/2024

0
Maximization of Communication Network Throughput using Dynamic Traffic Allocation Scheme
Md. Arquam, Suchi Kumari
Optimizing network throughput in real-world dynamic systems is critical, especially for diverse and delay-sensitive multimedia data types such as VoIP and video streaming. Traditional routing protocols, which rely on static metrics and single shortest-path algorithms, were unable in managing this complex information. To address these challenges, we propose a novel approach that enhances resource utilization while maintaining Quality of Service (QoS). Our dynamic traffic allocation model prioritizes different data types based on their delay sensitivity and allocates traffic by considering factors such as bandwidth, latency, and network failures. This approach is shown to significantly improve network throughput compared to static load balancing, especially for multimedia applications. Simulation results confirm the effectiveness of this dynamic method in maximizing network throughput and maintaining QoS across various data types.
Read more9/10/2024


0
Experimenting with Adaptive Bitrate Algorithms for Virtual Reality Streaming over Wi-Fi
Ferran Maura, Miguel Casasnovas, Boris Bellalta
Interactive Virtual Reality (VR) streaming over Wi-Fi networks encounters significant challenges due to bandwidth fluctuations caused by channel contention and user mobility. Adaptive BitRate (ABR) algorithms dynamically adjust the video encoding bitrate based on the available network capacity, aiming to maximize image quality while mitigating congestion and preserving the user's Quality of Experience (QoE). In this paper, we experiment with ABR algorithms for VR streaming using Air Light VR (ALVR), an open-source VR streaming solution. We extend ALVR with a comprehensive set of metrics that provide a robust characterization of the network's state, enabling more informed bitrate adjustments. To demonstrate the utility of these performance indicators, we develop and test the Network-aware Step-wise ABR algorithm for VR streaming (NeSt-VR). Results validate the accuracy of the newly implemented network performance metrics and demonstrate NeSt-VR's video bitrate adaptation capabilities.
Read more7/23/2024
🚀

0
Performance Analysis of Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) Variants
Mansukh Pamarath, Dweep Gogia
There are various TCP variants such as Reno, Tahoe, Vegas, SACK and so on. These variants implement algorithms that handle congestion control. In our experiments we have used these variants to measure their performance such as throughput, delay (latency), and drop rate with respect to time and Constant Bit Rate (CBR) - no congestion control, specified bandwidth and sends packets at a specified rate. We have used the NS2 network simulator to perform all our experiments to analyze TCP performance.
Read more7/22/2024