Compressed Deepfake Video Detection Based on 3D Spatiotemporal Trajectories

0
🔎
Sign in to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🔎

0
Compressed Deepfake Video Detection Based on 3D Spatiotemporal Trajectories
Zongmei Chen, Xin Liao, Xiaoshuai Wu, Yanxiang Chen
The misuse of deepfake technology by malicious actors poses a potential threat to nations, societies, and individuals. However, existing methods for detecting deepfakes primarily focus on uncompressed videos, such as noise characteristics, local textures, or frequency statistics. When applied to compressed videos, these methods experience a decrease in detection performance and are less suitable for real-world scenarios. In this paper, we propose a deepfake video detection method based on 3D spatiotemporal trajectories. Specifically, we utilize a robust 3D model to construct spatiotemporal motion features, integrating feature details from both 2D and 3D frames to mitigate the influence of large head rotation angles or insufficient lighting within frames. Furthermore, we separate facial expressions from head movements and design a sequential analysis method based on phase space motion trajectories to explore the feature differences between genuine and fake faces in deepfake videos. We conduct extensive experiments to validate the performance of our proposed method on several compressed deepfake benchmarks. The robustness of the well-designed features is verified by calculating the consistent distribution of facial landmarks before and after video compression.Our method yields satisfactory results and showcases its potential for practical applications.
Read more4/30/2024


0
Generalizing Deepfake Video Detection with Plug-and-Play: Video-Level Blending and Spatiotemporal Adapter Tuning
Zhiyuan Yan, Yandan Zhao, Shen Chen, Xinghe Fu, Taiping Yao, Shouhong Ding, Li Yuan
Three key challenges hinder the development of current deepfake video detection: (1) Temporal features can be complex and diverse: how can we identify general temporal artifacts to enhance model generalization? (2) Spatiotemporal models often lean heavily on one type of artifact and ignore the other: how can we ensure balanced learning from both? (3) Videos are naturally resource-intensive: how can we tackle efficiency without compromising accuracy? This paper attempts to tackle the three challenges jointly. First, inspired by the notable generality of using image-level blending data for image forgery detection, we investigate whether and how video-level blending can be effective in video. We then perform a thorough analysis and identify a previously underexplored temporal forgery artifact: Facial Feature Drift (FFD), which commonly exists across different forgeries. To reproduce FFD, we then propose a novel Video-level Blending data (VB), where VB is implemented by blending the original image and its warped version frame-by-frame, serving as a hard negative sample to mine more general artifacts. Second, we carefully design a lightweight Spatiotemporal Adapter (StA) to equip a pretrained image model (both ViTs and CNNs) with the ability to capture both spatial and temporal features jointly and efficiently. StA is designed with two-stream 3D-Conv with varying kernel sizes, allowing it to process spatial and temporal features separately. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of the proposed methods; and show our approach can generalize well to previously unseen forgery videos, even the just-released (in 2024) SoTAs. We release our code and pretrained weights at url{https://github.com/YZY-stack/StA4Deepfake}.
Read more9/2/2024


0
What Matters in Detecting AI-Generated Videos like Sora?
Chirui Chang, Zhengzhe Liu, Xiaoyang Lyu, Xiaojuan Qi
Recent advancements in diffusion-based video generation have showcased remarkable results, yet the gap between synthetic and real-world videos remains under-explored. In this study, we examine this gap from three fundamental perspectives: appearance, motion, and geometry, comparing real-world videos with those generated by a state-of-the-art AI model, Stable Video Diffusion. To achieve this, we train three classifiers using 3D convolutional networks, each targeting distinct aspects: vision foundation model features for appearance, optical flow for motion, and monocular depth for geometry. Each classifier exhibits strong performance in fake video detection, both qualitatively and quantitatively. This indicates that AI-generated videos are still easily detectable, and a significant gap between real and fake videos persists. Furthermore, utilizing the Grad-CAM, we pinpoint systematic failures of AI-generated videos in appearance, motion, and geometry. Finally, we propose an Ensemble-of-Experts model that integrates appearance, optical flow, and depth information for fake video detection, resulting in enhanced robustness and generalization ability. Our model is capable of detecting videos generated by Sora with high accuracy, even without exposure to any Sora videos during training. This suggests that the gap between real and fake videos can be generalized across various video generative models. Project page: https://justin-crchang.github.io/3DCNNDetection.github.io/
Read more7/1/2024
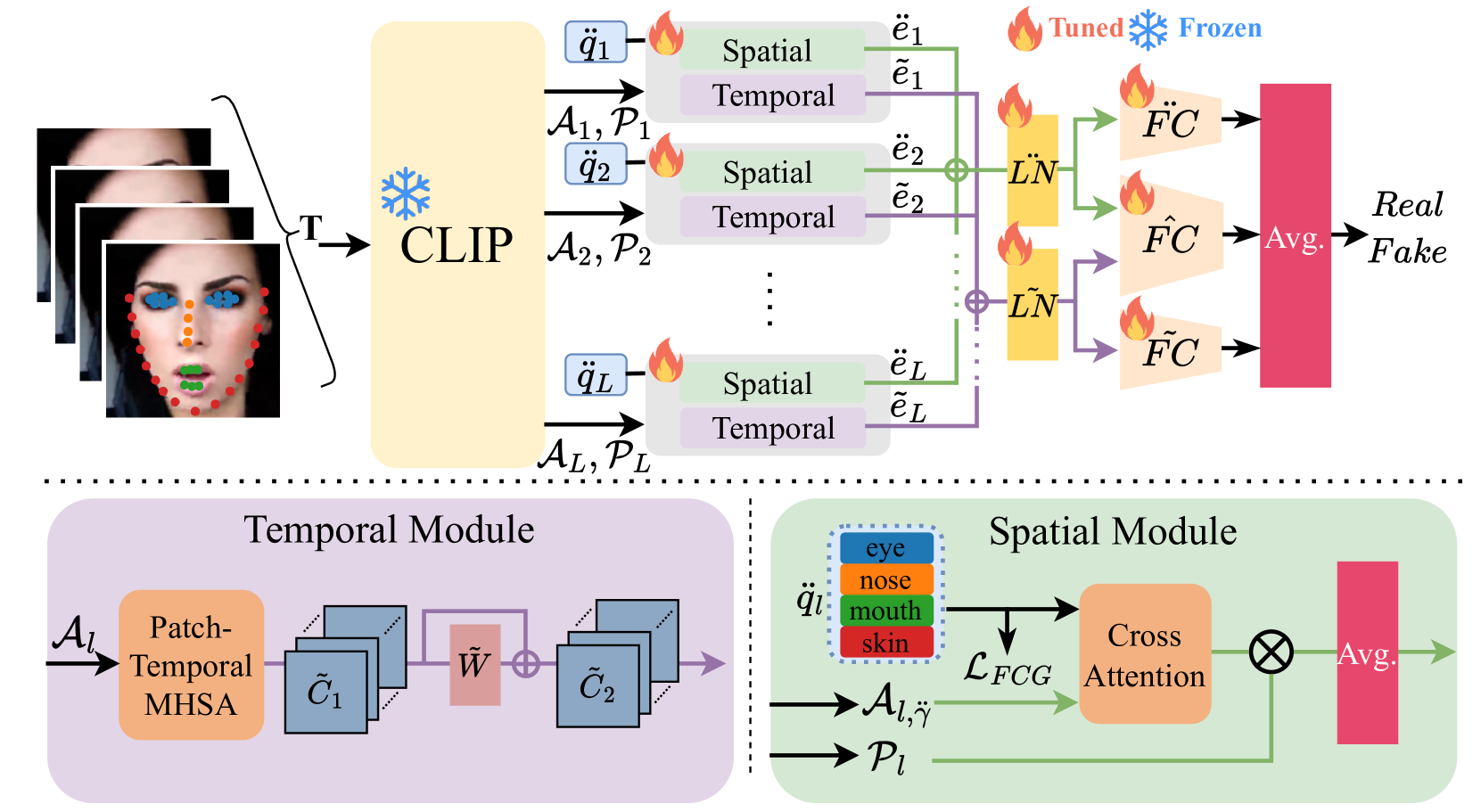

0
Towards More General Video-based Deepfake Detection through Facial Feature Guided Adaptation for Foundation Model
Yue-Hua Han, Tai-Ming Huang, Shu-Tzu Lo, Po-Han Huang, Kai-Lung Hua, Jun-Cheng Chen
With the rise of deep learning, generative models have enabled the creation of highly realistic synthetic images, presenting challenges due to their potential misuse. While research in Deepfake detection has grown rapidly in response, many detection methods struggle with unseen Deepfakes generated by new synthesis techniques. To address this generalisation challenge, we propose a novel Deepfake detection approach by adapting the Foundation Models with rich information encoded inside, specifically using the image encoder from CLIP which has demonstrated strong zero-shot capability for downstream tasks. Inspired by the recent advances of parameter efficient fine-tuning, we propose a novel side-network-based decoder to extract spatial and temporal cues from the given video clip, with the promotion of the Facial Component Guidance (FCG) to encourage the spatial feature to include features of key facial parts for more robust and general Deepfake detection. Through extensive cross-dataset evaluations, our approach exhibits superior effectiveness in identifying unseen Deepfake samples, achieving notable performance improvement even with limited training samples and manipulation types. Our model secures an average performance enhancement of 0.9% AUROC in cross-dataset assessments comparing with state-of-the-art methods, especially a significant lead of achieving 4.4% improvement on the challenging DFDC dataset.
Read more6/6/2024