Data-Efficient Multimodal Fusion on a Single GPU
2312.10144

0
18
🌀
Abstract
The goal of multimodal alignment is to learn a single latent space that is shared between multimodal inputs. The most powerful models in this space have been trained using massive datasets of paired inputs and large-scale computational resources, making them prohibitively expensive to train in many practical scenarios. We surmise that existing unimodal encoders pre-trained on large amounts of unimodal data should provide an effective bootstrap to create multimodal models from unimodal ones at much lower costs. We therefore propose FuseMix, a multimodal augmentation scheme that operates on the latent spaces of arbitrary pre-trained unimodal encoders. Using FuseMix for multimodal alignment, we achieve competitive performance -- and in certain cases outperform state-of-the art methods -- in both image-text and audio-text retrieval, with orders of magnitude less compute and data: for example, we outperform CLIP on the Flickr30K text-to-image retrieval task with $sim ! 600times$ fewer GPU days and $sim ! 80times$ fewer image-text pairs. Additionally, we show how our method can be applied to convert pre-trained text-to-image generative models into audio-to-image ones. Code is available at: https://github.com/layer6ai-labs/fusemix.
Get summaries of the top AI research delivered straight to your inbox:
The paper introduces FuseMix, a multimodal augmentation scheme that learns a shared latent space between different modalities, such as images, text, and audio, by leveraging pre-trained unimodal encoders. The key advantages of FuseMix are its competitive performance compared to state-of-the-art methods and its significantly lower computational and data requirements.
Specifically, FuseMix outperforms CLIP, a prominent image-text retrieval model, on the Flickr30K text-to-image retrieval task while using approximately 600 times fewer GPU days and 80 times fewer image-text pairs during training. Additionally, the paper demonstrates how FuseMix can convert pre-trained text-to-image generative models into audio-to-image ones, showcasing its versatility.
The authors argue that pre-trained unimodal encoders, which are trained on large amounts of unimodal data, provide an effective starting point for creating multimodal models at a much lower cost compared to training from scratch on massive datasets of paired inputs.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
📈
New!Improving Multimodal Learning with Multi-Loss Gradient Modulation
Konstantinos Kontras, Christos Chatzichristos, Matthew Blaschko, Maarten De Vos

0
0
Learning from multiple modalities, such as audio and video, offers opportunities for leveraging complementary information, enhancing robustness, and improving contextual understanding and performance. However, combining such modalities presents challenges, especially when modalities differ in data structure, predictive contribution, and the complexity of their learning processes. It has been observed that one modality can potentially dominate the learning process, hindering the effective utilization of information from other modalities and leading to sub-optimal model performance. To address this issue the vast majority of previous works suggest to assess the unimodal contributions and dynamically adjust the training to equalize them. We improve upon previous work by introducing a multi-loss objective and further refining the balancing process, allowing it to dynamically adjust the learning pace of each modality in both directions, acceleration and deceleration, with the ability to phase out balancing effects upon convergence. We achieve superior results across three audio-video datasets: on CREMA-D, models with ResNet backbone encoders surpass the previous best by 1.9% to 12.4%, and Conformer backbone models deliver improvements ranging from 2.8% to 14.1% across different fusion methods. On AVE, improvements range from 2.7% to 7.7%, while on UCF101, gains reach up to 6.1%.
5/14/2024
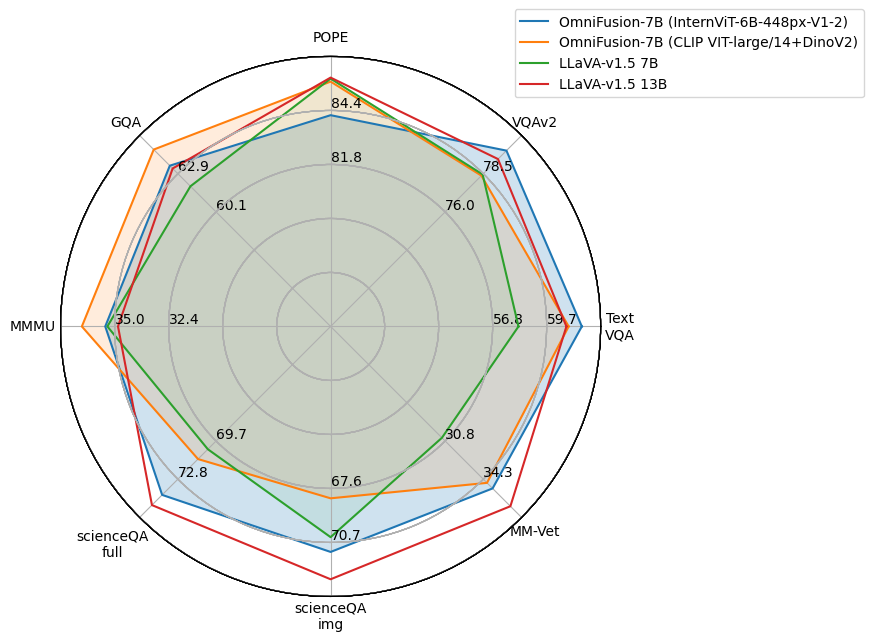
OmniFusion Technical Report
Elizaveta Goncharova, Anton Razzhigaev, Matvey Mikhalchuk, Maxim Kurkin, Irina Abdullaeva, Matvey Skripkin, Ivan Oseledets, Denis Dimitrov, Andrey Kuznetsov

0
0
Last year, multimodal architectures served up a revolution in AI-based approaches and solutions, extending the capabilities of large language models (LLM). We propose an textit{OmniFusion} model based on a pretrained LLM and adapters for visual modality. We evaluated and compared several architecture design principles for better text and visual data coupling: MLP and transformer adapters, various CLIP ViT-based encoders (SigLIP, InternVIT, etc.), and their fusing approach, image encoding method (whole image or tiles encoding) and two 7B LLMs (the proprietary one and open-source Mistral). Experiments on 8 visual-language benchmarks show the top score for the best OmniFusion setup in terms of different VQA tasks in comparison with open-source LLaVA-like solutions: VizWiz, Pope, MM-Vet, ScienceQA, MMBench, TextVQA, VQAv2, MMMU. We also propose a variety of situations, where OmniFusion provides highly-detailed answers in different domains: housekeeping, sightseeing, culture, medicine, handwritten and scanned equations recognition, etc. Mistral-based OmniFusion model is an open-source solution with weights, training and inference scripts available at https://github.com/AIRI-Institute/OmniFusion.
4/10/2024
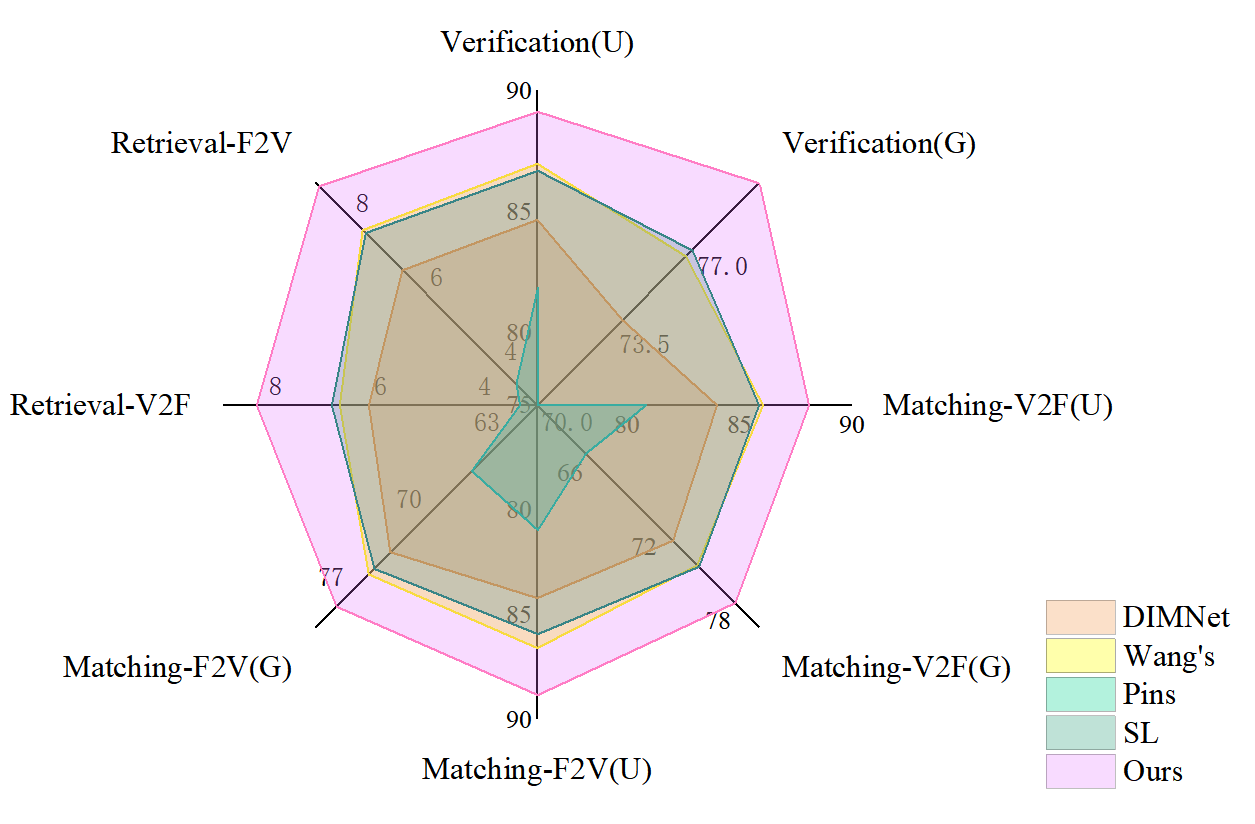
Fuse after Align: Improving Face-Voice Association Learning via Multimodal Encoder
Chong Peng, Liqiang He, Dan Su

0
0
Today, there have been many achievements in learning the association between voice and face. However, most previous work models rely on cosine similarity or L2 distance to evaluate the likeness of voices and faces following contrastive learning, subsequently applied to retrieval and matching tasks. This method only considers the embeddings as high-dimensional vectors, utilizing a minimal scope of available information. This paper introduces a novel framework within an unsupervised setting for learning voice-face associations. By employing a multimodal encoder after contrastive learning and addressing the problem through binary classification, we can learn the implicit information within the embeddings in a more effective and varied manner. Furthermore, by introducing an effective pair selection method, we enhance the learning outcomes of both contrastive learning and the matching task. Empirical evidence demonstrates that our framework achieves state-of-the-art results in voice-face matching, verification, and retrieval tasks, improving verification by approximately 3%, matching by about 2.5%, and retrieval by around 1.3%.
4/16/2024
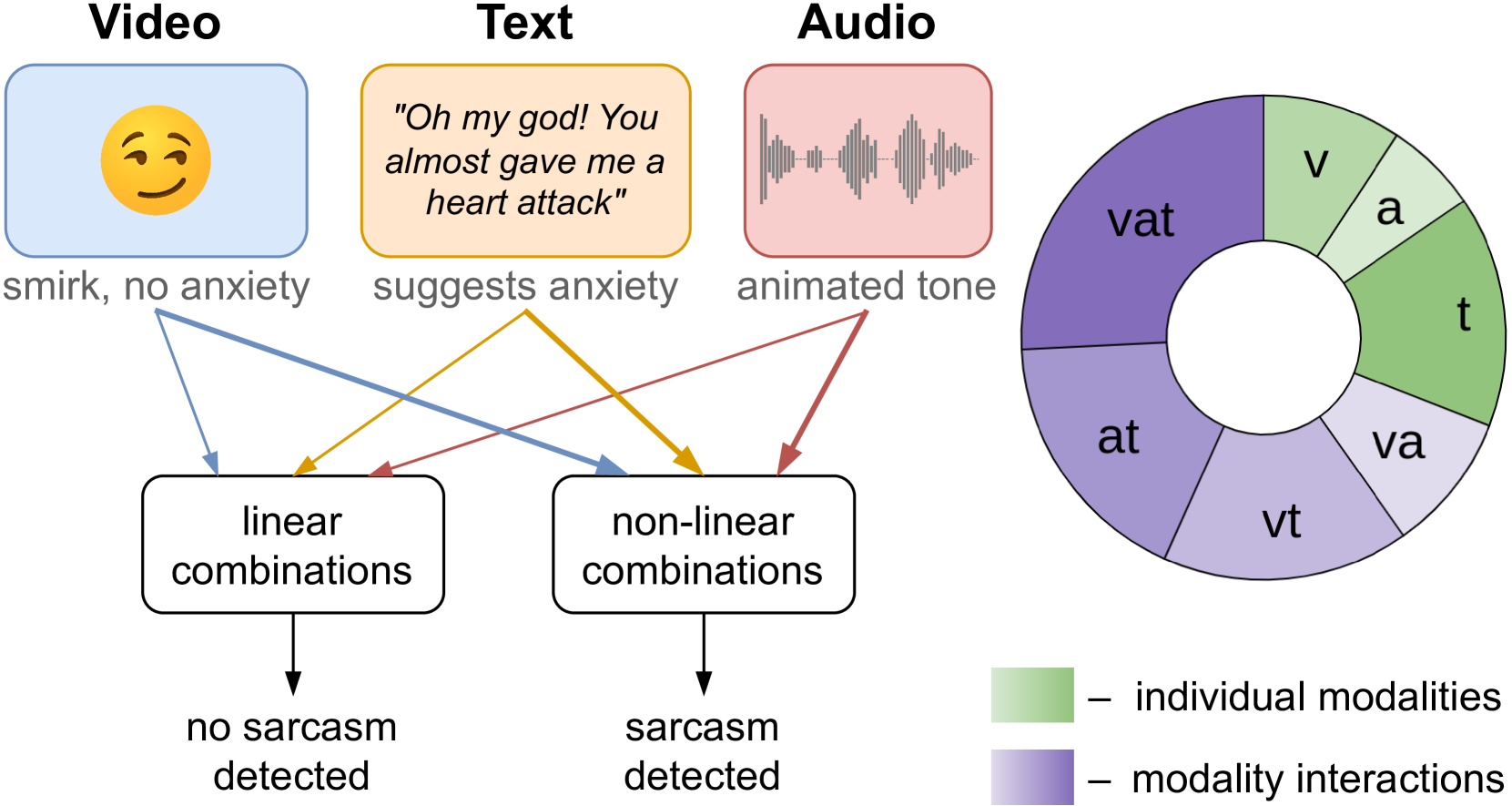
Interpretable Tensor Fusion
Saurabh Varshneya, Antoine Ledent, Philipp Liznerski, Andriy Balinskyy, Purvanshi Mehta, Waleed Mustafa, Marius Kloft

0
0
Conventional machine learning methods are predominantly designed to predict outcomes based on a single data type. However, practical applications may encompass data of diverse types, such as text, images, and audio. We introduce interpretable tensor fusion (InTense), a multimodal learning method for training neural networks to simultaneously learn multimodal data representations and their interpretable fusion. InTense can separately capture both linear combinations and multiplicative interactions of diverse data types, thereby disentangling higher-order interactions from the individual effects of each modality. InTense provides interpretability out of the box by assigning relevance scores to modalities and their associations. The approach is theoretically grounded and yields meaningful relevance scores on multiple synthetic and real-world datasets. Experiments on six real-world datasets show that InTense outperforms existing state-of-the-art multimodal interpretable approaches in terms of accuracy and interpretability.
5/9/2024