Data Poisoning Attacks in Intelligent Transportation Systems: A Survey

0
📊
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) are being transformed by emerging technologies.
- This transformation has led to cybersecurity concerns, including the threat of data poisoning attacks.
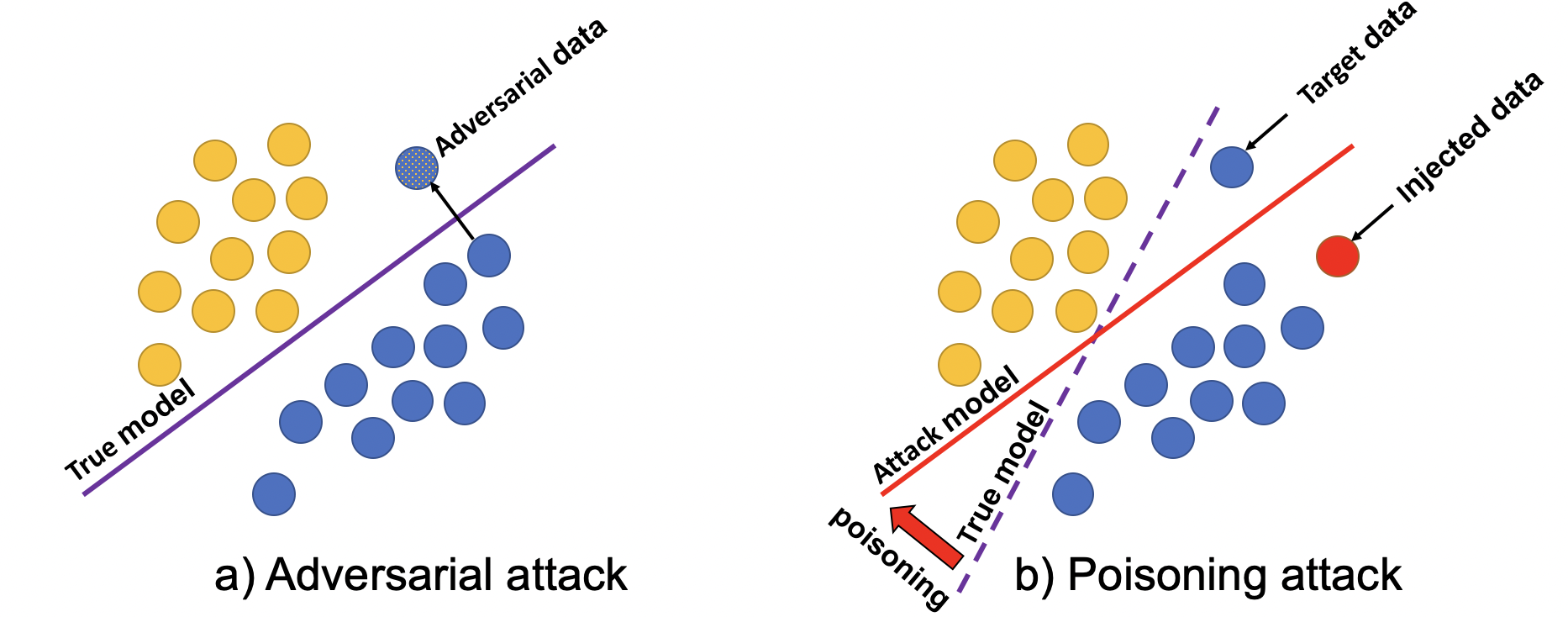
- In data poisoning attacks, attackers inject malicious perturbations into datasets, potentially leading to inaccurate results in offline learning and real-time decision-making processes.
- This paper focuses on data poisoning attack models against ITS.
Plain English Explanation
Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) are technologies that help manage transportation networks, such as traffic signals, road sensors, and autonomous vehicles. As these systems become more advanced, they rely more on data to make decisions.
This reliance on data has introduced new cybersecurity concerns, one of which is data poisoning attacks. In a data poisoning attack, an attacker deliberately introduces small, hard-to-detect changes into the data that powers an ITS system. These changes can cause the system to make incorrect decisions, leading to problems like traffic congestion or unsafe driving conditions.
The researchers in this paper aimed to better understand the threat of data poisoning attacks against ITS. They identified the types of data that ITS systems use and the ways that attackers could manipulate that data to cause problems. The researchers then developed a framework for categorizing and analyzing different data poisoning attack models in the context of ITS applications.
Technical Explanation
The researchers first identified the key data sources in ITS that could be vulnerable to poisoning attacks, such as vehicle sensor data, traffic signal data, and road condition data. They then explored various application scenarios where data poisoning could be used to disrupt ITS, such as causing traffic congestion or manipulating autonomous vehicle behavior.
Based on a thorough review of cybersecurity research, the researchers developed a general framework for analyzing data poisoning attacks against ITS. This framework covers the attacker's goals, the types of data that could be targeted, the attack mechanisms, and the potential impacts on ITS applications.
Using this framework, the researchers then categorized and analyzed a variety of data poisoning attack models that could be applied to ITS. They discussed the technical details of these attack models, as well as their potential effectiveness and limitations.
Critical Analysis
The researchers acknowledge that their framework and analysis of data poisoning attacks against ITS is not exhaustive. They note that the field of ITS cybersecurity is rapidly evolving, and new attack models and vulnerabilities may emerge over time.
Additionally, the researchers highlight the need for further research into effective countermeasures and defense mechanisms to protect ITS from data poisoning attacks. While they provide a useful starting point for understanding the threat, more work is needed to develop robust solutions that can withstand sophisticated attackers.
Conclusion
This paper provides a comprehensive overview of the threat of data poisoning attacks against Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS). By identifying vulnerable data sources, exploring attack scenarios, and developing a analytical framework, the researchers have laid the groundwork for better understanding and addressing this emerging cybersecurity challenge.
The findings from this study can help ITS developers and operators to be more aware of the risks posed by data poisoning and to take proactive steps to mitigate these threats. As ITS systems become increasingly relied upon for safe and efficient transportation, ensuring their resilience against cyber attacks will be of paramount importance.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
📊

0
Data Poisoning Attacks in Intelligent Transportation Systems: A Survey
Feilong Wang, Xin Wang, Xuegang Ban
Emerging technologies drive the ongoing transformation of Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS). This transformation has given rise to cybersecurity concerns, among which data poisoning attack emerges as a new threat as ITS increasingly relies on data. In data poisoning attacks, attackers inject malicious perturbations into datasets, potentially leading to inaccurate results in offline learning and real-time decision-making processes. This paper concentrates on data poisoning attack models against ITS. We identify the main ITS data sources vulnerable to poisoning attacks and application scenarios that enable staging such attacks. A general framework is developed following rigorous study process from cybersecurity but also considering specific ITS application needs. Data poisoning attacks against ITS are reviewed and categorized following the framework. We then discuss the current limitations of these attack models and the future research directions. Our work can serve as a guideline to better understand the threat of data poisoning attacks against ITS applications, while also giving a perspective on the future development of trustworthy ITS.
Read more7/24/2024


0
Poisoning Attacks and Defenses in Recommender Systems: A Survey
Zongwei Wang, Junliang Yu, Min Gao, Wei Yuan, Guanhua Ye, Shazia Sadiq, Hongzhi Yin
Modern recommender systems (RS) have profoundly enhanced user experience across digital platforms, yet they face significant threats from poisoning attacks. These attacks, aimed at manipulating recommendation outputs for unethical gains, exploit vulnerabilities in RS through injecting malicious data or intervening model training. This survey presents a unique perspective by examining these threats through the lens of an attacker, offering fresh insights into their mechanics and impacts. Concretely, we detail a systematic pipeline that encompasses four stages of a poisoning attack: setting attack goals, assessing attacker capabilities, analyzing victim architecture, and implementing poisoning strategies. The pipeline not only aligns with various attack tactics but also serves as a comprehensive taxonomy to pinpoint focuses of distinct poisoning attacks. Correspondingly, we further classify defensive strategies into two main categories: poisoning data filtering and robust training from the defender's perspective. Finally, we highlight existing limitations and suggest innovative directions for further exploration in this field.
Read more6/6/2024

0
Manipulating Recommender Systems: A Survey of Poisoning Attacks and Countermeasures
Thanh Toan Nguyen, Quoc Viet Hung Nguyen, Thanh Tam Nguyen, Thanh Trung Huynh, Thanh Thi Nguyen, Matthias Weidlich, Hongzhi Yin
Recommender systems have become an integral part of online services to help users locate specific information in a sea of data. However, existing studies show that some recommender systems are vulnerable to poisoning attacks, particularly those that involve learning schemes. A poisoning attack is where an adversary injects carefully crafted data into the process of training a model, with the goal of manipulating the system's final recommendations. Based on recent advancements in artificial intelligence, such attacks have gained importance recently. While numerous countermeasures to poisoning attacks have been developed, they have not yet been systematically linked to the properties of the attacks. Consequently, assessing the respective risks and potential success of mitigation strategies is difficult, if not impossible. This survey aims to fill this gap by primarily focusing on poisoning attacks and their countermeasures. This is in contrast to prior surveys that mainly focus on attacks and their detection methods. Through an exhaustive literature review, we provide a novel taxonomy for poisoning attacks, formalise its dimensions, and accordingly organise 30+ attacks described in the literature. Further, we review 40+ countermeasures to detect and/or prevent poisoning attacks, evaluating their effectiveness against specific types of attacks. This comprehensive survey should serve as a point of reference for protecting recommender systems against poisoning attacks. The article concludes with a discussion on open issues in the field and impactful directions for future research. A rich repository of resources associated with poisoning attacks is available at https://github.com/tamlhp/awesome-recsys-poisoning.
Read more4/24/2024


0
Data Poisoning: An Overlooked Threat to Power Grid Resilience
Nora Agah, Javad Mohammadi, Alex Aved, David Ferris, Erika Ardiles Cruz, Philip Morrone
As the complexities of Dynamic Data Driven Applications Systems increase, preserving their resilience becomes more challenging. For instance, maintaining power grid resilience is becoming increasingly complicated due to the growing number of stochastic variables (such as renewable outputs) and extreme weather events that add uncertainty to the grid. Current optimization methods have struggled to accommodate this rise in complexity. This has fueled the growing interest in data-driven methods used to operate the grid, leading to more vulnerability to cyberattacks. One such disruption that is commonly discussed is the adversarial disruption, where the intruder attempts to add a small perturbation to input data in order to manipulate the system operation. During the last few years, work on adversarial training and disruptions on the power system has gained popularity. In this paper, we will first review these applications, specifically on the most common types of adversarial disruptions: evasion and poisoning disruptions. Through this review, we highlight the gap between poisoning and evasion research when applied to the power grid. This is due to the underlying assumption that model training is secure, leading to evasion disruptions being the primary type of studied disruption. Finally, we will examine the impacts of data poisoning interventions and showcase how they can endanger power grid resilience.
Read more7/23/2024