DDRM: Distributed Drone Reputation Management for Trust and Reliability in Crowdsourced Drone Services

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Reputation management system for crowdsourced drone services
- Utilizes blockchain technology to ensure trust and reliability
- Provides a distributed approach to managing drone reputations
Plain English Explanation
The paper proposes a Distributed Drone Reputation Management (DDRM) system to address trust and reliability concerns in crowdsourced drone services. Drone services, where people can hire drones for tasks like aerial photography or delivery, are becoming more common. However, there are challenges in ensuring the drones and their operators are reliable and trustworthy.
The DDRM system uses blockchain technology to create a decentralized reputation management platform. This means there is no single authority controlling the system - instead, it is distributed across many participants. Each drone and operator builds up a reputation score based on feedback from past customers. This reputation score is recorded on the blockchain, which is a secure and transparent digital ledger.
By using the blockchain, the DDRM system ensures the reputation information is tamper-proof and can be accessed by anyone. Customers can check a drone's reputation before hiring it, and drone operators are incentivized to maintain a good reputation to continue getting business. This helps build trust in the crowdsourced drone services ecosystem.
The paper also discusses how the DDRM system could incorporate local differential privacy techniques to protect the privacy of customers providing feedback. This allows the reputation system to function without compromising individual privacy.
Technical Explanation
The DDRM system architecture consists of several key components:
-
Drone Reputation Management Module: This module is responsible for managing the reputation scores of drones and operators. It collects feedback from customers, calculates reputation scores, and stores this information on the blockchain.
-
Blockchain Network: The blockchain acts as a distributed, tamper-resistant database to store the reputation data. Multiple nodes on the network validate and maintain the integrity of the blockchain.
-
Reputation Scoring Algorithm: The paper proposes a novel reputation scoring algorithm that takes into account factors like customer feedback, drone capabilities, and operator experience. This produces a comprehensive reputation score for each drone-operator pair.
-
Feedback Collection and Incentivization: The system incentivizes customers to provide honest feedback through mechanisms like anonymous reviews. It also incorporates local differential privacy to protect customer privacy.
-
Service Matching and Selection: Customers can search for and select drone services based on the reputation scores displayed in the system. Drones with higher reputations are more likely to be chosen.
The paper also presents a proof-of-concept implementation and evaluation of the DDRM system, demonstrating its feasibility and effectiveness in improving trust and reliability in crowdsourced drone services.
Critical Analysis
The DDRM system presents a promising approach to addressing trust and reliability issues in the growing drone services industry. By leveraging blockchain technology and a robust reputation management system, the paper offers a decentralized solution that could help build confidence in this emerging market.
One potential limitation discussed in the paper is the need to incentivize customers to provide honest and timely feedback. While the proposed anonymous review mechanism and privacy-preserving techniques help, there may still be challenges in ensuring a sufficient volume of reliable feedback to maintain accurate reputation scores.
Additionally, the paper does not explore potential vulnerabilities or attack vectors that could be used to manipulate the reputation system. Further research may be needed to ensure the DDRM system is resilient to malicious attempts to game the reputation scores.
Overall, the DDRM system demonstrates a thoughtful and innovative approach to enhancing trust and reliability in crowdsourced drone services. The incorporation of blockchain and privacy-preserving techniques is particularly noteworthy and could inspire similar solutions in other sharing economy or peer-to-peer service domains.
Conclusion
The DDRM paper presents a distributed drone reputation management system that leverages blockchain technology to build trust and reliability in crowdsourced drone services. By creating a tamper-resistant and transparent reputation system, the DDRM approach aims to empower customers to make informed decisions and incentivize drone operators to maintain high-quality service.
The paper's technical contributions, including the reputation scoring algorithm and privacy-preserving feedback mechanisms, demonstrate the potential of this approach to address key challenges in the emerging drone services market. While some limitations and areas for further research are identified, the DDRM system offers a compelling blueprint for enhancing trust and reliability in the rapidly evolving drone economy.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
DDRM: Distributed Drone Reputation Management for Trust and Reliability in Crowdsourced Drone Services
Junaid Akram, Ali Anaissi
This study introduces the Distributed Drone Reputation Management (DDRM) framework, designed to fortify trust and authenticity within the Internet of Drone Things (IoDT) ecosystem. As drones increasingly play a pivotal role across diverse sectors, integrating crowdsourced drone services within the IoDT has emerged as a vital avenue for democratizing access to these services. A critical challenge, however, lies in ensuring the authenticity and reliability of drone service reviews. Leveraging the Ethereum blockchain, DDRM addresses this challenge by instituting a verifiable and transparent review mechanism. The framework innovates with a dual-token system, comprising the Service Review Authorization Token (SRAT) for facilitating review authorization and the Drone Reputation Enhancement Token (DRET) for rewarding and recognizing drones demonstrating consistent reliability. Comprehensive analysis within this paper showcases DDRM's resilience against various reputation frauds and underscores its operational effectiveness, particularly in enhancing the efficiency and reliability of drone services.
Read more7/2/2024

0
Privacy-First Crowdsourcing: Blockchain and Local Differential Privacy in Crowdsourced Drone Services
Junaid Akram, Ali Anaissi
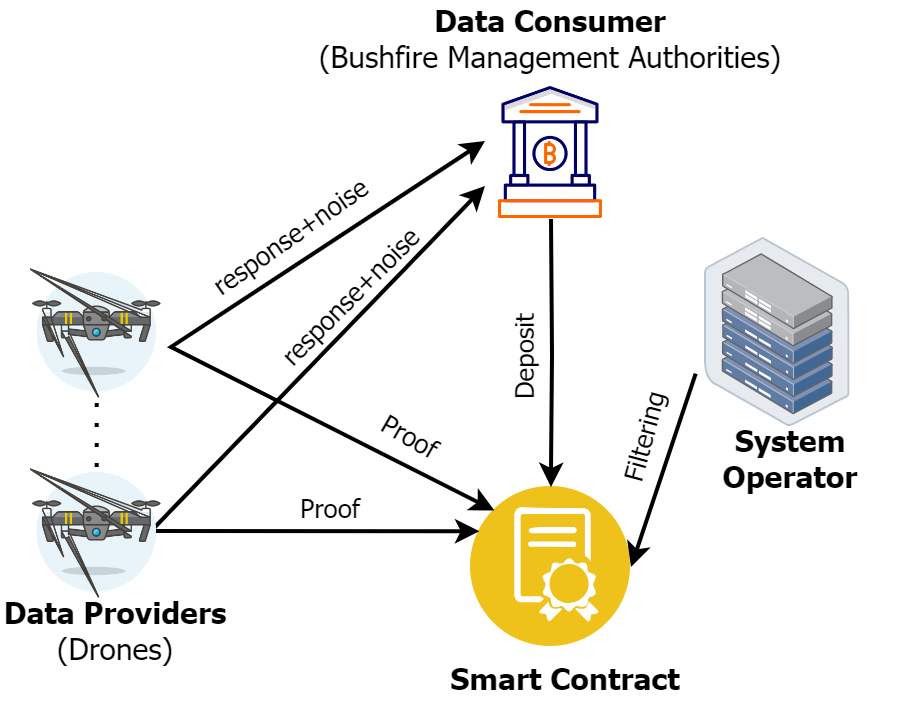
We introduce a privacy-preserving framework for integrating consumer-grade drones into bushfire management. This system creates a marketplace where bushfire management authorities obtain essential data from drone operators. Key features include local differential privacy to protect data providers and a blockchain-based solution ensuring fair data exchanges and accountability. The framework is validated through a proof-of-concept implementation, demonstrating its scalability and potential for various large-scale data collection scenarios. This approach addresses privacy concerns and compliance with regulations like Australia's Privacy Act 1988, offering a practical solution for enhancing bushfire detection and management through crowdsourced drone services.
Read more7/2/2024


0
Trustworthy DNN Partition for Blockchain-enabled Digital Twin in Wireless IIoT Networks
Xiumei Deng, Jun Li, Long Shi, Kang Wei, Ming Ding, Yumeng Shao, Wen Chen, Shi Jin
Digital twin (DT) has emerged as a promising solution to enhance manufacturing efficiency in industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) networks. To promote the efficiency and trustworthiness of DT for wireless IIoT networks, we propose a blockchain-enabled DT (B-DT) framework that employs deep neural network (DNN) partitioning technique and reputation-based consensus mechanism, wherein the DTs maintained at the gateway side execute DNN inference tasks using the data collected from their associated IIoT devices. First, we employ DNN partitioning technique to offload the top-layer DNN inference tasks to the access point (AP) side, which alleviates the computation burden at the gateway side and thereby improves the efficiency of DNN inference. Second, we propose a reputation-based consensus mechanism that integrates Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). Specifically, the proposed consensus mechanism evaluates the off-chain reputation of each AP according to its computation resource contributions to the DNN inference tasks, and utilizes the off-chain reputation as a stake to adjust the block generation difficulty. Third, we formulate a stochastic optimization problem of communication resource (i.e., partition point) and computation resource allocation (i.e., computation frequency of APs for top-layer DNN inference and block generation) to minimize system latency under the time-varying channel state and long-term constraints of off-chain reputation, and solve the problem using Lyapunov optimization method. Experimental results show that the proposed dynamic DNN partitioning and resource allocation (DPRA) algorithm outperforms the baselines in terms of reducing the overall latency while guaranteeing the trustworthiness of the B-DT system.
Read more5/29/2024

0
A Novel Joint DRL-Based Utility Optimization for UAV Data Services
Xuli Cai, Poonam Lohan, Burak Kantarci
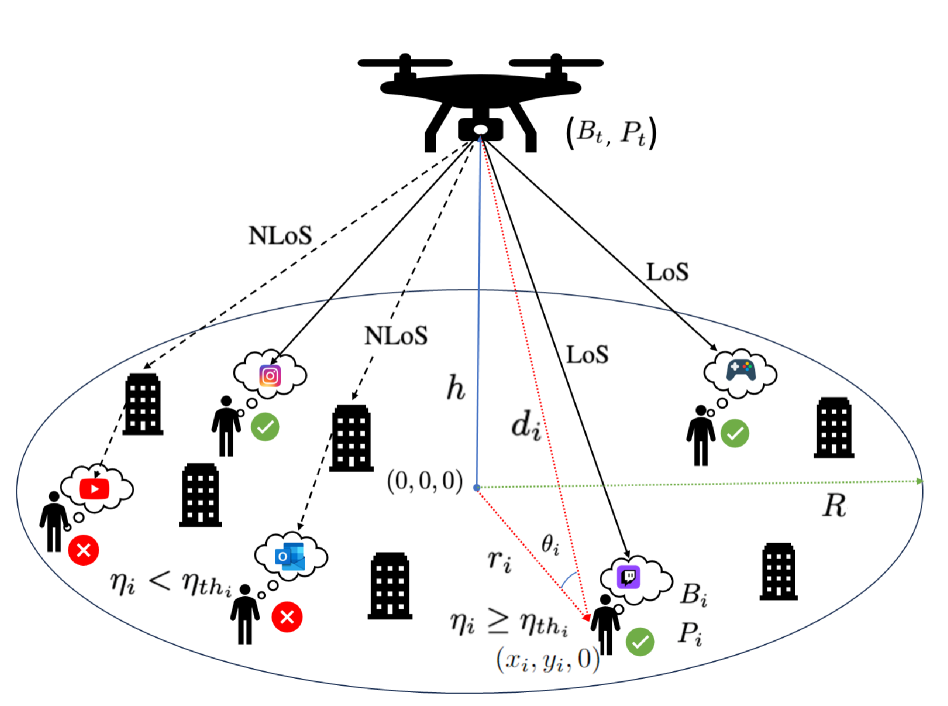
In this paper, we propose a novel joint deep reinforcement learning (DRL)-based solution to optimize the utility of an uncrewed aerial vehicle (UAV)-assisted communication network. To maximize the number of users served within the constraints of the UAV's limited bandwidth and power resources, we employ deep Q-Networks (DQN) and deep deterministic policy gradient (DDPG) algorithms for optimal resource allocation to ground users with heterogeneous data rate demands. The DQN algorithm dynamically allocates multiple bandwidth resource blocks to different users based on current demand and available resource states. Simultaneously, the DDPG algorithm manages power allocation, continuously adjusting power levels to adapt to varying distances and fading conditions, including Rayleigh fading for non-line-of-sight (NLoS) links and Rician fading for line-of-sight (LoS) links. Our joint DRL-based solution demonstrates an increase of up to 41% in the number of users served compared to scenarios with equal bandwidth and power allocation.
Read more6/18/2024