Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network (DePIN): Challenges and Opportunities

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network (DePIN) is a concept that explores the challenges and opportunities of building a decentralized network for managing physical infrastructure.
- The paper discusses the potential benefits of using blockchain and Web 3.0 technologies to create a more transparent, secure, and efficient infrastructure management system.
- Key topics include decentralized governance, data ownership, and the integration of digital twins with physical assets.
Plain English Explanation
The paper looks at the idea of a Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network (DePIN), which is a way of managing physical infrastructure like roads, power grids, and water systems in a decentralized way using blockchain and other Web 3.0 technologies. The main goal is to create a more transparent, secure, and efficient system for managing this critical infrastructure.
One key advantage of a decentralized approach is that it could give people and organizations more control over the data related to the infrastructure they use or own. Instead of a central authority controlling all the information, a decentralized network would allow for shared ownership and management of the data. This could lead to better decision-making and more accountability.
The paper also discusses how integrating "digital twins" (virtual models of physical assets) with the blockchain-based network could provide even more benefits. Digital twins could help monitor the condition of infrastructure in real-time and enable predictive maintenance. Overall, the authors see a lot of potential in applying decentralized and Web 3.0 ideas to the world of physical infrastructure.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes a framework for a Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network (DePIN) that leverages blockchain, digital twins, and other Web 3.0 technologies. The key components include:
-
Decentralized Governance: Instead of a centralized authority managing the infrastructure, DePIN would use a decentralized governance model where stakeholders (e.g., citizens, businesses, government agencies) collectively make decisions about the network.
-
Data Ownership and Sharing: The decentralized architecture would allow data related to the physical infrastructure to be owned and shared among the stakeholders, rather than controlled by a single entity.
-
Digital Twins Integration: The network would integrate digital twins - virtual models of physical assets - to monitor infrastructure conditions in real-time and enable predictive maintenance.
-
Use Cases: The authors outline potential use cases like smart city management, supply chain optimization, and disaster response coordination that could benefit from a DePIN approach.
The paper also discusses the technical challenges involved, such as scalability, interoperability, and the need for robust security and privacy measures in a decentralized system.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a compelling vision for how decentralized technologies like blockchain could revolutionize the way physical infrastructure is managed. By giving stakeholders more control over data and decision-making, DePIN could lead to increased transparency, accountability, and efficiency.
However, the authors acknowledge that there are significant technical and organizational hurdles to overcome. Integrating legacy infrastructure systems with emerging blockchain and digital twin technologies will require extensive coordination and standardization efforts. There are also unanswered questions about governance models, incentive structures, and data privacy that need to be addressed.
Additionally, the paper does not delve deeply into the potential social and economic impacts of a DePIN system. Decentralization could empower local communities, but it could also create new power imbalances if not implemented thoughtfully. The authors could have explored these implications in more depth.
Overall, the paper offers a thought-provoking vision, but more research and real-world pilots will be necessary to assess the feasibility and scalability of the DePIN concept. As the authors note, the transition to a decentralized physical infrastructure network will be a long and complex process.
Conclusion
The Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network (DePIN) concept presented in this paper represents a promising approach to modernizing the management of critical physical infrastructure using blockchain, digital twins, and other Web 3.0 technologies. By shifting control and data ownership to a decentralized network of stakeholders, DePIN could lead to greater transparency, efficiency, and resilience in areas like smart city management, supply chain logistics, and disaster response.
However, significant technical, organizational, and social challenges must be overcome before DePIN can be widely adopted. Ongoing research and real-world experimentation will be essential to refine the DePIN model and address issues around scalability, interoperability, governance, and the equitable distribution of benefits.
If successful, the DePIN framework could pave the way for a fundamental transformation in how we design, build, and maintain the physical infrastructure that underpins our modern societies. The potential impacts on sustainability, economic opportunity, and community empowerment are substantial and worth continued exploration.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network (DePIN): Challenges and Opportunities
Zhibin Lin, Taotao Wang, Long Shi, Shengli Zhang, Bin Cao
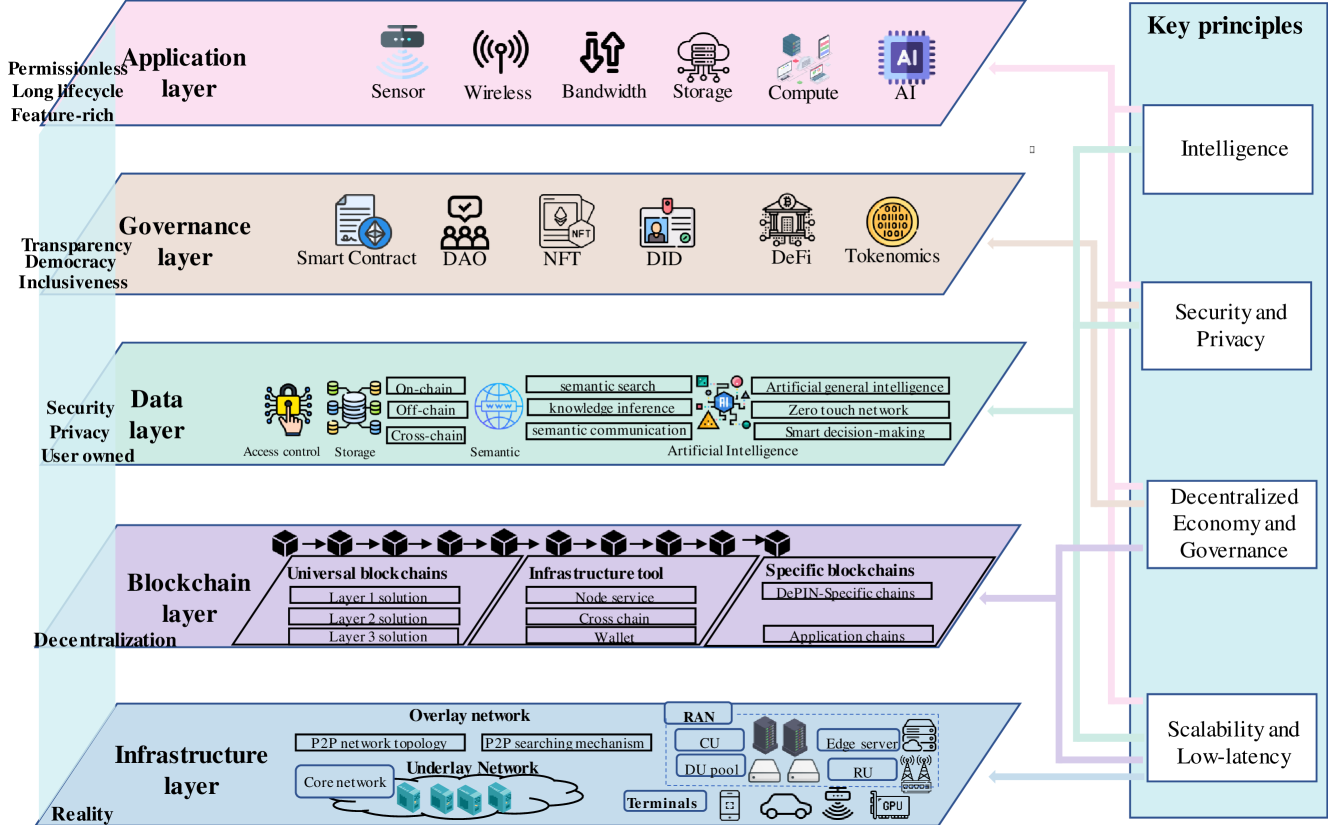
The widespread use of the Internet has posed challenges to existing centralized physical infrastructure networks. Issues such as data privacy risks, service disruptions, and substantial expansion costs have emerged. To address these challenges, an innovative network architecture called Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network (DePIN) has emerged. DePIN leverages blockchain technology to decentralize the control and management of physical devices, addressing limitations of traditional infrastructure network. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of DePIN, presenting its five-layer architecture, key design principles. Furthermore, it presents a detailed survey of the extant applications, operating mechanisms, and provides an in-depth analysis of market data pertaining to DePIN. Finally, it discusses a wide range of the open challenges faced by DePIN.
Read more6/5/2024


0
Performance Analysis of Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks and Centralized Clouds
Jan von der Assen, Christian Killer, Alessandro De Carli, Burkhard Stiller
The advent of Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePIN) represents a shift in the digital infrastructure of today's Internet. While Centralized Service Providers (CSP) monopolize cloud computing, DePINs aim to enhance data sovereignty and confidentiality and increase resilience against a single point of failure. Due to the novelty of the emerging field of DePIN, this work focuses on the potential of DePINs to disrupt traditional centralized architectures by taking advantage of the Internet of Things (IoT) devices and crypto-economic design in combination with blockchains. This combination yields Acurast, a more distributed, resilient, and user-centric physical infrastructure deployment. Through comparative analysis with centralized systems, particularly in serverless computing contexts, this work seeks to lay the first steps in scientifically evaluating DePINs and quantitatively comparing them in terms of efficiency and effectiveness in real-world applications. The findings suggest DePINs' potential to (i) reduce trust assumptions and physically decentralized infrastructure, (ii) increase efficiency and performance simultaneously while improving the computation's (iii) confidentiality and verifiability.
Read more4/15/2024
🖼️

0
LooPIN: A PinFi protocol for decentralized computing
Yunwei Mao, Qi He, Ju Li
Networked computing power is a critical utility in the era of artificial intelligence. This paper presents a novel Physical Infrastructure Finance (PinFi) protocol designed to facilitate the distribution of computing power within networks in a decentralized manner. Addressing the core challenges of coordination, pricing, and liquidity in decentralized physical infrastructure networks (DePIN), the PinFi protocol introduces a distinctive dynamic pricing mechanism. It enables providers to allocate excess computing resources to a dissipative PinFi liquidity pool, distinct from traditional DeFi liquidity pools, ensuring seamless access for clients at equitable, market-based prices. This approach significantly reduces the costs of accessing computing power, potentially to as low as 1% compared to existing services, while simultaneously enhancing security and dependability. The PinFi protocol is poised to transform the dynamics of supply and demand in computing power networks, setting a new standard for efficiency and accessibility.
Read more6/17/2024


0
Towards Credential-based Device Registration in DApps for DePINs with ZKPs
Jonathan Heiss, Fernando Castillo, Xinxin Fan
Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePINS) are secured and governed by blockchains but beyond crypto-economic incentives, they lack measures to establish trust in participating devices and their services. The verification of relevant device credentials during device registration helps to overcome this problem. However, on-chain verification in decentralized applications (dApp) discloses potentially confidential device attributes whereas off-chain verification introduces undesirable trust assumptions. In this paper, we propose a credential-based device registration (CDR) mechanism that verifies device credentials on the blockchain and leverages zero-knowledge proofs (ZKP) to protect confidential device attributes from being disclosed. We characterize CDR for DePINs, present a general system model, and technically evaluate CDR using zkSNARKs with Groth16 and Marlin. Our experiments give first insights into performance impacts and reveal a tradeoff between the applied proof systems.
Read more6/28/2024