LooPIN: A PinFi protocol for decentralized computing

0
🖼️
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Networked computing power is crucial in the era of artificial intelligence
- This paper presents a novel Physical Infrastructure Finance (PinFi) protocol
- PinFi aims to facilitate the distribution of computing power within networks in a decentralized manner
- It addresses challenges of coordination, pricing, and liquidity in decentralized physical infrastructure networks (DePIN)
- PinFi introduces a dynamic pricing mechanism to enable providers to allocate excess computing resources
Plain English Explanation
The paper introduces a new system called PinFi that is designed to make it easier to share and access computing power over networks in a decentralized way.
Today, accessing computing power can be expensive and centralized, controlled by a few major providers. PinFi aims to change this by creating a new way for computing power providers to share their excess capacity and for users to access it at fair, market-based prices.
The key innovation of PinFi is a pricing mechanism that automatically adjusts the cost of accessing computing power based on supply and demand. Providers can contribute their extra computing resources to a shared "liquidity pool," similar to how liquidity pools work in decentralized finance (DeFi). Users can then access this pool and pay a fair, dynamic price that reflects the current market conditions.
This approach has the potential to significantly reduce the costs of accessing computing power, potentially down to as little as 1% of current service prices. At the same time, it enhances security and reliability by distributing computing resources across a decentralized network.
Technical Explanation
The PinFi protocol introduces a distinctive dynamic pricing mechanism to address the core challenges of decentralized physical infrastructure networks (DePIN).
Providers can contribute their excess computing resources to a dissipative PinFi liquidity pool, distinct from traditional DeFi liquidity pools. This ensures seamless access for clients at equitable, market-based prices, determined by the supply and demand within the network.
The paper also presents the FPSpin platform, an FPGA-based open hardware research platform, as a practical implementation of the PinFi protocol. This demonstrates the feasibility and potential of the proposed approach.
Critical Analysis
While the PinFi protocol presents an innovative solution to the challenges of decentralized physical infrastructure networks, the paper does not address certain potential limitations or areas for further research.
For example, the paper does not delve into the security implications of a fully decentralized computing power network, or how to ensure honest participation in the system. Additionally, the scalability of the proposed approach and its ability to handle large-scale computing demands are not thoroughly explored.
Further research and experimentation would be necessary to fully validate the PinFi protocol's effectiveness and address these potential concerns. Nonetheless, the core ideas presented in the paper offer a promising direction for democratizing access to computing power and transforming the dynamics of supply and demand in this critical infrastructure.
Conclusion
The PinFi protocol introduces a novel approach to facilitating the distribution of computing power within networks in a decentralized manner. By addressing the challenges of coordination, pricing, and liquidity in decentralized physical infrastructure networks, the protocol has the potential to significantly reduce the costs of accessing computing power while enhancing security and reliability.
This research represents an important step towards democratizing access to decentralized AI and large language model inference, a critical utility in the era of artificial intelligence. As the demand for computing power continues to grow, the PinFi protocol offers a promising solution to ensure equitable and efficient distribution of this vital resource.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🖼️

0
LooPIN: A PinFi protocol for decentralized computing
Yunwei Mao, Qi He, Ju Li
Networked computing power is a critical utility in the era of artificial intelligence. This paper presents a novel Physical Infrastructure Finance (PinFi) protocol designed to facilitate the distribution of computing power within networks in a decentralized manner. Addressing the core challenges of coordination, pricing, and liquidity in decentralized physical infrastructure networks (DePIN), the PinFi protocol introduces a distinctive dynamic pricing mechanism. It enables providers to allocate excess computing resources to a dissipative PinFi liquidity pool, distinct from traditional DeFi liquidity pools, ensuring seamless access for clients at equitable, market-based prices. This approach significantly reduces the costs of accessing computing power, potentially to as low as 1% compared to existing services, while simultaneously enhancing security and dependability. The PinFi protocol is poised to transform the dynamics of supply and demand in computing power networks, setting a new standard for efficiency and accessibility.
Read more6/17/2024


0
Performance Analysis of Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks and Centralized Clouds
Jan von der Assen, Christian Killer, Alessandro De Carli, Burkhard Stiller
The advent of Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePIN) represents a shift in the digital infrastructure of today's Internet. While Centralized Service Providers (CSP) monopolize cloud computing, DePINs aim to enhance data sovereignty and confidentiality and increase resilience against a single point of failure. Due to the novelty of the emerging field of DePIN, this work focuses on the potential of DePINs to disrupt traditional centralized architectures by taking advantage of the Internet of Things (IoT) devices and crypto-economic design in combination with blockchains. This combination yields Acurast, a more distributed, resilient, and user-centric physical infrastructure deployment. Through comparative analysis with centralized systems, particularly in serverless computing contexts, this work seeks to lay the first steps in scientifically evaluating DePINs and quantitatively comparing them in terms of efficiency and effectiveness in real-world applications. The findings suggest DePINs' potential to (i) reduce trust assumptions and physically decentralized infrastructure, (ii) increase efficiency and performance simultaneously while improving the computation's (iii) confidentiality and verifiability.
Read more4/15/2024
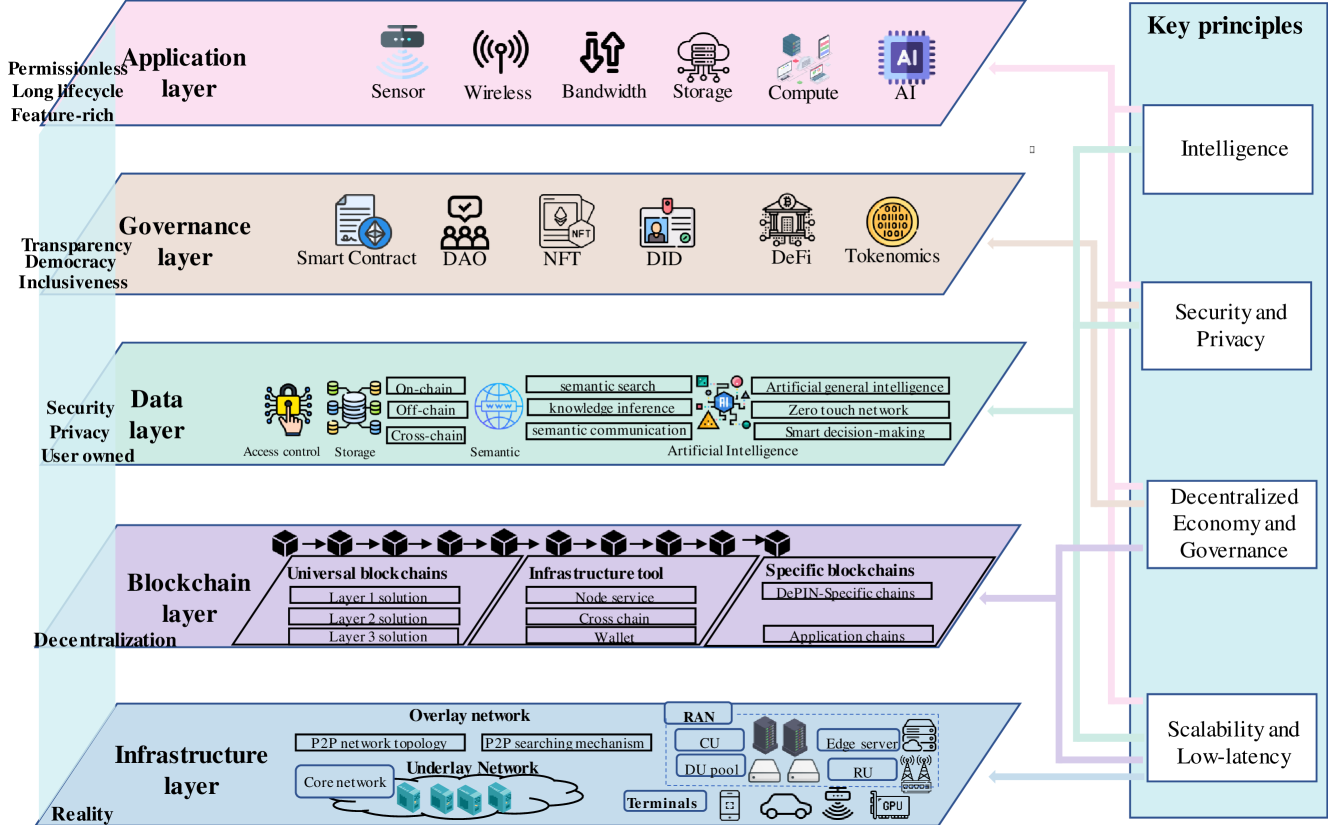

0
Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network (DePIN): Challenges and Opportunities
Zhibin Lin, Taotao Wang, Long Shi, Shengli Zhang, Bin Cao
The widespread use of the Internet has posed challenges to existing centralized physical infrastructure networks. Issues such as data privacy risks, service disruptions, and substantial expansion costs have emerged. To address these challenges, an innovative network architecture called Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network (DePIN) has emerged. DePIN leverages blockchain technology to decentralize the control and management of physical devices, addressing limitations of traditional infrastructure network. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of DePIN, presenting its five-layer architecture, key design principles. Furthermore, it presents a detailed survey of the extant applications, operating mechanisms, and provides an in-depth analysis of market data pertaining to DePIN. Finally, it discusses a wide range of the open challenges faced by DePIN.
Read more6/5/2024


0
Bounds of Block Rewards in Honest PinFi Systems
Qi He, Yunwei Mao, Ju Li
PinFi is a class of novel protocols for decentralized pricing of dissipative assets, whose value naturally declines over time. Central to the protocol's functionality and its market efficiency is the role of liquidity providers (LPs). This study addresses critical stability and sustainability challenges within the protocol, namely: the propensity of LPs to prefer selling in external markets over participation in the protocol; a similar inclination towards selling within the PinFi system rather than contributing as LPs; and a scenario where LPs are disinclined to sell within the protocol. Employing a game-theoretic approach, we explore PinFi's mechanisms and its broader ramifications. Our findings reveal that, under a variety of common conditions and with an assumption of participant integrity, PinFi is capable of fostering a dynamic equilibrium among LPs, sellers, and buyers. This balance is maintained through a carefully calibrated range of block rewards for LPs, ensuring the protocol's long-term stability and utility.
Read more4/4/2024