Decoding Decentralized Finance Transactions through Ego Network Motif Mining

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper proposes a method for decoding decentralized finance (DeFi) transactions using ego network motif mining.
- The researchers analyze transaction data from the Ethereum blockchain to uncover patterns and structures that can provide insights into DeFi activities.
- The findings of this research could help improve fraud detection, risk assessment, and other applications in the DeFi space.
Plain English Explanation
The paper focuses on decentralized finance (DeFi), which is a rapidly growing area of cryptocurrency and blockchain-based financial services. DeFi transactions can be complex and difficult to understand, so the researchers in this study wanted to find a way to "decode" these transactions and uncover hidden patterns.
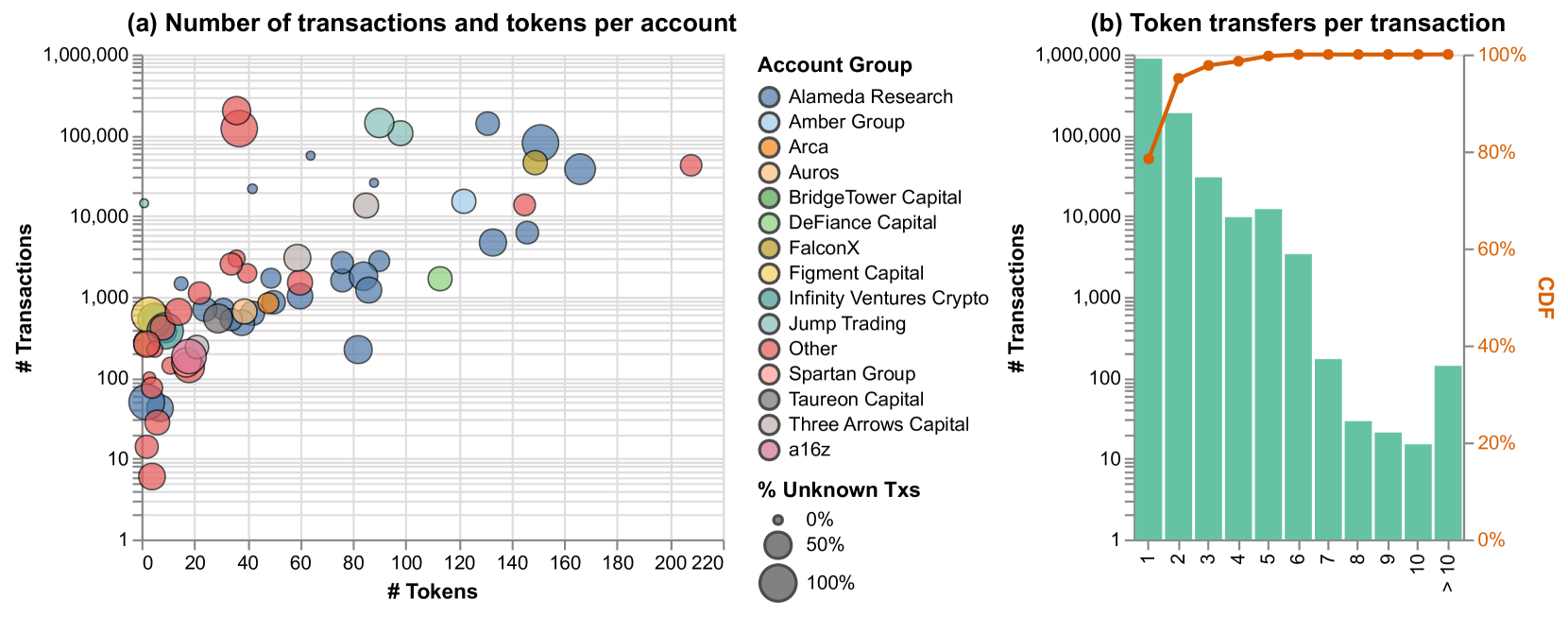
To do this, they used a technique called "ego network motif mining." This involves analyzing the network of transactions around a particular Ethereum address (the "ego") to identify common transaction structures or "motifs." By looking at these motifs, the researchers were able to gain insights into the types of DeFi activities taking place, such as fraud detection and risk assessment.
The findings of this research could be useful for a variety of applications in the DeFi space, such as improving fraud detection, better understanding market behavior, and trend detection in the cryptocurrency and blockchain ecosystem.
Technical Explanation
The researchers in this study used a technique called "ego network motif mining" to analyze Ethereum blockchain transaction data. They started by selecting a specific Ethereum address (the "ego") and then examining the network of transactions around that address, including the addresses of the senders and receivers.
By looking for common patterns or "motifs" in these ego networks, the researchers were able to identify different types of DeFi activities, such as lending, borrowing, and trading. They then used these motifs to develop a classification model that could automatically detect and categorize DeFi transactions based on their underlying structure.
The researchers evaluated their approach using a large dataset of Ethereum transactions and found that their method was able to accurately identify a range of DeFi activities, including several types of fraud. They also demonstrated how the insights gained from this analysis could be used to improve risk assessment and other applications in the DeFi space.
Critical Analysis
One potential limitation of this research is that it focuses solely on Ethereum blockchain data, which may not be representative of the broader DeFi ecosystem. Additionally, the researchers acknowledge that their approach may not be able to detect more complex or sophisticated DeFi activities that do not fit within the predefined motif patterns.
Another area for further research could be to explore how this ego network motif mining approach could be applied to other blockchain networks or even traditional financial systems to uncover hidden patterns and structures. Additionally, the researchers could investigate ways to incorporate other data sources, such as social media or news reports, to provide a more holistic understanding of DeFi activities and trends.
Overall, this research represents an important step forward in our ability to decode and understand the complex world of decentralized finance. By leveraging network analysis techniques, the researchers have demonstrated the potential for uncovering valuable insights that could have significant implications for fraud detection, risk management, and other critical applications in the DeFi space.
Conclusion
This paper presents a novel approach for decoding decentralized finance transactions using ego network motif mining. By analyzing the network of transactions around specific Ethereum addresses, the researchers were able to identify common patterns or "motifs" that provide insights into the types of DeFi activities taking place.
The findings of this research could have important implications for a range of applications in the DeFi space, including fraud detection, risk assessment, and trend detection. As the DeFi ecosystem continues to evolve and grow, tools like this that can provide deeper insights into transaction patterns and structures will become increasingly valuable for both researchers and practitioners working in this fast-paced and complex domain.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Decoding Decentralized Finance Transactions through Ego Network Motif Mining
Natkamon Tovanich, C'elestin Coquid'e, R'emy Cazabet
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is increasingly studied and adopted for its potential to provide accessible and transparent financial services. Analyzing how investors use DeFi is important for reaching a better understanding of their usage and for regulation purposes. However, analyzing DeFi transactions is challenging due to often incomplete or inaccurate labeled data. This paper presents a method to extract ego network motifs from the token transfer network, capturing the transfer of tokens between users and smart contracts. Our results demonstrate that smart contract methods performing specific DeFi operations can be efficiently identified by analyzing these motifs while providing insights into account activities.
Read more8/23/2024
🌐

0
New!Inside Alameda Research: A Multi-Token Network Analysis
C'elestin Coquid'e, R'emy Cazabet, Natkamon Tovanich
We analyze the token transfer network on Ethereum, focusing on accounts associated with Alameda Research, a cryptocurrency trading firm implicated in the misuse of FTX customer funds. Using a multi-token network representation, we examine node centralities and the network backbone to identify critical accounts, tokens, and activity groups. The temporal evolution of Alameda accounts reveals shifts in token accumulation and distribution patterns leading up to its bankruptcy in November 2022. Through network analysis, our work offers insights into the activities and dynamics that shape the DeFi ecosystem.
Read more9/18/2024


0
Enhancing Ethereum Fraud Detection via Generative and Contrastive Self-supervision
Chenxiang Jin, Jiajun Zhou, Chenxuan Xie, Shanqing Yu, Qi Xuan, Xiaoniu Yang
The rampant fraudulent activities on Ethereum hinder the healthy development of the blockchain ecosystem, necessitating the reinforcement of regulations. However, multiple imbalances involving account interaction frequencies and interaction types in the Ethereum transaction environment pose significant challenges to data mining-based fraud detection research. To address this, we first propose the concept of meta-interactions to refine interaction behaviors in Ethereum, and based on this, we present a dual self-supervision enhanced Ethereum fraud detection framework, named Meta-IFD. This framework initially introduces a generative self-supervision mechanism to augment the interaction features of accounts, followed by a contrastive self-supervision mechanism to differentiate various behavior patterns, and ultimately characterizes the behavioral representations of accounts and mines potential fraud risks through multi-view interaction feature learning. Extensive experiments on real Ethereum datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our framework in detecting common Ethereum fraud behaviors such as Ponzi schemes and phishing scams. Additionally, the generative module can effectively alleviate the interaction distribution imbalance in Ethereum data, while the contrastive module significantly enhances the framework's ability to distinguish different behavior patterns. The source code will be released on GitHub soon.
Read more8/2/2024
🤖

0
Decoding Social Sentiment in DAO: A Comparative Analysis of Blockchain Governance Communities
Yutong Quan, Xintong Wu, Wanlin Deng, Luyao Zhang
Blockchain technology is leading a revolutionary transformation across diverse industries, with effective governance being critical for the success and sustainability of blockchain projects. Community forums, pivotal in engaging decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), significantly impact blockchain governance decisions. Concurrently, Natural Language Processing (NLP), particularly sentiment analysis, provides powerful insights from textual data. While prior research has explored the potential of NLP tools in social media sentiment analysis, there is a gap in understanding the sentiment landscape of blockchain governance communities. The evolving discourse and sentiment dynamics on the forums of top DAOs remain largely unknown. This paper delves deep into the evolving discourse and sentiment dynamics on the public forums of leading DeFi projects: Aave, Uniswap, Curve DAO, Yearn.finance, Merit Circle, and Balancer, focusing primarily on discussions related to governance issues. Our study shows that participants in decentralized communities generally express positive sentiments during Discord discussions. Furthermore, there is a potential interaction between discussion intensity and sentiment dynamics; higher discussion volume may contribute to a more stable sentiment from code analysis. The insights gained from this study are valuable for decision-makers in blockchain governance, underscoring the pivotal role of sentiment analysis in interpreting community emotions and its evolving impact on the landscape of blockchain governance. This research significantly contributes to the interdisciplinary exploration of the intersection of blockchain and society, specifically emphasizing the decentralized blockchain governance ecosystem. We provide our data and code for replicability as open access on GitHub.
Read more5/28/2024