Deep Learning for Multi-Label Learning: A Comprehensive Survey
2401.16549

23
0
🤿
Abstract
Multi-label learning is a rapidly growing research area that aims to predict multiple labels from a single input data point. In the era of big data, tasks involving multi-label classification (MLC) or ranking present significant and intricate challenges, capturing considerable attention in diverse domains. Inherent difficulties in MLC include dealing with high-dimensional data, addressing label correlations, and handling partial labels, for which conventional methods prove ineffective. Recent years have witnessed a notable increase in adopting deep learning (DL) techniques to address these challenges more effectively in MLC. Notably, there is a burgeoning effort to harness the robust learning capabilities of DL for improved modelling of label dependencies and other challenges in MLC. However, it is noteworthy that comprehensive studies specifically dedicated to DL for multi-label learning are limited. Thus, this survey aims to thoroughly review recent progress in DL for multi-label learning, along with a summary of open research problems in MLC. The review consolidates existing research efforts in DL for MLC,including deep neural networks, transformers, autoencoders, and convolutional and recurrent architectures. Finally, the study presents a comparative analysis of the existing methods to provide insightful observations and stimulate future research directions in this domain.
Create account to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

A Survey on Incomplete Multi-label Learning: Recent Advances and Future Trends
Xiang Li, Jiexi Liu, Xinrui Wang, Songcan Chen

0
0
In reality, data often exhibit associations with multiple labels, making multi-label learning (MLL) become a prominent research topic. The last two decades have witnessed the success of MLL, which is indispensable from complete and accurate supervised information. However, obtaining such information in practice is always laborious and sometimes even impossible. To circumvent this dilemma, incomplete multi-label learning (InMLL) has emerged, aiming to learn from incomplete labeled data. To date, enormous InMLL works have been proposed to narrow the performance gap with complete MLL, whereas a systematic review for InMLL is still absent. In this paper, we not only attempt to fill the lacuna but also strive to pave the way for innovative research. Specifically, we retrospect the origin of InMLL, analyze the challenges of InMLL, and make a taxonomy of InMLL from the data-oriented and algorithm-oriented perspectives, respectively. Besides, we also present real applications of InMLL in various domains. More importantly, we highlight several potential future trends, including four open problems that are more in line with practice and three under-explored/unexplored techniques in addressing the challenges of InMLL, which may shed new light on developing novel research directions in the field of InMLL.
6/11/2024
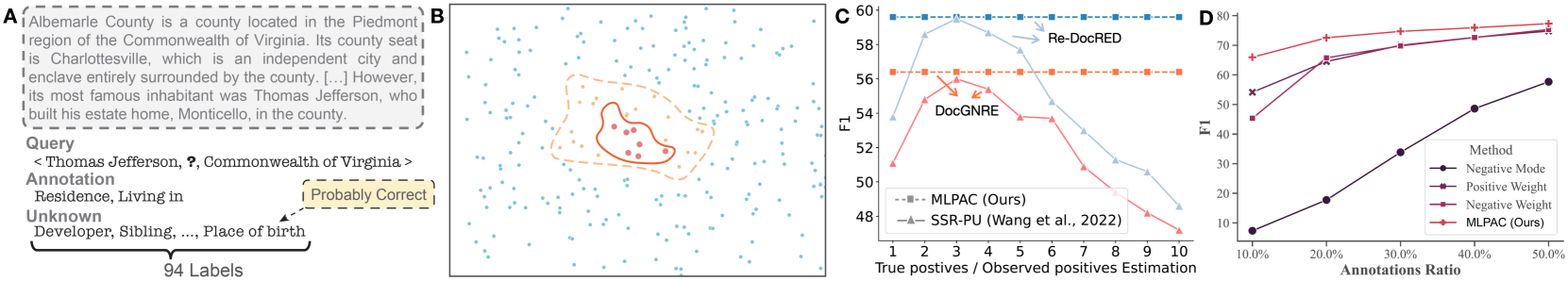
Combining Supervised Learning and Reinforcement Learning for Multi-Label Classification Tasks with Partial Labels
Zixia Jia, Junpeng Li, Shichuan Zhang, Anji Liu, Zilong Zheng

0
0
Traditional supervised learning heavily relies on human-annotated datasets, especially in data-hungry neural approaches. However, various tasks, especially multi-label tasks like document-level relation extraction, pose challenges in fully manual annotation due to the specific domain knowledge and large class sets. Therefore, we address the multi-label positive-unlabelled learning (MLPUL) problem, where only a subset of positive classes is annotated. We propose Mixture Learner for Partially Annotated Classification (MLPAC), an RL-based framework combining the exploration ability of reinforcement learning and the exploitation ability of supervised learning. Experimental results across various tasks, including document-level relation extraction, multi-label image classification, and binary PU learning, demonstrate the generalization and effectiveness of our framework.
6/26/2024
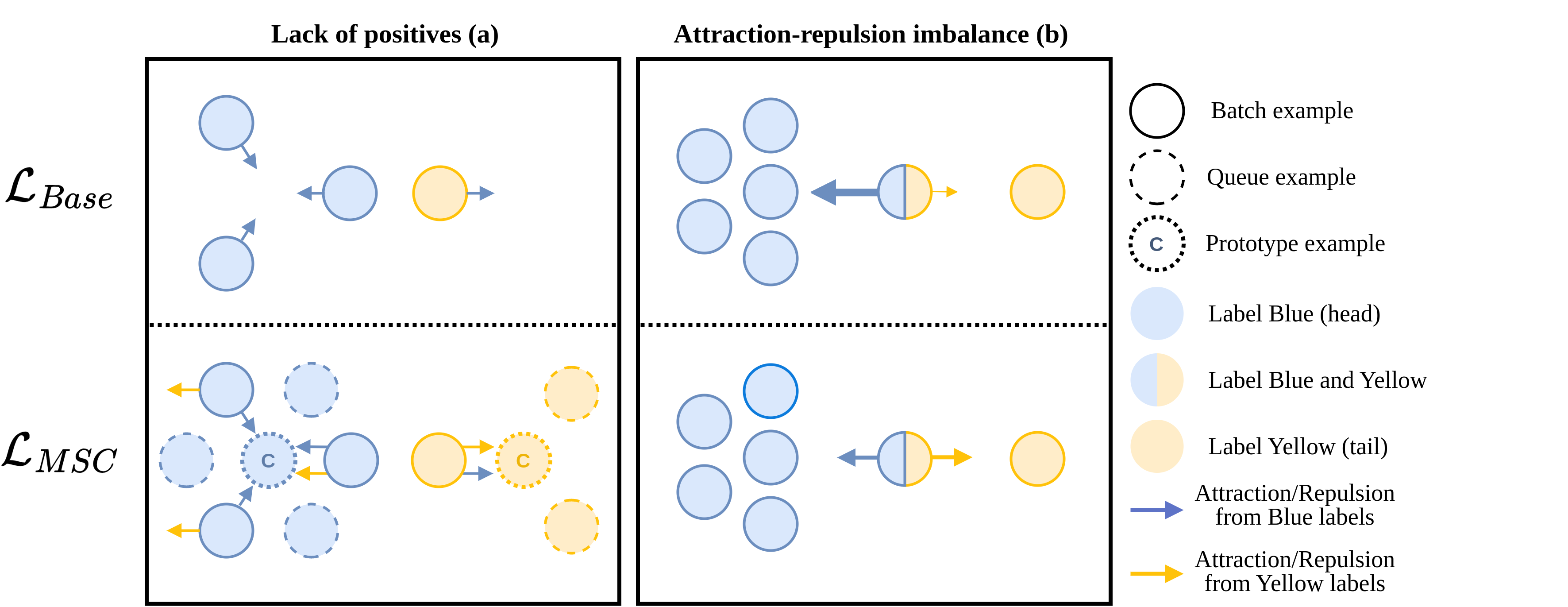
Exploring Contrastive Learning for Long-Tailed Multi-Label Text Classification
Alexandre Audibert, Aur'elien Gauffre, Massih-Reza Amini

0
0
Learning an effective representation in multi-label text classification (MLTC) is a significant challenge in NLP. This challenge arises from the inherent complexity of the task, which is shaped by two key factors: the intricate connections between labels and the widespread long-tailed distribution of the data. To overcome this issue, one potential approach involves integrating supervised contrastive learning with classical supervised loss functions. Although contrastive learning has shown remarkable performance in multi-class classification, its impact in the multi-label framework has not been thoroughly investigated. In this paper, we conduct an in-depth study of supervised contrastive learning and its influence on representation in MLTC context. We emphasize the importance of considering long-tailed data distributions to build a robust representation space, which effectively addresses two critical challenges associated with contrastive learning that we identify: the lack of positives and the attraction-repulsion imbalance. Building on this insight, we introduce a novel contrastive loss function for MLTC. It attains Micro-F1 scores that either match or surpass those obtained with other frequently employed loss functions, and demonstrates a significant improvement in Macro-F1 scores across three multi-label datasets.
4/16/2024
🌿
Multi-Task Learning in Natural Language Processing: An Overview
Shijie Chen, Yu Zhang, Qiang Yang

0
0
Deep learning approaches have achieved great success in the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP). However, directly training deep neural models often suffer from overfitting and data scarcity problems that are pervasive in NLP tasks. In recent years, Multi-Task Learning (MTL), which can leverage useful information of related tasks to achieve simultaneous performance improvement on these tasks, has been used to handle these problems. In this paper, we give an overview of the use of MTL in NLP tasks. We first review MTL architectures used in NLP tasks and categorize them into four classes, including parallel architecture, hierarchical architecture, modular architecture, and generative adversarial architecture. Then we present optimization techniques on loss construction, gradient regularization, data sampling, and task scheduling to properly train a multi-task model. After presenting applications of MTL in a variety of NLP tasks, we introduce some benchmark datasets. Finally, we make a conclusion and discuss several possible research directions in this field.
4/30/2024