Developing Situational Awareness for Joint Action with Autonomous Vehicles
2404.11800

0
0

Abstract
Unanswered questions about how human-AV interaction designers can support rider's informational needs hinders Autonomous Vehicles (AV) adoption. To achieve joint human-AV action goals - such as safe transportation, trust, or learning from an AV - sufficient situational awareness must be held by the human, AV, and human-AV system collectively. We present a systems-level framework that integrates cognitive theories of joint action and situational awareness as a means to tailor communications that meet the criteria necessary for goal success. This framework is based on four components of the shared situation: AV traits, action goals, subject-specific traits and states, and the situated driving context. AV communications should be tailored to these factors and be sensitive when they change. This framework can be useful for understanding individual, shared, and distributed human-AV situational awareness and designing for future AV communications that meet the informational needs and goals of diverse groups and in diverse driving contexts.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores the concept of developing situational awareness for joint action between autonomous vehicles (AVs) and humans.
- It proposes a framework for situated joint action within a human-AV system, which aims to enable effective collaboration and coordination between AVs and human users.
- The paper discusses the importance of situational awareness, challenges in achieving it, and the potential benefits of joint action between AVs and humans.
Plain English Explanation
The paper focuses on the idea of helping autonomous vehicles (AVs) and humans work together effectively. AVs are becoming more common, but they still face challenges in understanding the surrounding environment and interacting with people. This paper suggests a way to improve this by developing "situational awareness" - the ability of the AV to understand the current situation and what's happening around it.
By having better situational awareness, the AV can coordinate its actions with the humans it interacts with, like drivers or pedestrians. This "joint action" allows the AV and the human to work together towards a common goal, like navigating through traffic safely. The paper outlines a framework for how this could work in practice, addressing the key challenges and potential benefits.
The main idea is to enable the AV and the human to each have a good understanding of the current situation, and then use that shared awareness to guide their joint actions. This could lead to smoother, more efficient, and safer interactions between AVs and the people around them. The paper suggests this is an important step in making AVs work seamlessly with human users.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes a framework for situated joint action within a human-AV system. This framework aims to enable effective collaboration and coordination between autonomous vehicles (AVs) and human users.
The key elements of the framework include:
-
Situational Awareness: The ability of the AV to perceive, comprehend, and project the state of the environment and other actors (humans, other AVs, etc.). This allows the AV to understand the current situation.
-
Joint Action: The coordination of actions between the AV and human users to achieve a shared goal, such as safe and efficient navigation. This requires the AV and human to have a common understanding of the situation.
-
Interaction Mechanisms: The channels and protocols used for the AV and human to communicate and exchange information to develop shared situational awareness and coordinate their actions.
The paper discusses the challenges in achieving effective situational awareness and joint action, such as imperfect sensor data, uncertainty in human intent and behavior, and the need for explanations and transparency to build trust.
The proposed framework aims to address these challenges and enable seamless human-AV interaction by facilitating the development of shared situational awareness and coordinated joint action.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a thoughtful and well-structured approach to the important challenge of developing situational awareness for effective collaboration between autonomous vehicles and human users. However, the authors acknowledge several caveats and limitations that warrant further consideration:
-
Sensor Imperfections: The framework relies on the AV's ability to perceive the environment accurately, but as noted, sensor data can be imperfect and incomplete. Strategies for handling sensor uncertainties and errors are crucial for the framework's real-world applicability.
-
Modeling Human Behavior: Accurately modeling and predicting human behavior, especially in complex, dynamic traffic situations, is a significant challenge. The framework's effectiveness may be limited by the AV's ability to understand and anticipate human actions and intentions.
-
Trust and Transparency: As the paper acknowledges, building trust between humans and AVs is essential for effective joint action. The framework would benefit from a more in-depth discussion of how to achieve the necessary level of transparency and explanations to foster this trust.
-
Scalability and Generalizability: The paper focuses on a specific illustrative example, but it is unclear how well the proposed framework would scale to more complex, real-world situations involving multiple AVs and human actors. Further research is needed to assess the framework's generalizability.
Overall, the paper presents a promising approach to a critical challenge in the development of autonomous vehicles. However, the authors would do well to address the identified limitations and explore the framework's practical implementation and evaluation in more depth.
Conclusion
This paper proposes a framework for developing situational awareness to enable effective joint action between autonomous vehicles (AVs) and human users. The key elements of the framework include situational awareness, joint action, and interaction mechanisms.
The framework aims to address the challenges of achieving seamless human-AV interaction, such as imperfect sensor data, uncertainty in human behavior, and the need for trust and transparency. By facilitating the development of shared situational awareness and coordinated joint action, the framework has the potential to enable safer, more efficient, and more effective collaboration between AVs and the people they interact with.
While the paper provides a strong conceptual foundation, further research is needed to address the identified limitations and evaluate the framework's practical implementation and real-world performance. Nonetheless, this work represents an important step towards realizing the full potential of autonomous vehicles to work seamlessly with human users.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🤿
Expansion of situations theory for exploring shared awareness in human-intelligent autonomous systems
Scott A. Humr, Mustafa Canan, Mustafa Demir

0
0
Intelligent autonomous systems are part of a system of systems that interact with other agents to accomplish tasks in complex environments. However, intelligent autonomous systems integrated system of systems add additional layers of complexity based on their limited cognitive processes, specifically shared situation awareness that allows a team to respond to novel tasks. Intelligent autonomous systems' lack of shared situation awareness adversely influences team effectiveness in complex task environments, such as military command-and-control. A complementary approach of shared situation awareness, called situations theory, is beneficial for understanding the relationship between system of systems shared situation awareness and effectiveness. The current study elucidates a conceptual discussion on situations theory to investigate the development of an system of systems shared situational awareness when humans team with intelligent autonomous system agents. To ground the discussion, the reviewed studies expanded situations theory within the context of a system of systems that result in three major conjectures that can be beneficial to the design and development of future systems of systems.
6/10/2024
👁️
Towards Context-Aware Modeling of Situation Awareness in Conditionally Automated Driving
Lilit Avetisyan, X. Jessie Yang, Feng Zhou

0
0
Maintaining adequate situation awareness (SA) is crucial for the safe operation of conditionally automated vehicles (AVs), which requires drivers to regain control during takeover (TOR) events. This study developed a predictive model for real-time assessment of driver SA using multimodal data (e.g., galvanic skin response, heart rate and eye tracking data, and driver characteristics) collected in a simulated driving environment. Sixty-seven participants experienced automated driving scenarios with TORs, with conditions varying in risk perception and the presence of automation errors. A LightGBM (Light Gradient Boosting Machine) model trained on the top 12 predictors identified by SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) achieved promising performance with RMSE=0.89, MAE=0.71, and Corr=0.78. These findings have implications towards context-aware modeling of SA in conditionally automated driving, paving the way for safer and more seamless driver-AV interactions.
5/14/2024
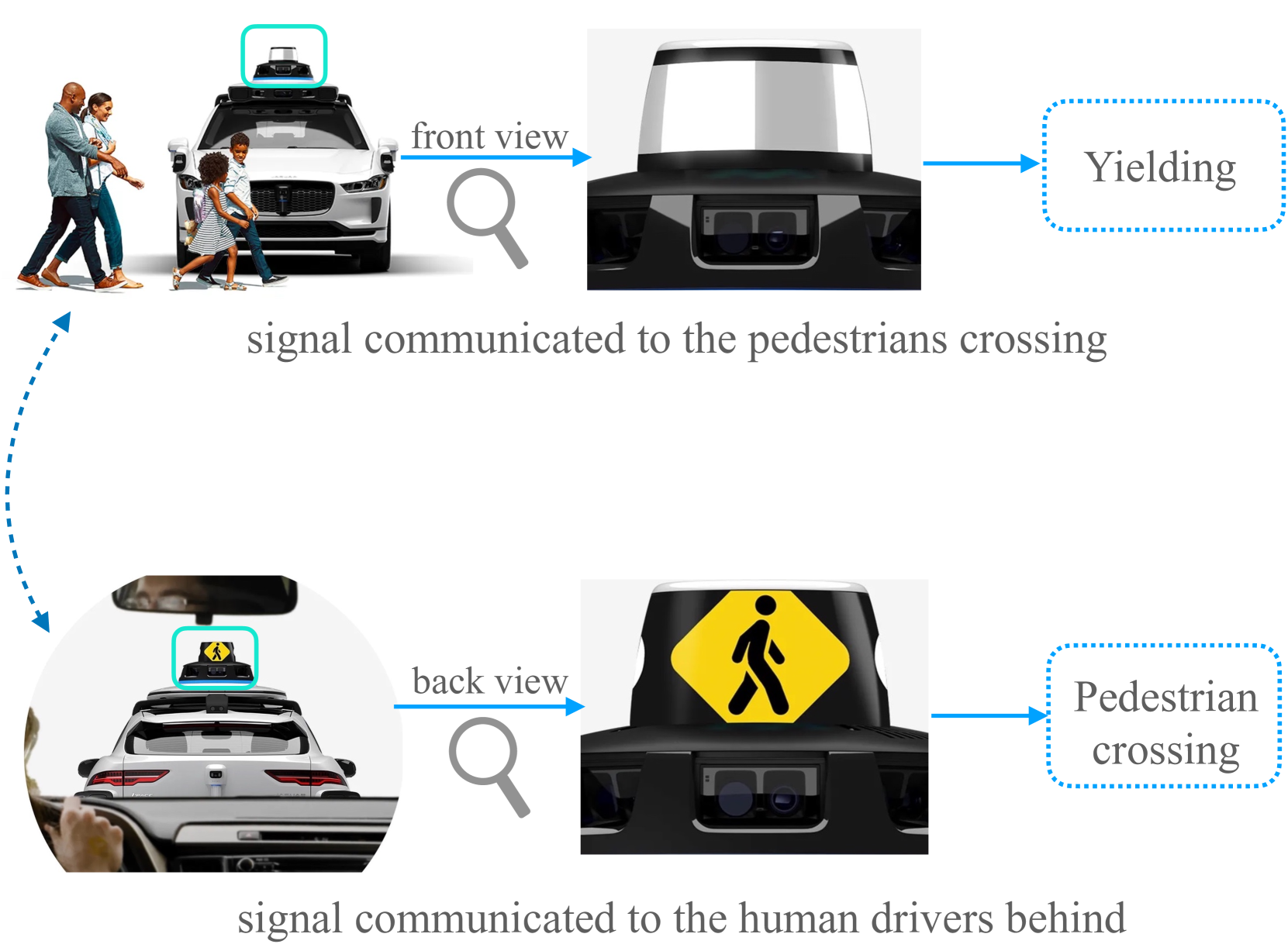
Incorporating Explanations into Human-Machine Interfaces for Trust and Situation Awareness in Autonomous Vehicles
Shahin Atakishiyev, Mohammad Salameh, Randy Goebel

0
0
Autonomous vehicles often make complex decisions via machine learning-based predictive models applied to collected sensor data. While this combination of methods provides a foundation for real-time actions, self-driving behavior primarily remains opaque to end users. In this sense, explainability of real-time decisions is a crucial and natural requirement for building trust in autonomous vehicles. Moreover, as autonomous vehicles still cause serious traffic accidents for various reasons, timely conveyance of upcoming hazards to road users can help improve scene understanding and prevent potential risks. Hence, there is also a need to supply autonomous vehicles with user-friendly interfaces for effective human-machine teaming. Motivated by this problem, we study the role of explainable AI and human-machine interface jointly in building trust in vehicle autonomy. We first present a broad context of the explanatory human-machine systems with the 3W1H (what, whom, when, how) approach. Based on these findings, we present a situation awareness framework for calibrating users' trust in self-driving behavior. Finally, we perform an experiment on our framework, conduct a user study on it, and validate the empirical findings with hypothesis testing.
4/12/2024
🔎
Leveraging Artificial Intelligence to Promote Awareness in Augmented Reality Systems
Wangfan Li, Rohit Mallick, Carlos Toxtli-Hernandez, Christopher Flathmann, Nathan J. McNeese

0
0
Recent developments in artificial intelligence (AI) have permeated through an array of different immersive environments, including virtual, augmented, and mixed realities. AI brings a wealth of potential that centers on its ability to critically analyze environments, identify relevant artifacts to a goal or action, and then autonomously execute decision-making strategies to optimize the reward-to-risk ratio. However, the inherent benefits of AI are not without disadvantages as the autonomy and communication methodology can interfere with the human's awareness of their environment. More specifically in the case of autonomy, the relevant human-computer interaction literature cites that high autonomy results in an out-of-the-loop experience for the human such that they are not aware of critical artifacts or situational changes that require their attention. At the same time, low autonomy of an AI system can limit the human's own autonomy with repeated requests to approve its decisions. In these circumstances, humans enter into supervisor roles, which tend to increase their workload and, therefore, decrease their awareness in a multitude of ways. In this position statement, we call for the development of human-centered AI in immersive environments to sustain and promote awareness. It is our position then that we believe with the inherent risk presented in both AI and AR/VR systems, we need to examine the interaction between them when we integrate the two to create a new system for any unforeseen risks, and that it is crucial to do so because of its practical application in many high-risk environments.
5/10/2024