Diffusion Model Based Resource Allocation Strategy in Ultra-Reliable Wireless Networked Control Systems

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- The paper presents a diffusion model-based resource allocation strategy for ultra-reliable wireless networked control systems.
- It aims to address the challenges of providing reliable and low-latency communication in industrial automation and control applications.
- The proposed approach uses a diffusion-based optimization algorithm to dynamically allocate resources and improve system performance.
Plain English Explanation
The paper focuses on improving the reliability and responsiveness of wireless communication networks used in industrial automation and control systems. These systems, known as ultra-reliable wireless networked control systems, require very low latency and high reliability to ensure the smooth operation of industrial processes.
The researchers developed a new approach that uses a diffusion model to dynamically allocate communication resources, such as network bandwidth and transmit power. This diffusion-based optimization algorithm adaptively distributes the available resources among the different devices and sensors in the network, based on their real-time needs and communication requirements.
The goal is to ensure that critical data, such as sensor readings and control commands, are transmitted reliably and with minimal delay, even in the face of challenging wireless conditions. By using a diffusion-based approach, the system can respond quickly to changes in the network and adjust the resource allocation accordingly.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a diffusion model-based resource allocation strategy for ultra-reliable wireless networked control systems. The authors develop a distributed optimization algorithm that uses a diffusion model to dynamically allocate communication resources, such as bandwidth and transmit power, among the various devices and sensors in the network.
The system model consists of a wireless network with multiple nodes, each representing a device or sensor in an industrial automation or control application. The nodes communicate with a central controller, which is responsible for coordinating the resource allocation and ensuring reliable and low-latency data transmission.
The diffusion-based optimization algorithm works by iteratively updating the resource allocation based on local information exchange between neighboring nodes. This distributed approach allows the system to adapt quickly to changes in the network conditions, such as varying channel quality or changes in the communication demands of the different devices.
Through simulations and analysis, the authors demonstrate that the proposed diffusion model-based resource allocation strategy can significantly improve the reliability and responsiveness of the wireless networked control system, compared to traditional fixed resource allocation schemes.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a novel and promising approach to addressing the challenges of providing reliable and low-latency communication in industrial automation and control applications. The use of a diffusion-based optimization algorithm is an interesting and potentially effective way to dynamically allocate resources in response to changing network conditions.
However, the paper does not provide a comprehensive evaluation of the proposed strategy, and there are some potential limitations that could be addressed in future research. For example, the authors do not discuss the scalability of the approach as the number of nodes in the network increases, or the robustness of the system to more severe network disruptions, such as node failures or temporary communication blackouts.
Additionally, the paper could benefit from a more in-depth discussion of the practical considerations and implementation challenges associated with deploying such a system in a real-world industrial setting. Factors such as hardware constraints, integration with existing control systems, and the impact of the resource allocation strategy on the overall system performance and stability could be explored further.
Conclusion
The paper presents a novel diffusion model-based resource allocation strategy for ultra-reliable wireless networked control systems. The proposed approach uses a distributed optimization algorithm to dynamically adjust the allocation of communication resources, such as bandwidth and transmit power, in response to changing network conditions.
The authors demonstrate through simulations that the diffusion-based strategy can significantly improve the reliability and responsiveness of the wireless networked control system, compared to traditional fixed resource allocation schemes. This work represents an important contribution to the field of industrial automation and control, as it addresses the critical challenge of providing reliable and low-latency communication in these mission-critical applications.
While the paper shows promising results, further research is needed to address potential limitations and explore the practical considerations of deploying such a system in real-world industrial settings. Nonetheless, the diffusion model-based approach presented in this paper offers a valuable new tool for enhancing the performance and resilience of ultra-reliable wireless networked control systems.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Diffusion Model Based Resource Allocation Strategy in Ultra-Reliable Wireless Networked Control Systems
Amirhassan Babazadeh Darabi, Sinem Coleri
Diffusion models are vastly used in generative AI, leveraging their capability to capture complex data distributions. However, their potential remains largely unexplored in the field of resource allocation in wireless networks. This paper introduces a novel diffusion model-based resource allocation strategy for Wireless Networked Control Systems (WNCSs) with the objective of minimizing total power consumption through the optimization of the sampling period in the control system, and blocklength and packet error probability in the finite blocklength regime of the communication system. The problem is first reduced to the optimization of blocklength only based on the derivation of the optimality conditions. Then, the optimization theory solution collects a dataset of channel gains and corresponding optimal blocklengths. Finally, the Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model (DDPM) uses this collected dataset to train the resource allocation algorithm that generates optimal blocklength values conditioned on the channel state information (CSI). Via extensive simulations, the proposed approach is shown to outperform previously proposed Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) based approaches with close to optimal performance regarding total power consumption. Moreover, an improvement of up to eighteen-fold in the reduction of critical constraint violations is observed, further underscoring the accuracy of the solution.
Read more7/23/2024

0
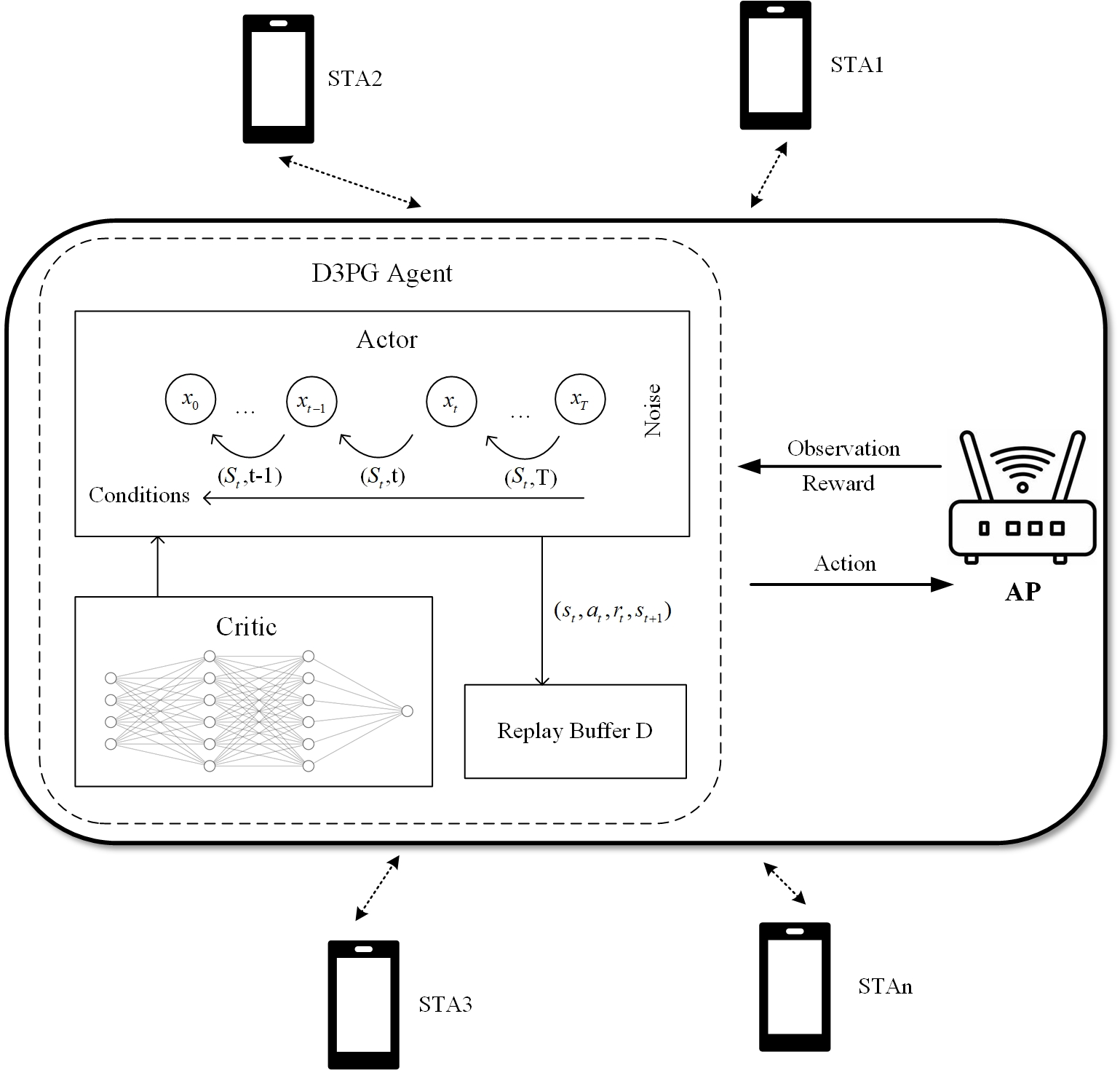
Wi-Fi Optimization with Deep Diffusion Deterministic Policy
Tie Liu, Xuming Fang, Rong He
Generative Diffusion Models (GDMs), have made significant strides in modeling complex data distributions across diverse domains. Meanwhile, Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) has demonstrated substantial improvements in optimizing Wi-Fi network performance. Wi-Fi optimization problems are highly challenging to model mathematically, and DRL methods can bypass complex mathematical modeling, while GDMs excel in handling complex data modeling. Therefore, combining DRL with GDMs can mutually enhance their capabilities. The current MAC layer access mechanism in Wi-Fi networks is the Distributed Coordination Function (DCF), which dramatically declines in performance with a high number of terminals. In this paper, we apply diffusion models to deep deterministic policy gradient (DDPG), namely the Deep Diffusion Deterministic Policy (D3PG) algorithm to optimize the Wi-Fi performance. Although similar integrations of reinforcement learning with generative diffusion models have been explored previously, we are the first to apply this approach to Wi-Fi network performance optimization. We propose an access mechanism that jointly adjusts the contention window and aggregation frame length based on the D3PG algorithm. Through simulations, we have demonstrated that this mechanism significantly outperforms existing Wi-Fi standards in dense Wi-Fi scenarios, maintaining performance even as the number of users sharply increases.
Read more9/5/2024


0
Uplink resource allocation optimization for user-centric cell-free MIMO networks
Zehua Li, Raviraj Adve
We examine the problem of optimizing resource allocation in the uplink for a user-centric, cell-free, multi-input multi-output network. We start by modeling and developing resource allocation algorithms for two standard network operation modes. The centralized mode provides high data rates but suffers multiple issues, including scalability. On the other hand, the distributed mode has the opposite problem: relatively low rates, but is scalable. To address these challenges, we combine the strength of the two standard modes, creating a new semi-distributed operation mode. To avoid the need for information exchange between access points, we introduce a new quality of service metric to decentralize the resource allocation algorithms. Our results show that we can eliminate the need for information exchange with a relatively small penalty on data rates.
Read more6/11/2024
📊

0
Conditional Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models for Data Reconstruction Enhancement in Wireless Communications
Mehdi Letafati, Samad Ali, Matti Latva-aho
In this paper, conditional denoising diffusion probabilistic models (DDPMs) are proposed to enhance the data transmission and reconstruction over wireless channels. The underlying mechanism of DDPM is to decompose the data generation process over the so-called denoising steps. Inspired by this, the key idea is to leverage the generative prior of diffusion models in learning a noisy-to-clean transformation of the information signal to help enhance data reconstruction. The proposed scheme could be beneficial for communication scenarios in which a prior knowledge of the information content is available, e.g., in multimedia transmission. Hence, instead of employing complicated channel codes that reduce the information rate, one can exploit diffusion priors for reliable data reconstruction, especially under extreme channel conditions due to low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), or hardware-impaired communications. The proposed DDPM-assisted receiver is tailored for the scenario of wireless image transmission using MNIST dataset. Our numerical results highlight the reconstruction performance of our scheme compared to the conventional digital communication, as well as the deep neural network (DNN)-based benchmark. It is also shown that more than 10 dB improvement in the reconstruction could be achieved in low SNR regimes, without the need to reduce the information rate for error correction.
Read more6/5/2024