DR-RAG: Applying Dynamic Document Relevance to Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Question-Answering
2406.07348

0
0
Abstract
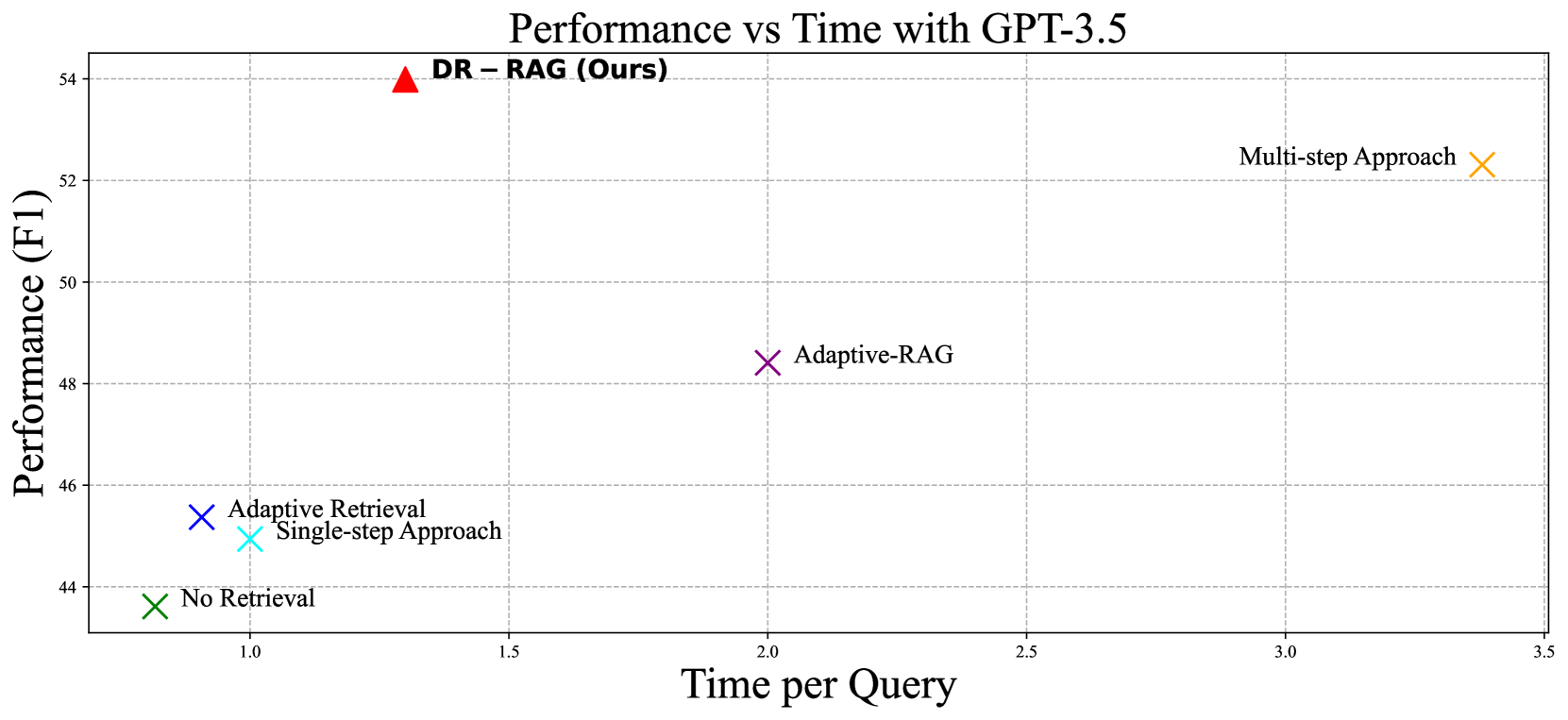
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has recently demonstrated the performance of Large Language Models (LLMs) in the knowledge-intensive tasks such as Question-Answering (QA). RAG expands the query context by incorporating external knowledge bases to enhance the response accuracy. However, it would be inefficient to access LLMs multiple times for each query and unreliable to retrieve all the relevant documents by a single query. We have found that even though there is low relevance between some critical documents and query, it is possible to retrieve the remaining documents by combining parts of the documents with the query. To mine the relevance, a two-stage retrieval framework called Dynamic-Relevant Retrieval-Augmented Generation (DR-RAG) is proposed to improve document retrieval recall and the accuracy of answers while maintaining efficiency. Additionally, a compact classifier is applied to two different selection strategies to determine the contribution of the retrieved documents to answering the query and retrieve the relatively relevant documents. Meanwhile, DR-RAG call the LLMs only once, which significantly improves the efficiency of the experiment. The experimental results on multi-hop QA datasets show that DR-RAG can significantly improve the accuracy of the answers and achieve new progress in QA systems.
Create account to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🛸
DuetRAG: Collaborative Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Dian Jiao, Li Cai, Jingsheng Huang, Wenqiao Zhang, Siliang Tang, Yueting Zhuang

0
0
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) methods augment the input of Large Language Models (LLMs) with relevant retrieved passages, reducing factual errors in knowledge-intensive tasks. However, contemporary RAG approaches suffer from irrelevant knowledge retrieval issues in complex domain questions (e.g., HotPot QA) due to the lack of corresponding domain knowledge, leading to low-quality generations. To address this issue, we propose a novel Collaborative Retrieval-Augmented Generation framework, DuetRAG. Our bootstrapping philosophy is to simultaneously integrate the domain fintuning and RAG models to improve the knowledge retrieval quality, thereby enhancing generation quality. Finally, we demonstrate DuetRAG' s matches with expert human researchers on HotPot QA.
5/24/2024
DRAGIN: Dynamic Retrieval Augmented Generation based on the Information Needs of Large Language Models
Weihang Su, Yichen Tang, Qingyao Ai, Zhijing Wu, Yiqun Liu

0
0
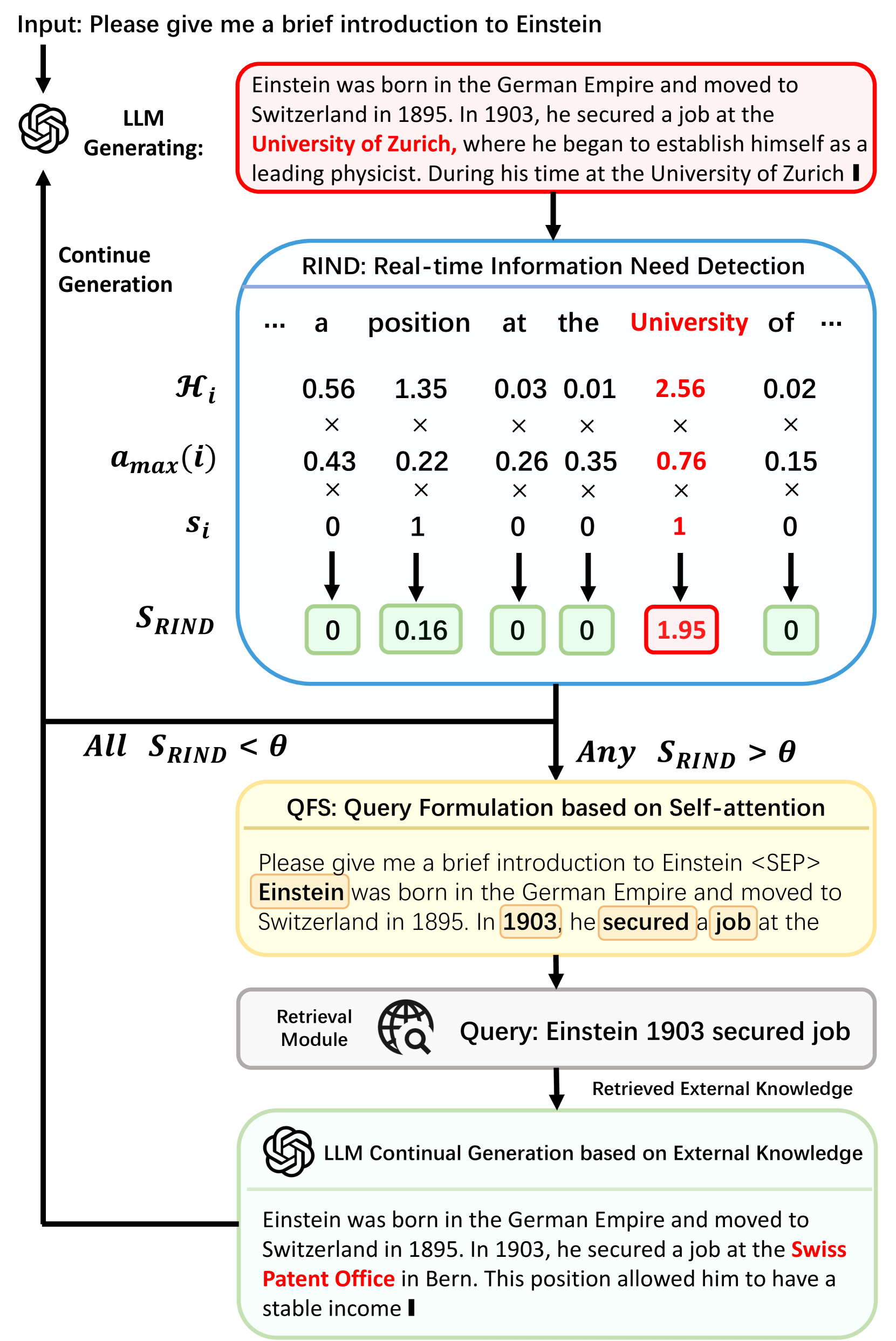
Dynamic retrieval augmented generation (RAG) paradigm actively decides when and what to retrieve during the text generation process of Large Language Models (LLMs). There are two key elements of this paradigm: identifying the optimal moment to activate the retrieval module (deciding when to retrieve) and crafting the appropriate query once retrieval is triggered (determining what to retrieve). However, current dynamic RAG methods fall short in both aspects. Firstly, the strategies for deciding when to retrieve often rely on static rules. Moreover, the strategies for deciding what to retrieve typically limit themselves to the LLM's most recent sentence or the last few tokens, while the LLM's real-time information needs may span across the entire context. To overcome these limitations, we introduce a new framework, DRAGIN, i.e., Dynamic Retrieval Augmented Generation based on the real-time Information Needs of LLMs. Our framework is specifically designed to make decisions on when and what to retrieve based on the LLM's real-time information needs during the text generation process. We evaluate DRAGIN along with existing methods comprehensively over 4 knowledge-intensive generation datasets. Experimental results show that DRAGIN achieves superior performance on all tasks, demonstrating the effectiveness of our method. We have open-sourced all the code, data, and models in GitHub: https://github.com/oneal2000/DRAGIN/tree/main
6/7/2024
Improving Retrieval for RAG based Question Answering Models on Financial Documents
Spurthi Setty, Katherine Jijo, Eden Chung, Natan Vidra

0
0
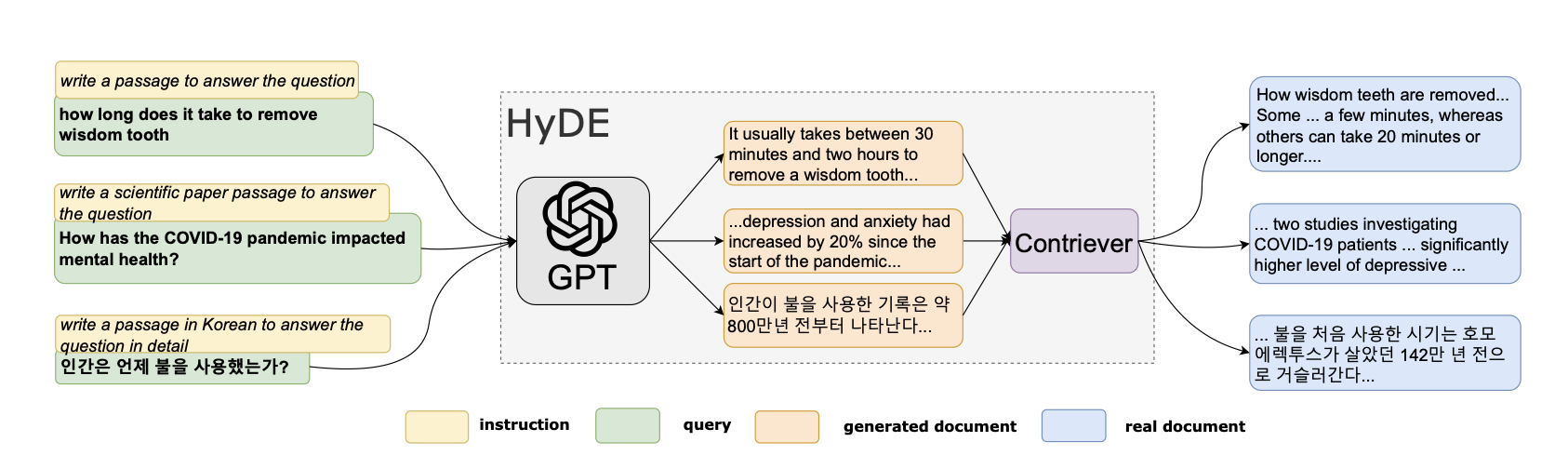
The effectiveness of Large Language Models (LLMs) in generating accurate responses relies heavily on the quality of input provided, particularly when employing Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) techniques. RAG enhances LLMs by sourcing the most relevant text chunk(s) to base queries upon. Despite the significant advancements in LLMs' response quality in recent years, users may still encounter inaccuracies or irrelevant answers; these issues often stem from suboptimal text chunk retrieval by RAG rather than the inherent capabilities of LLMs. To augment the efficacy of LLMs, it is crucial to refine the RAG process. This paper explores the existing constraints of RAG pipelines and introduces methodologies for enhancing text retrieval. It delves into strategies such as sophisticated chunking techniques, query expansion, the incorporation of metadata annotations, the application of re-ranking algorithms, and the fine-tuning of embedding algorithms. Implementing these approaches can substantially improve the retrieval quality, thereby elevating the overall performance and reliability of LLMs in processing and responding to queries.
4/12/2024
New!Searching for Best Practices in Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Xiaohua Wang, Zhenghua Wang, Xuan Gao, Feiran Zhang, Yixin Wu, Zhibo Xu, Tianyuan Shi, Zhengyuan Wang, Shizheng Li, Qi Qian, Ruicheng Yin, Changze Lv, Xiaoqing Zheng, Xuanjing Huang

0
0
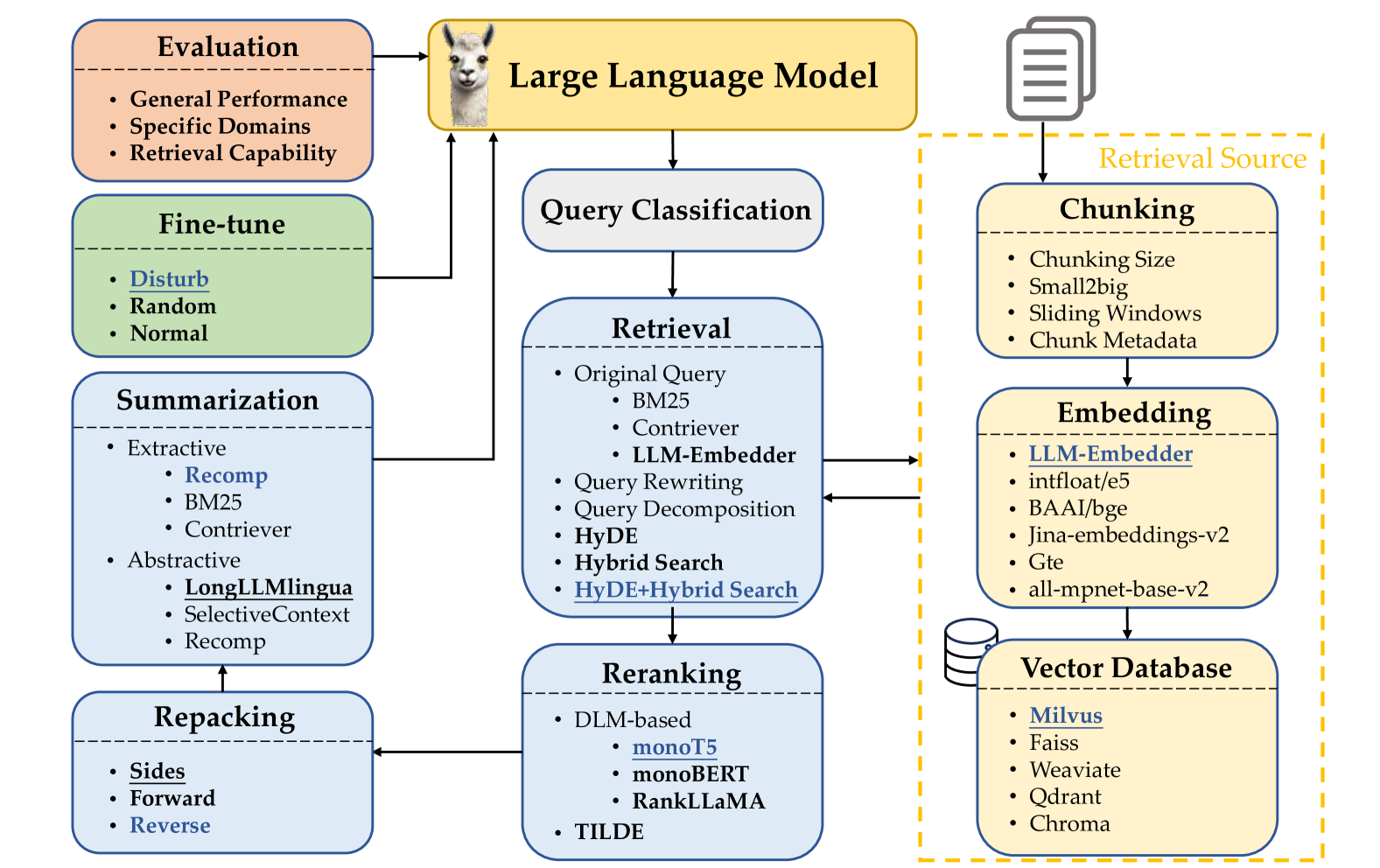
Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) techniques have proven to be effective in integrating up-to-date information, mitigating hallucinations, and enhancing response quality, particularly in specialized domains. While many RAG approaches have been proposed to enhance large language models through query-dependent retrievals, these approaches still suffer from their complex implementation and prolonged response times. Typically, a RAG workflow involves multiple processing steps, each of which can be executed in various ways. Here, we investigate existing RAG approaches and their potential combinations to identify optimal RAG practices. Through extensive experiments, we suggest several strategies for deploying RAG that balance both performance and efficiency. Moreover, we demonstrate that multimodal retrieval techniques can significantly enhance question-answering capabilities about visual inputs and accelerate the generation of multimodal content using a retrieval as generation strategy.
7/2/2024