DRL-Assisted Dynamic QoT-Aware Service Provisioning in Multi-Band Elastic Optical Networks

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper provides guidelines and best practices for writing technical research papers.
- It covers key sections of a paper, formatting of paragraphs and styles, and proper citation and referencing.
- The recommendations aim to help researchers communicate their work effectively to the scientific community.
Plain English Explanation
The provided paper offers guidance on how to structure and format academic research papers. It explains the key sections that should be included, such as the introduction, methods, results, and discussion. The paper also discusses proper formatting of paragraphs, headings, and citations to ensure a clear and consistent presentation.
The goal is to help researchers write papers that are easy for the scientific community to understand and navigate. By following these recommendations, authors can effectively communicate their work and findings in a professional manner. This can increase the impact and visibility of their research within their field.
Technical Explanation
The paper outlines the standard sections of a research paper, including the introduction, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. It provides guidance on the purpose and content of each section.
For paragraph formatting, the paper recommends using clear, concise language and proper spacing and alignment. It also covers best practices for headings, figures, tables, and citations to ensure a consistent and polished presentation.
The recommendations aim to help authors organize their work in a logical and reader-friendly way, making it easier for the scientific community to understand and build upon the research.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive set of guidelines that, if followed, can significantly improve the quality and clarity of research papers. By adhering to these recommendations, authors can enhance the readability and impact of their work within the scientific community.
However, the paper does not address potential limitations or caveats that may arise when applying these guidelines in practice. For example, there may be discipline-specific conventions or journal requirements that could conflict with the recommended formatting.
Additionally, the paper does not discuss strategies for effective visual communication of research findings through figures and diagrams, which are often crucial for conveying complex ideas.
Conclusion
This paper provides a valuable set of guidelines and best practices for writing high-quality research papers. By following the recommendations on paper structure, formatting, and citation, researchers can enhance the clarity, organization, and overall impact of their work within the scientific community.
While the paper does not address all potential challenges, it serves as a strong foundation for authors to effectively communicate their research findings and contribute to the advancement of their respective fields.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
DRL-Assisted Dynamic QoT-Aware Service Provisioning in Multi-Band Elastic Optical Networks
Yiran Teng, Carlos Natalino, Farhad Arpanaei, Alfonso S'anchez-Maci'an, Paolo Monti, Shuangyi Yan, Dimitra Simeonidou
We propose a DRL-assisted approach for service provisioning in multi-band elastic optical networks. Our simulation environment uses an accurate QoT estimator based on the GN/EGN model. Results show that the proposed approach reduces request blocking by 50% compared with heuristics from the literature.
Read more8/7/2024

0
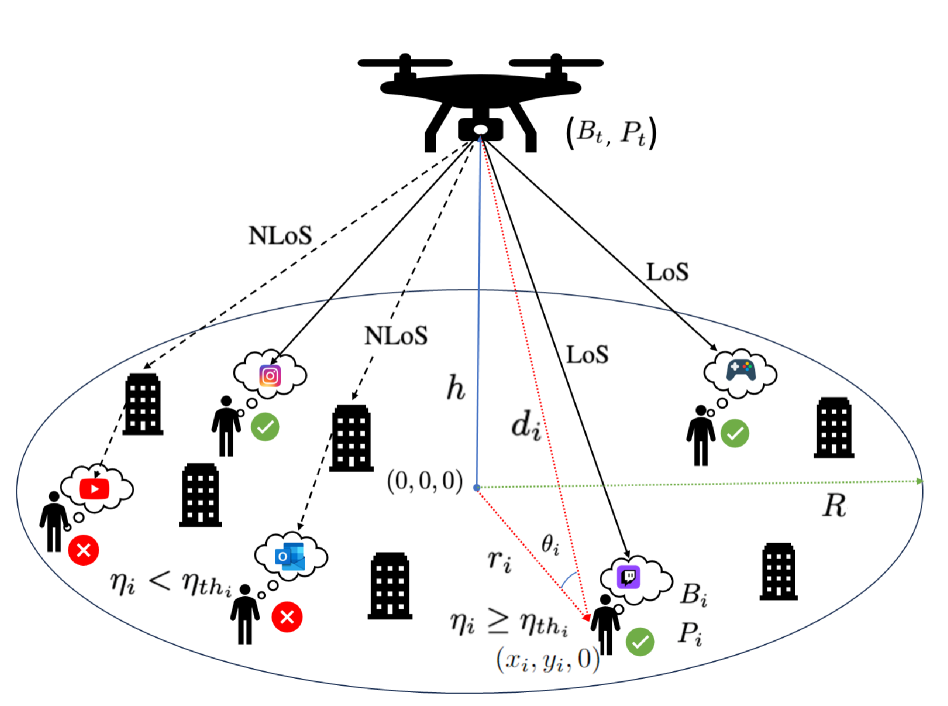
A Novel Joint DRL-Based Utility Optimization for UAV Data Services
Xuli Cai, Poonam Lohan, Burak Kantarci
In this paper, we propose a novel joint deep reinforcement learning (DRL)-based solution to optimize the utility of an uncrewed aerial vehicle (UAV)-assisted communication network. To maximize the number of users served within the constraints of the UAV's limited bandwidth and power resources, we employ deep Q-Networks (DQN) and deep deterministic policy gradient (DDPG) algorithms for optimal resource allocation to ground users with heterogeneous data rate demands. The DQN algorithm dynamically allocates multiple bandwidth resource blocks to different users based on current demand and available resource states. Simultaneously, the DDPG algorithm manages power allocation, continuously adjusting power levels to adapt to varying distances and fading conditions, including Rayleigh fading for non-line-of-sight (NLoS) links and Rician fading for line-of-sight (LoS) links. Our joint DRL-based solution demonstrates an increase of up to 41% in the number of users served compared to scenarios with equal bandwidth and power allocation.
Read more6/18/2024


0
Statistical QoS Provision in Business-Centric Networks
Chang Wu, Yuang Chen, Hancheng Lu
More refined resource management and Quality of Service (QoS) provisioning is a critical goal of wireless communication technologies. In this paper, we propose a novel Business-Centric Network (BCN) aimed at enabling scalable QoS provisioning, based on a cross-layer framework that captures the relationship between application, transport parameters, and channels. We investigate both continuous flow and event-driven flow models, presenting key QoS metrics such as throughput, delay, and reliability. By jointly considering power and bandwidth allocation, transmission parameters, and AP network topology across layers, we optimize weighted resource efficiency with statistical QoS provisioning. To address the coupling among parameters, we propose a novel deep reinforcement learning (DRL) framework, which is Collaborative Optimization among Heterogeneous Actors with Experience Sharing (COHA-ES). Power and sub-channel (SC) Actors representing multiple APs are jointly optimized under the unified guidance of a common critic. Additionally, we introduce a novel multithreaded experience-sharing mechanism to accelerate training and enhance rewards. Extensive comparative experiments validate the effectiveness of our DRL framework in terms of convergence and efficiency. Moreover, comparative analyses demonstrate the comprehensive advantages of the BCN structure in enhancing both spectral and energy efficiency.
Read more8/29/2024
🖼️

0
Dynamic realization of miscellaneous profile services in elastic optical networks using spectrum partitioning
Behnam Gheysari (EE Department, K. N. Toosi University of Technology, Iran), Arash Rezaee (EE Department, K. N. Toosi University of Technology, Iran), Lotfollah Beygi (EE Department, K. N. Toosi University of Technology, Iran)
Optical backbone networks are required to be highly dynamic in supporting requests with flexible bandwidth granularities to cope with the demands of new broadband wireless and fixed access networks. To provide this flexibility, services are offered by taking requested bandwidth profile into consideration, instead of assigning a fixed amount of bandwidth to each request. New techniques are developed for the resource management of the elastic optical networks to realize services with a specified bandwidth profile, consisting of minimum, average, and maximum required number of spectrum slots, in addition to holding time. In this work, two new schemes are proposed to realize such services, exploiting a probabilistic spectrum partitioning approach. This new probabilistic spectrum partitioning scheme is devised to enhance the chance of accommodating requests and consequently lower request blocking probability. It enforces different probabilities to contributing spectrum partitions in a certain service realization. Taking advantage of this probabilistic spectrum partitioning and a profile-based routing, we introduce two multistage spectrum assignment methods to make a certain lightpath meet the requested service profile constraints, considering the time-weighted average of the assigned spectrum slots. The results indicate that our algorithms can successfully realize the requests with the probability of 0.993 for the offered loads less than 400 erlang.
Read more5/3/2024