DSL-FIQA: Assessing Facial Image Quality via Dual-Set Degradation Learning and Landmark-Guided Transformer

0
Sign in to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
DSL-FIQA: Assessing Facial Image Quality via Dual-Set Degradation Learning and Landmark-Guided Transformer
Wei-Ting Chen, Gurunandan Krishnan, Qiang Gao, Sy-Yen Kuo, Sizhuo Ma, Jian Wang
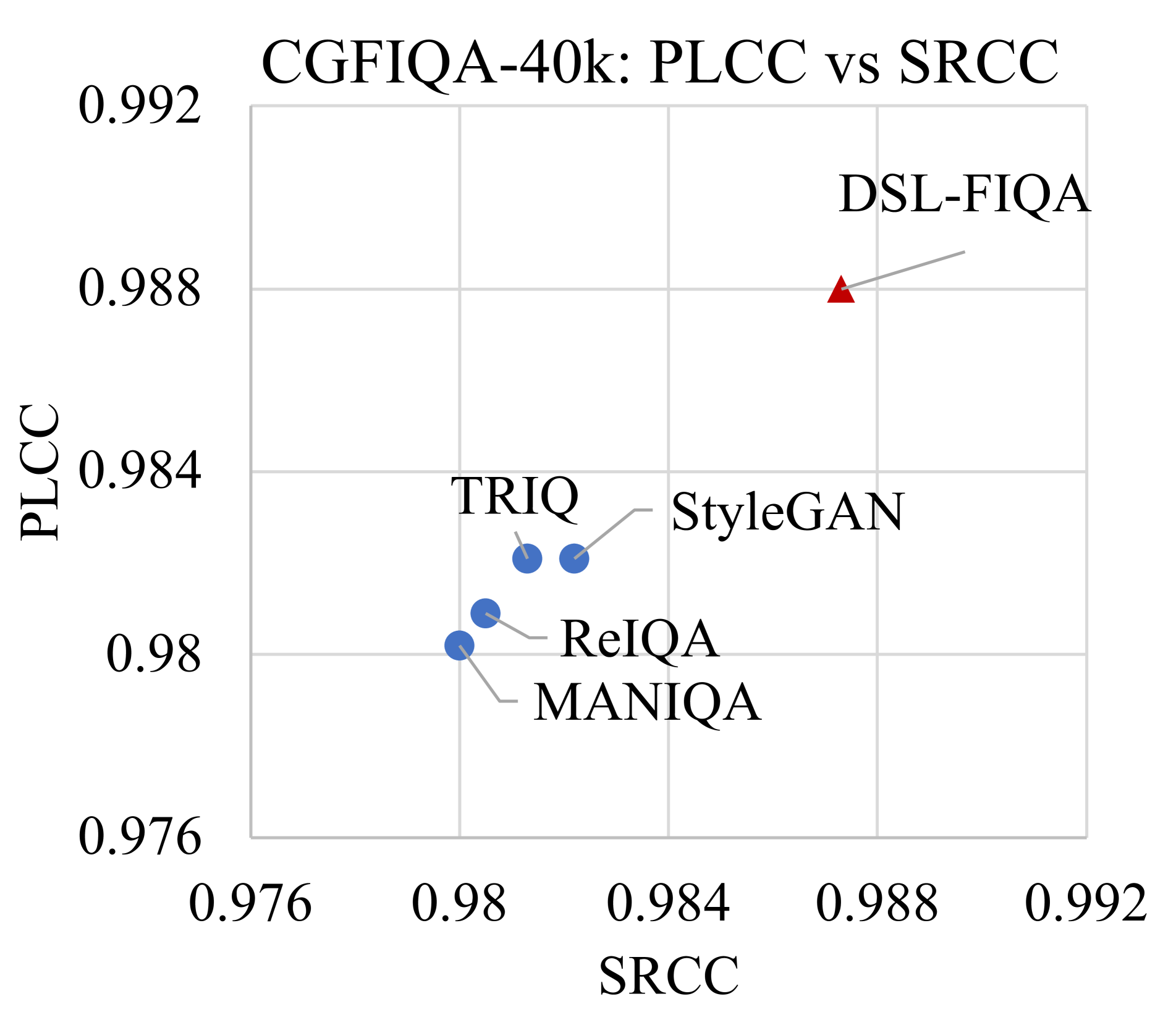
Generic Face Image Quality Assessment (GFIQA) evaluates the perceptual quality of facial images, which is crucial in improving image restoration algorithms and selecting high-quality face images for downstream tasks. We present a novel transformer-based method for GFIQA, which is aided by two unique mechanisms. First, a Dual-Set Degradation Representation Learning (DSL) mechanism uses facial images with both synthetic and real degradations to decouple degradation from content, ensuring generalizability to real-world scenarios. This self-supervised method learns degradation features on a global scale, providing a robust alternative to conventional methods that use local patch information in degradation learning. Second, our transformer leverages facial landmarks to emphasize visually salient parts of a face image in evaluating its perceptual quality. We also introduce a balanced and diverse Comprehensive Generic Face IQA (CGFIQA-40k) dataset of 40K images carefully designed to overcome the biases, in particular the imbalances in skin tone and gender representation, in existing datasets. Extensive analysis and evaluation demonstrate the robustness of our method, marking a significant improvement over prior methods.
Read more6/17/2024
🌐

0
Dual-Branch Network for Portrait Image Quality Assessment
Wei Sun, Weixia Zhang, Yanwei Jiang, Haoning Wu, Zicheng Zhang, Jun Jia, Yingjie Zhou, Zhongpeng Ji, Xiongkuo Min, Weisi Lin, Guangtao Zhai
Portrait images typically consist of a salient person against diverse backgrounds. With the development of mobile devices and image processing techniques, users can conveniently capture portrait images anytime and anywhere. However, the quality of these portraits may suffer from the degradation caused by unfavorable environmental conditions, subpar photography techniques, and inferior capturing devices. In this paper, we introduce a dual-branch network for portrait image quality assessment (PIQA), which can effectively address how the salient person and the background of a portrait image influence its visual quality. Specifically, we utilize two backbone networks (textit{i.e.,} Swin Transformer-B) to extract the quality-aware features from the entire portrait image and the facial image cropped from it. To enhance the quality-aware feature representation of the backbones, we pre-train them on the large-scale video quality assessment dataset LSVQ and the large-scale facial image quality assessment dataset GFIQA. Additionally, we leverage LIQE, an image scene classification and quality assessment model, to capture the quality-aware and scene-specific features as the auxiliary features. Finally, we concatenate these features and regress them into quality scores via a multi-perception layer (MLP). We employ the fidelity loss to train the model via a learning-to-rank manner to mitigate inconsistencies in quality scores in the portrait image quality assessment dataset PIQ. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed model achieves superior performance in the PIQ dataset, validating its effectiveness. The code is available at url{https://github.com/sunwei925/DN-PIQA.git}.
Read more5/15/2024
🖼️

0
GraFIQs: Face Image Quality Assessment Using Gradient Magnitudes
Jan Niklas Kolf, Naser Damer, Fadi Boutros
Face Image Quality Assessment (FIQA) estimates the utility of face images for automated face recognition (FR) systems. We propose in this work a novel approach to assess the quality of face images based on inspecting the required changes in the pre-trained FR model weights to minimize differences between testing samples and the distribution of the FR training dataset. To achieve that, we propose quantifying the discrepancy in Batch Normalization statistics (BNS), including mean and variance, between those recorded during FR training and those obtained by processing testing samples through the pretrained FR model. We then generate gradient magnitudes of pretrained FR weights by backpropagating the BNS through the pretrained model. The cumulative absolute sum of these gradient magnitudes serves as the FIQ for our approach. Through comprehensive experimentation, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our training-free and quality labeling-free approach, achieving competitive performance to recent state-of-theart FIQA approaches without relying on quality labeling, the need to train regression networks, specialized architectures, or designing and optimizing specific loss functions.
Read more4/19/2024
🤷

0
Cross-IQA: Unsupervised Learning for Image Quality Assessment
Zhen Zhang
Automatic perception of image quality is a challenging problem that impacts billions of Internet and social media users daily. To advance research in this field, we propose a no-reference image quality assessment (NR-IQA) method termed Cross-IQA based on vision transformer(ViT) model. The proposed Cross-IQA method can learn image quality features from unlabeled image data. We construct the pretext task of synthesized image reconstruction to unsupervised extract the image quality information based ViT block. The pretrained encoder of Cross-IQA is used to fine-tune a linear regression model for score prediction. Experimental results show that Cross-IQA can achieve state-of-the-art performance in assessing the low-frequency degradation information (e.g., color change, blurring, etc.) of images compared with the classical full-reference IQA and NR-IQA under the same datasets.
Read more5/8/2024