Economics of Integrated Sensing and Communication service provision in 6G networks

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper examines the economic factors involved in providing integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) services in 6G networks.
- The work was supported by grants from the Spanish government and the European Union.
- The paper explores the costs and benefits of deploying ISAC systems and how service providers can optimize their offerings.
Plain English Explanation
The paper looks at the financial side of providing integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) services in 6G wireless networks. 6G is the next generation of mobile technology that will offer even faster speeds and more advanced capabilities than current 4G and 5G networks.
ISAC is a key feature of 6G, where the network can simultaneously sense the environment and communicate data. This allows the network to gather information about its surroundings, like the location of devices, while also transmitting data. The researchers look at the costs and benefits for service providers of offering ISAC services, and how they can structure their pricing and operations to be profitable.
The study was funded by the Spanish government and the European Union, as they are investing heavily in developing 6G technology. Understanding the economics of ISAC is important for ensuring these advanced wireless networks can be rolled out effectively and provide value to both consumers and businesses.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a framework for analyzing the economics of integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) service provision in the context of 6G networks. The authors develop a mathematical model to optimize the pricing and resource allocation decisions of an ISAC service provider.
The model considers factors such as the capital and operational expenditures required to deploy ISAC infrastructure, the demand for sensing and communication services, and the potential revenue streams. The authors analyze how the provider can maximize their profits by jointly optimizing the spectrum partitioning and power allocation between the sensing and communication functionalities.
The results show that ISAC service provision can be economically viable, but the provider must carefully balance the tradeoffs between sensing accuracy, communication quality, and cost. The authors also discuss how regulatory constraints and user preferences can impact the optimal ISAC service design and pricing.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive economic analysis of ISAC service provision in 6G networks. However, it does not address some important practical considerations:
-
The model assumes perfect knowledge of system parameters and user demand, which may not be realistic in a dynamic market environment. Further research is needed on ,[object Object], in real-world ISAC deployments.
-
The analysis focuses on a single service provider, but in practice there may be multiple competing providers. The impact of competition on pricing, service quality, and market adoption should be explored.
-
The paper does not consider the potential for cross-subsidization between sensing and communication services, or the ability to offer bundled packages to customers. These strategies could further improve the economic viability of ISAC.
-
The authors do not discuss the regulatory challenges or user privacy concerns that may arise from the widespread deployment of ISAC technologies. These socio-technical issues will be crucial in shaping the deployment and acceptance of ISAC services.
Overall, the paper provides a solid foundation for understanding the economics of ISAC, but additional research is needed to address the practical complexities of real-world 6G network deployments.
Conclusion
This paper presents a comprehensive economic analysis of providing integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) services in the context of 6G wireless networks. The researchers develop a mathematical model to optimize the pricing and resource allocation decisions for an ISAC service provider, considering factors such as infrastructure costs, user demand, and revenue potential.
The results suggest that ISAC service provision can be economically viable, but service providers must carefully balance the tradeoffs between sensing accuracy, communication quality, and cost. The analysis also highlights the importance of regulatory constraints and user preferences in shaping the optimal ISAC service design and pricing.
While the paper provides valuable insights, further research is needed to address practical considerations such as imperfect knowledge of system parameters, competition between providers, and the socio-technical implications of widespread ISAC deployment. Nonetheless, this work contributes to our understanding of the economic opportunities and challenges in realizing the full potential of integrated sensing and communication in the 6G era.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Economics of Integrated Sensing and Communication service provision in 6G networks
Luis Guijarro, Maurizio Naldi, Vicent Pla, Jose-Ramon Vidal
In Beyond5G and 6G networks, a common theme is that sensing will play a more significant role than ever before. Over this trend, Integrated Sensing and Communications (ISAC) is focused on unifying the sensing functionalities and the communications ones and to pursue direct tradeoffs between them as well as mutual performance gains. We frame the resource tradeoff between the SAC functionalities within an economic setting. We model a service provision by one operator to the users, the utility of which is derived from both SAC functionalities. The tradeoff between the resources that the operator assigns to the SAC functionalities is analyzed from the point of view of the service prices, quantities and profits. We demonstrate that equilibrium quantities and prices exist. And we provide relevant recommendations for enforcing regulatory limits of both power and bandwidth.
Read more5/17/2024


0
A Survey on Integrated Sensing, Communication, and Computation
Dingzhu Wen, Yong Zhou, Xiaoyang Li, Yuanming Shi, Kaibin Huang, Khaled B. Letaief
The forthcoming generation of wireless technology, 6G, promises a revolutionary leap beyond traditional data-centric services. It aims to usher in an era of ubiquitous intelligent services, where everything is interconnected and intelligent. This vision requires the seamless integration of three fundamental modules: Sensing for information acquisition, communication for information sharing, and computation for information processing and decision-making. These modules are intricately linked, especially in complex tasks such as edge learning and inference. However, the performance of these modules is interdependent, creating a resource competition for time, energy, and bandwidth. Existing techniques like integrated communication and computation (ICC), integrated sensing and computation (ISC), and integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) have made partial strides in addressing this challenge, but they fall short of meeting the extreme performance requirements. To overcome these limitations, it is essential to develop new techniques that comprehensively integrate sensing, communication, and computation. This integrated approach, known as Integrated Sensing, Communication, and Computation (ISCC), offers a systematic perspective for enhancing task performance. This paper begins with a comprehensive survey of historic and related techniques such as ICC, ISC, and ISAC, highlighting their strengths and limitations. It then explores the state-of-the-art signal designs for ISCC, along with network resource management strategies specifically tailored for ISCC. Furthermore, this paper discusses the exciting research opportunities that lie ahead for implementing ISCC in future advanced networks. By embracing ISCC, we can unlock the full potential of intelligent connectivity, paving the way for groundbreaking applications and services.
Read more8/16/2024

0
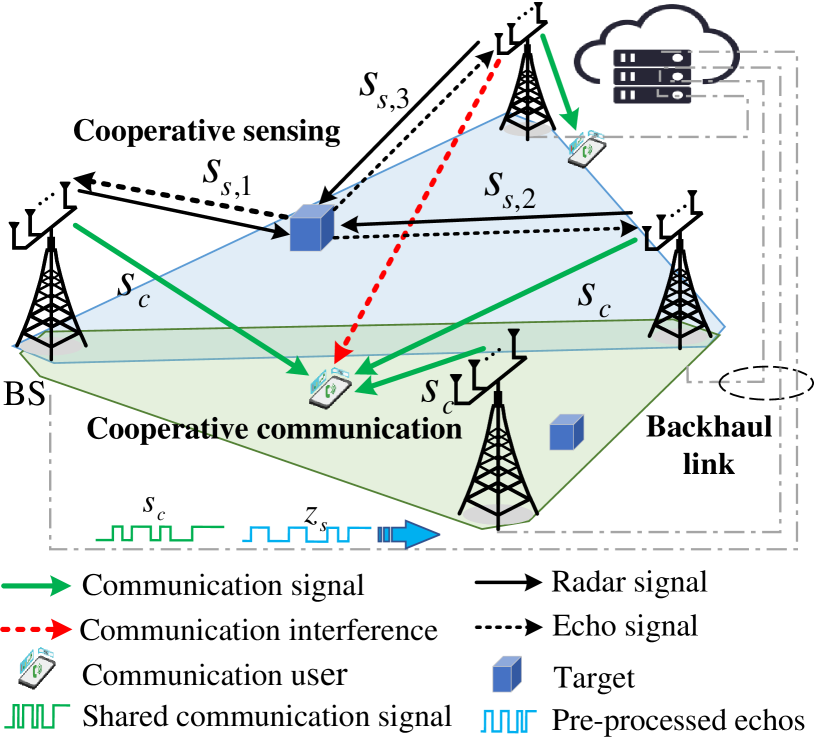
Cooperative Sensing and Communication for ISAC Networks: Performance Analysis and Optimization
Kaitao Meng, Christos Masouros
In this work, we study integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) networks intending to effectively balance sensing and communication (S&C) performance at the network level. Through the simultaneous utilization of multi-point (CoMP) coordinated joint transmission and distributed multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) radar techniques, we propose a cooperative networked ISAC scheme to enhance both S&C services. Then, the tool of stochastic geometry is exploited to capture the S&C performance, which allows us to illuminate key cooperative dependencies in the ISAC network. Remarkably, the derived expression of the Cramer-Rao lower bound (CRLB) of the localization accuracy unveils a significant finding: Deploying $N$ ISAC transceivers yields an enhanced sensing performance across the entire network, in accordance with the $ln^2N$ scaling law. Simulation results demonstrate that compared to the time-sharing scheme, the proposed cooperative ISAC scheme can effectively improve the average data rate and reduce the CRLB.
Read more4/1/2024


0
Integrated Sensing and Communications for Resource Allocation in Non-Terrestrial Networks
Israel Leyva-Mayorga, Fabio Saggese, Lintao Li, Petar Popovski
The integration of Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTNs) with Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite constellations into 5G and Beyond is essential to achieve truly global connectivity. A distinctive characteristic of LEO mega-constellations is that they constitute a global infrastructure with predictable dynamics, which enables the pre-planned allocation of the radio resources. However, the different bands that can be used for ground-to-satellite communication are affected differently by atmospheric conditions such as precipitation, which introduces uncertainty on the attenuation of the communication links at high frequencies. Based on this, we present a compelling case for applying integrated sensing and communications (ISAC) in heterogeneous and multi-layer LEO satellite constellations over wide areas. Specifically, we present an ISAC framework and frame structure to accurately estimate the attenuation in the communication links due to precipitation, with the aim of finding the optimal serving satellites and resource allocation for downlink communication with users on ground. The results show that, by dedicating an adequate amount of resources for sensing and solving the association and resource allocation problems jointly, it is feasible to increase the average throughput by 59% and the fairness by 600% when compared to solving these problems separately.
Read more7/10/2024