Emerging Technologies for 6G Non-Terrestrial-Networks: From Academia to Industrial Applications

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
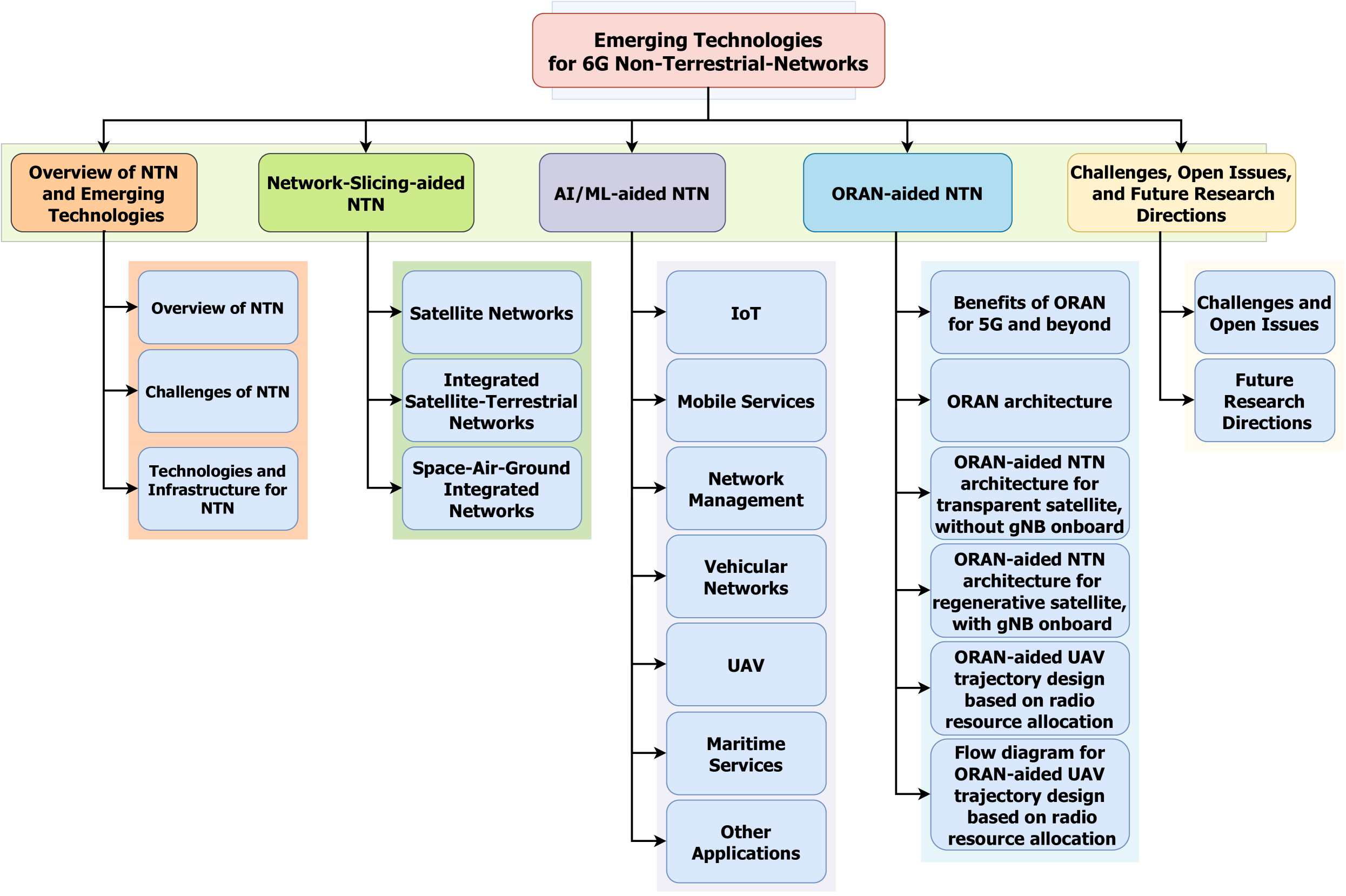
- NTN (Non-Terrestrial Networks): Emerging technologies that go beyond traditional terrestrial cellular networks, including satellites, high-altitude platforms, and unmanned aerial vehicles.
- Enabling Technologies: Advancements in areas like network slicing, AI/ML, and ORAN that can enhance the capabilities of NTN systems.
- 6G Networks: The next generation of wireless communication systems, which are expected to leverage NTN technologies to provide ubiquitous connectivity and new services.
Plain English Explanation
NTN refers to wireless communication networks that extend beyond traditional ground-based cellular towers. This includes technologies like satellites, high-altitude platforms, and drones. These NTN systems have the potential to provide connectivity in areas that are difficult for traditional networks to reach, like remote regions or disaster-affected areas.
The paper discusses several emerging technologies that can enhance the capabilities of NTN systems. For example, network slicing allows NTN networks to be divided into virtual "slices," each optimized for different types of traffic or users. AI and machine learning can be used to automatically manage and optimize the performance of NTN networks. And ORAN (Open Radio Access Network) technologies can make NTN systems more flexible and adaptable.
The researchers believe that by leveraging these emerging technologies, NTN systems can play a key role in the development of 6G wireless networks. 6G is the next generation of cellular technology, which is expected to provide faster speeds, lower latency, and new capabilities like integrated terrestrial and non-terrestrial services.
Technical Explanation
The paper provides an overview of the potential role of NTN technologies in the development of 6G wireless networks. It discusses several enabling technologies that can enhance the capabilities of NTN systems, including:
-
Network slicing: This allows NTN networks to be divided into virtual "slices," each optimized for different types of traffic or users, improving overall network efficiency and flexibility.
-
AI and machine learning: These techniques can be used to automatically manage and optimize the performance of NTN networks, adapting to changing conditions and user demands.
-
ORAN: Open Radio Access Network technologies can make NTN systems more flexible and adaptable, enabling the integration of different types of NTN assets (e.g., satellites, drones, high-altitude platforms) into a unified network.
The paper also discusses the potential for NTN technologies to support the development of integrated terrestrial and non-terrestrial services in 6G networks, providing ubiquitous connectivity and new capabilities.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive overview of the potential role of NTN technologies in 6G networks, highlighting several key enabling technologies. However, it does not delve deeply into the specific challenges and limitations of implementing these technologies in real-world NTN systems.
For example, the paper does not address the technical and regulatory hurdles associated with integrating diverse NTN assets, such as satellites, drones, and high-altitude platforms, into a seamless network. Additionally, the paper does not discuss the potential impact of environmental factors on the reliability and performance of NTN systems, which could be a significant concern, especially in extreme weather conditions or disaster scenarios.
Further research and analysis may be needed to fully understand the practical implementation and deployment challenges of leveraging NTN technologies in 6G networks, as well as to explore potential solutions and mitigation strategies.
Conclusion
This paper presents a promising vision for the role of NTN technologies in the development of 6G wireless networks. By leveraging emerging advancements in areas like network slicing, AI/ML, and ORAN, NTN systems have the potential to provide ubiquitous connectivity and enable new services that can benefit a wide range of applications, from disaster response to remote healthcare.
However, the successful integration and deployment of NTN technologies in 6G networks will require addressing a range of technical and regulatory challenges. Continued research and collaboration between academia and industry will be crucial to realizing the full potential of NTN in the 6G era and beyond.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Emerging Technologies for 6G Non-Terrestrial-Networks: From Academia to Industrial Applications
Cong T. Nguyen, Yuris Mulya Saputra, Nguyen Van Huynh, Tan N. Nguyen, Dinh Thai Hoang, Diep N Nguyen, Van-Quan Pham, Miroslav Voznak, Symeon Chatzinotas, Dinh-Hieu Tran
Terrestrial networks form the fundamental infrastructure of modern communication systems, serving more than 4 billion users globally. However, terrestrial networks are facing a wide range of challenges, from coverage and reliability to interference and congestion. As the demands of the 6G era are expected to be much higher, it is crucial to address these challenges to ensure a robust and efficient communication infrastructure for the future. To address these problems, Non-terrestrial Network (NTN) has emerged to be a promising solution. NTNs are communication networks that leverage airborne (e.g., unmanned aerial vehicles) and spaceborne vehicles (e.g., satellites) to facilitate ultra-reliable communications and connectivity with high data rates and low latency over expansive regions. This article aims to provide a comprehensive survey on the utilization of network slicing, Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning (AI/ML), and Open Radio Access Network (ORAN) to address diverse challenges of NTNs from the perspectives of both academia and industry. Particularly, we first provide an in-depth tutorial on NTN and the key enabling technologies including network slicing, AI/ML, and ORAN. Then, we provide a comprehensive survey on how network slicing and AI/ML have been leveraged to overcome the challenges that NTNs are facing. Moreover, we present how ORAN can be utilized for NTNs. Finally, we highlight important challenges, open issues, and future research directions of NTN in the 6G era.
Read more7/4/2024
🏷️

0
Agricultural On-Demand Networks for 6G enabled by THz Communication
Daniel Lindenschmitt, Christoph Fischer, Simon Haussmann, Marc Kalter, Ingmar Kallfass, Hans D. Schotten
The transforming process in the scope of agriculture towards Smart Agriculture is an essential step to fulfill growing demands in respect to nourishment. Crucial challenges include establishing robust wireless communication in rural areas, enabling collaboration among agricultural machines, and integrating artificial intelligence into farming practices. Addressing these challenges necessitates a consistent communication system, with wireless communication emerging as a key enabler. Cellular technologies, as 5G and its successor 6G, can offer a comprehensive solution here. Leveraging technologies following the ITU-R M. 2160 recommendation like THz communication, low-latency wireless AI, and embedded sensing, can provide a flexible and energy-efficient infrastructure. This paper introduces on-demand networks based on the OpenRAN approach and a 7.2 functional split. By implementing THz front-hauling between components, a flexible application of 5G or future 6G networks can be realized. Experiments demonstrate that THz communication is suitable for data transmission over the eCPRI interface, particularly in terms of data rate, thereby reducing the need for wired alternatives such as fiber optic cables. Furthermore, limitations such as limited range are discussed, and possible initial solutions are presented. The integration of the OpenRAN standard further enhances flexibility, which is crucial in dynamic agricultural environments. This research contributes to the ongoing discourse on the transformative potential of 6G-enabled wireless communication in shaping the future of smart agriculture.
Read more8/29/2024
🔗

0
Multi-Tier Non-Terrestrial Networking for Disaster Communications: A Layered Clustering Approach
Metin Ozturk, Berk c{C}ilou{g}lu, Gorkem Berkay Koc{c}, Halim Yanikomeroglu
It is crucial to deploy temporary non-terrestrial networks (NTN) in disaster situations where terrestrial networks are no longer operable. Deploying uncrewed aerial vehicle base stations (UAV-BSs) can provide a radio access network (RAN); however, the backhaul link may also be damaged and unserviceable in such disaster conditions. In this regard, high-altitude platform stations (HAPS) spark attention as they can be deployed as super macro base stations (SMBS) and data centers. Therefore, in this study, we investigate a three-layer heterogeneous network with different topologies to prolong the lifespan of the temporary network by using UAV-BSs for RAN services and HAPS-SMBS as a backhaul. Furthermore, a two-layer clustering algorithm is proposed to handle the UAV-BS ad-hoc networking effectively.
Read more4/24/2024
🌐

0
On the Role of Non-Terrestrial Networks for Boosting Terrestrial Network Performance in Dynamic Traffic Scenarios
Henri Alam, Antonio de Domenico, Florian Kaltenberger, David L'opez-P'erez
Due to an ever-expansive network deployment, numerous questions are being raised regarding the energy consumption of the mobile network. Recently, Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTNs) have proven to be a useful, and complementary solution to Terrestrial Networks (TN) to provide ubiquitous coverage. In this paper, we consider an integrated TN-NTN, and study how to maximize its resource usage in a dynamic traffic scenario. We introduce BLASTER, a framework designed to control User Equipment (UE) association, Base Station (BS) transmit power and activation, and bandwidth allocation between the terrestrial and non-terrestrial tiers. Our proposal is able to adapt to fluctuating daily traffic, focusing on reducing power consumption throughout the network during low traffic and distributing the load otherwise. Simulation results show an average daily decrease of total power consumption by 45% compared to a network model following 3GPP recommendation, as well as an average throughput increase of roughly 250%. Our paper underlines the central and dynamic role that the NTN plays in improving key areas of concern for network flexibility.
Read more5/24/2024